every thing is solved except from question A to g
also this is screenshots and one whole question nothing is missing
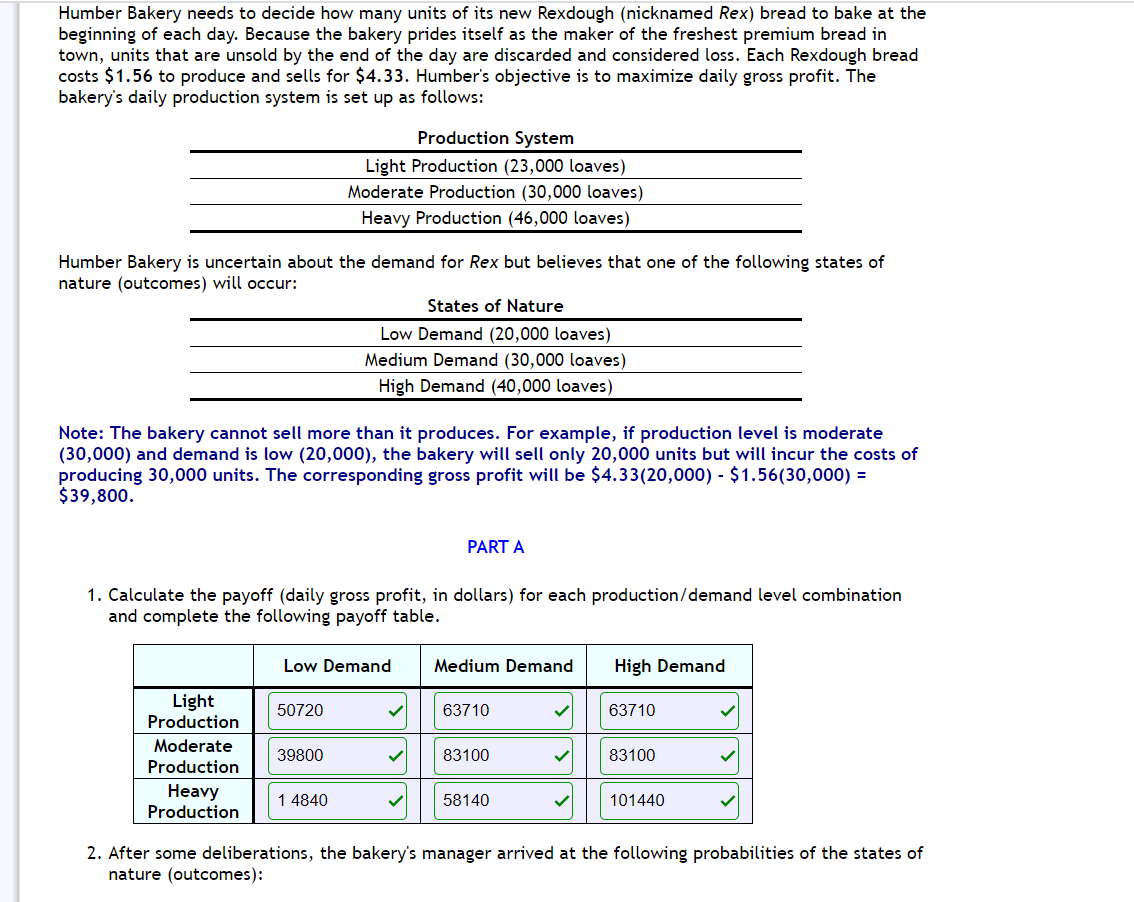
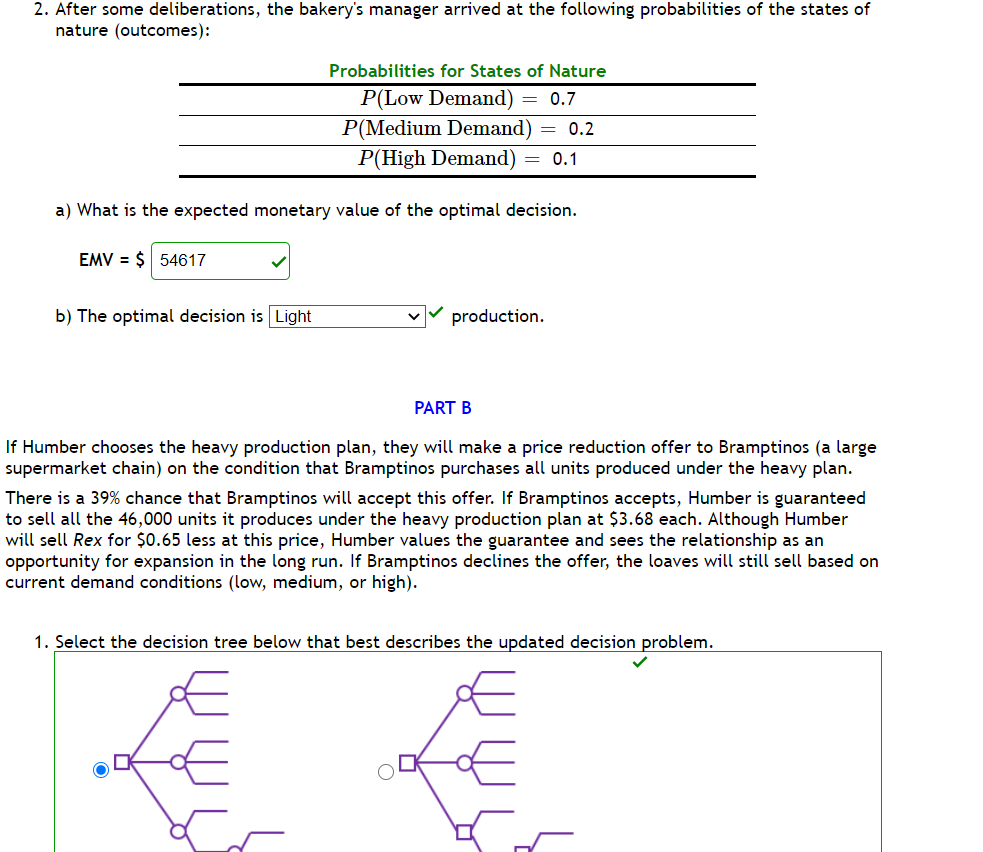
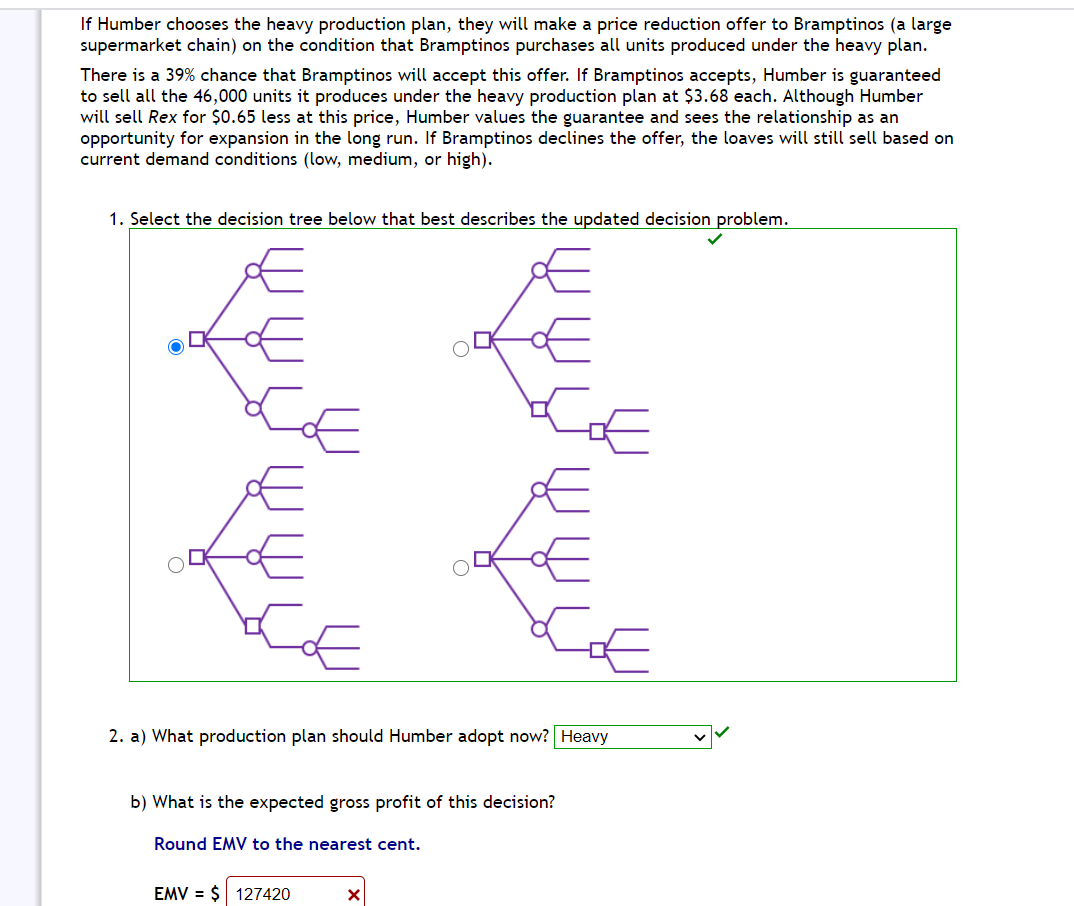
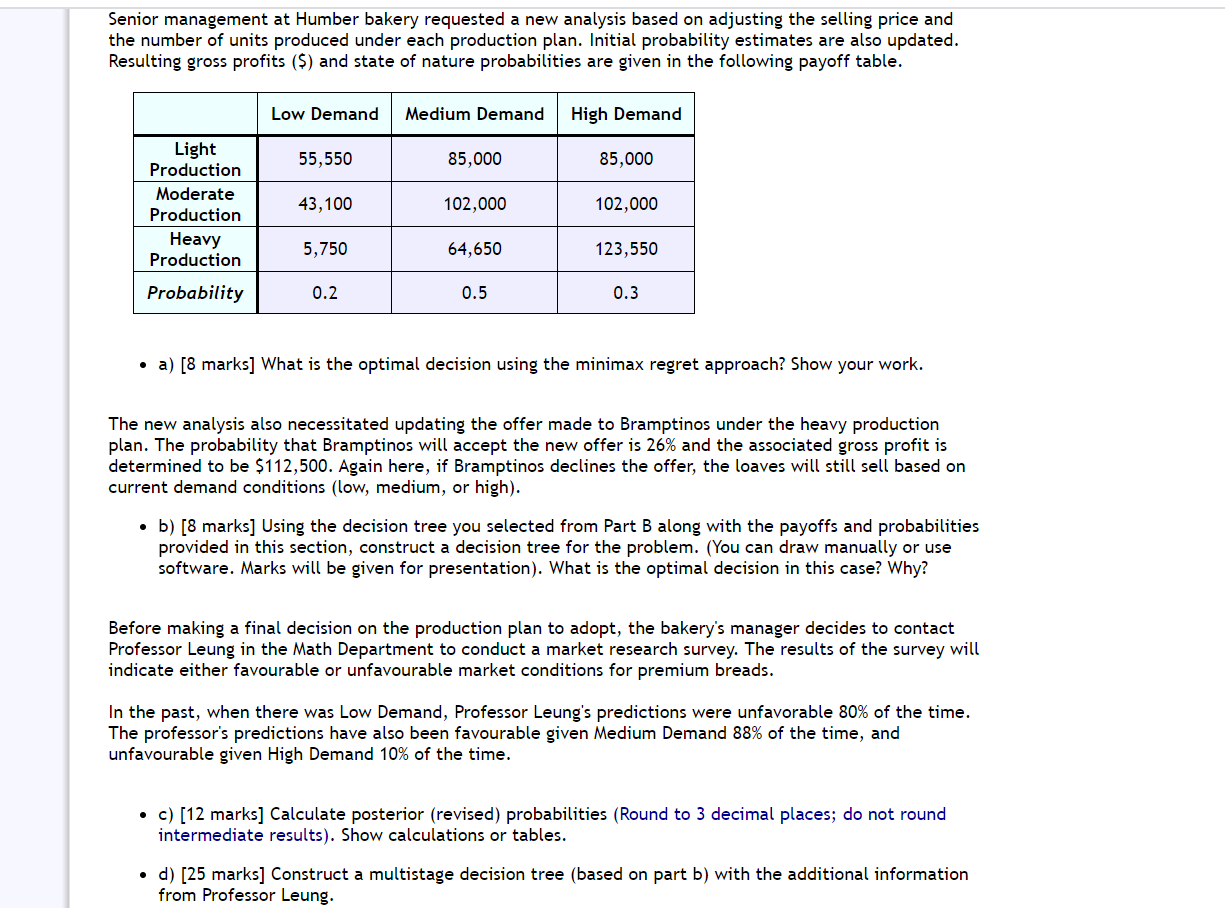
Humber Bakery needs to decide how many units of its new Rexdough (nicknamed Rex) bread to bake at the beginning of each day. Because the bakery prides itself as the maker of the freshest premium bread in town, units that are unsold by the end of the day are discarded and considered loss. Each Rexdough bread costs $1.56 to produce and sells for $4.33. Humber's objective is to maximize daily gross profit. The bakery's daily production system is set up as follows: Production System Light Production (23,000 loaves) Moderate Production {30,000 loaves) Heavy Production (46,000 loaves) Humber Bakery is uncertain about the demand for Rex but believes that one of the following states of nature {outcomes} will occur: States of Nature Low Demand (20,000 loaves) Medium Demand (30,000 loaves} High Demand (40,000 loaves) Note: The bakery cannot sell more than it produces. For example, if production level is moderate (30,000) and demand is low (20,000), the bakery will sell only 20,000 units but will incur the costs of producing 30,000 units. The corresponding gross profit will be $4.33[20,000) - $1 .56(30,000) = $39,800. PARTA 1. Calculate the payoff {daily gross profit, in dollars) for each production/demand level combination and complete the following payoff table. Low Demand Medium Demand High Demand nght. ' 50720 J' ' 63710 l ' 63710 l Production Moderate . 