| Examine the LCA presented in Exhibit 6 of the case in the context of the EPA definition. Critique the analysis based on the following questions: How does the assumption that the shipping distance is the same for each process affect the application of the LCA to Mark Jacobsons situation? How might a change in another assumption alter the results? How might the prioritization of other criteria (besides global warming potential) alter the assessment of the two processes? |

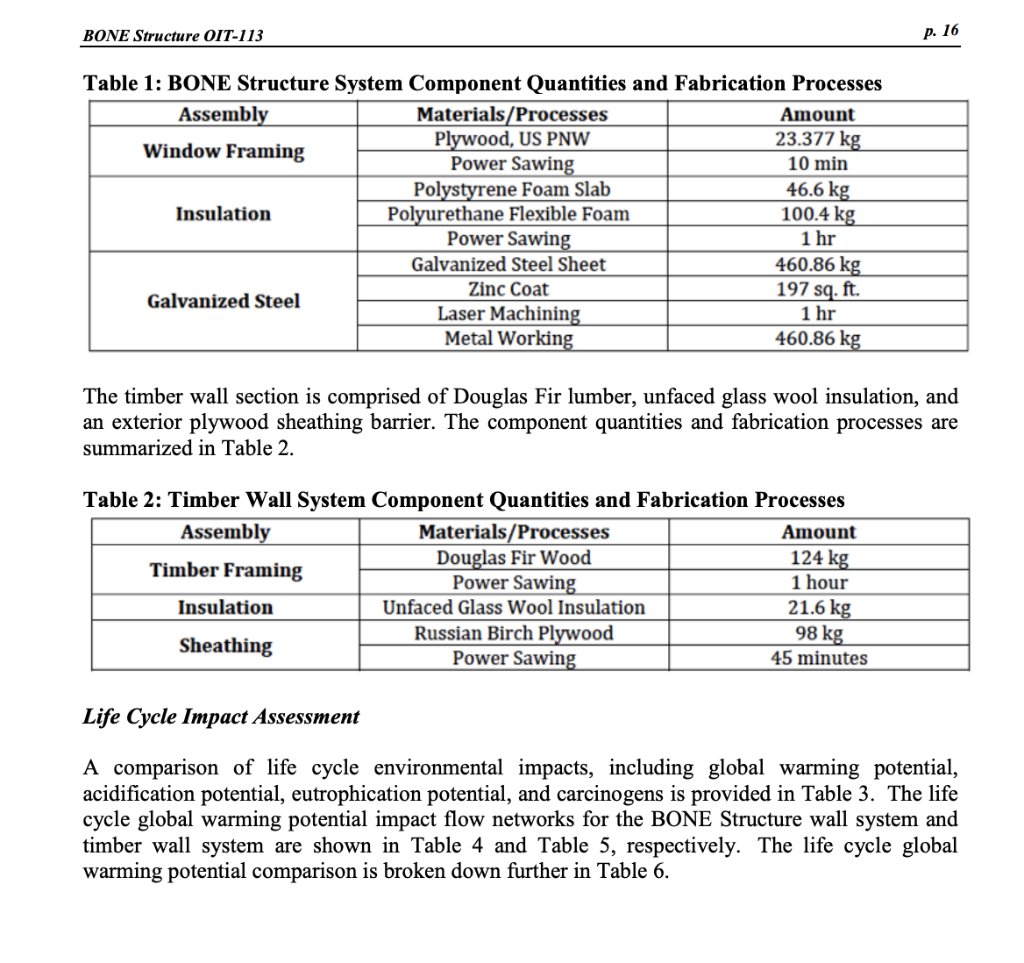
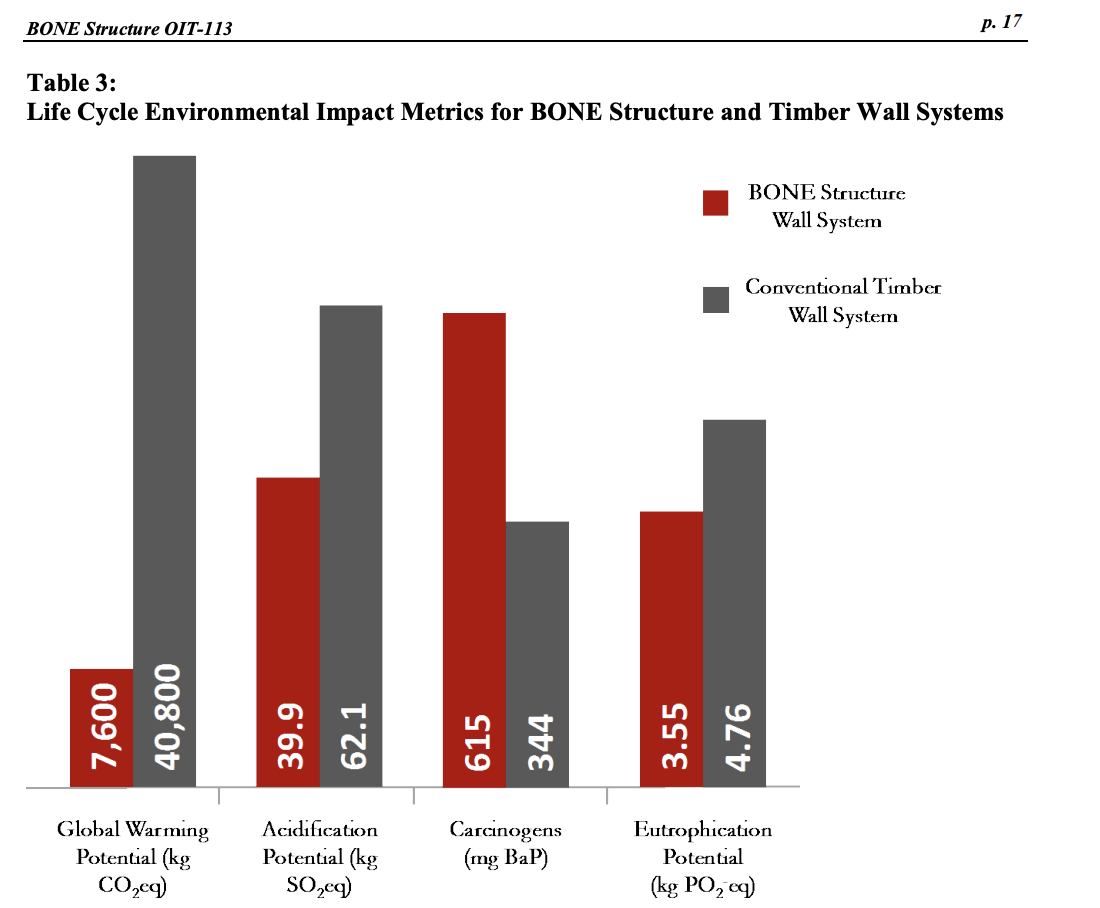