39800 J 83100 J 83100 J Production \"ea\"! l 14340 l l 58140 l l 101440 l Production 2. After some deliberations, the bakery's manager arrived at the following probabilities of the states of nature {outcomes}: 2. After some deliberations, the bakery's manager arrived at the following probabilities of the states of nature {outcomes): Probabilities for States of Nature P(Low Demand) = 0.7 P(Medinm Demand) 2 0.2 P(Hig]1 Demand) = 0.1 a} What is the expected monetary value of the optimal decision. b) The optimal decision is - production. PART B If Humber chooses the heavy production plan, they will make a price reduction offer to Bramptinos (a large supermarket chain) on the condition that Bramptinos purchases all units produced under the heavy plan. There is a 39% chance that Brampti nos will accept this offer. If Bramptinos accepts, Humber is guaranteed to sell all the 46,000 units it produces under the heavy production plan at $3.63 each. Although Humber will sell Rex for $0.65 less at this price, Humber values the guarantee and sees the relationship as an opportunity for expansion in the long run. If Bramptinos declines the offer, the loaves will still sell based on current demand conditions {low, medium, or high). 1. Select the decision tree below that best describes the updated decision problem. If Humber chooses the heavy production plan, they will make a price reduction offer to Bramptinos (a large supermarket chain) on the condition that Bramptinos purchases all units produced under the heavy plan. There is a 39% chance that Bramptinos will accept this offer. If Bramptinos accepts, Humber is guaranteed to sell all the 46,000 units it produces under the heavy production plan at $3.68 each. Although Humber will sell Rex for $0.65 less at this price, Humber values the guarantee and sees the relationship as an opportunity for expansion in the long run. If Bramptinos declines the offer, the loaves will still sell based on current demand conditions (low, medium, or high). 1. Select the decision tree below that best describes the updated decision problem. 0% 2. a} What production plan should Humber adopt now? - b) What is the expected gross profit of this decision? Round EMV to the nearest cent. EMV = $ 127420 X Senior management at Humber bakery requested a new analysis based on adjusting the selling price and the number of units produced under each production plan. Initial probability estimates are also updated. Resulting gross profits (5) and state of nature probabilities are given in the following payoff table. Low Demand Medium Demand High Demand Light Production 55,550 85,000 85,000 Mde"'.te 43,100 102,000 102,000 Production Heavy Production 5,750 64,650 123,550 Probability 0.2 0.5 0.3 I a} [8 marks] What is the optimal decision using the minimax regret approach? Show your work. The new analysis also necessitated updating the offer made to Brampti nos under the heavy production plan. The probability that Bramptinos will accept the new offer is 26% and the associated gross profit is determined to be $112,500. Again here, if Brampti nos declines the offer, the loaves will still sell based on current demand conditions (low, medium, or high). I b) [8 marks] Using the decision tree you selected from Part B along with the payoffs and probabilities provided in this section, construct a decision tree for the problem. (You can draw manually or use software. Marks will be given for presentation). What is the optimal decision in this case? Why? Before making a final decision on the production plan to adopt, the bakery's manager decides to contact Professor Leung in the Math Department to conduct a market research survey. The results of the survey wi ll indicate either favourable or unfavourable market conditions for premium breads. In the past, when there was Low Demand, Professor Leung's predictions were unfavorable 80% of the time. The professor's predictions have also been favourable given Medium Demand 88% of the time, and unfavourable given High Demand 10% of the time. I c) [12 marks] Calculate posterior (revised) probabilities (Round to 3 decimal places; do not round intermediate results). Show calculations or tables. I d) [25 marks] Construct a multistage decision tree {based on part b) with the additional information from Professor Leung. I e} [2 marks] What is the value of the sample information (EVSU provided by Professor Leung? I f l [3 marks] State the optimal decision strategy if Professor Leung's consulting fees were $500. I g) [2 marks] Does the strategy change if Professor Leung's consulting fees were 51500? If yes, state the new optimal strategy? If no, explain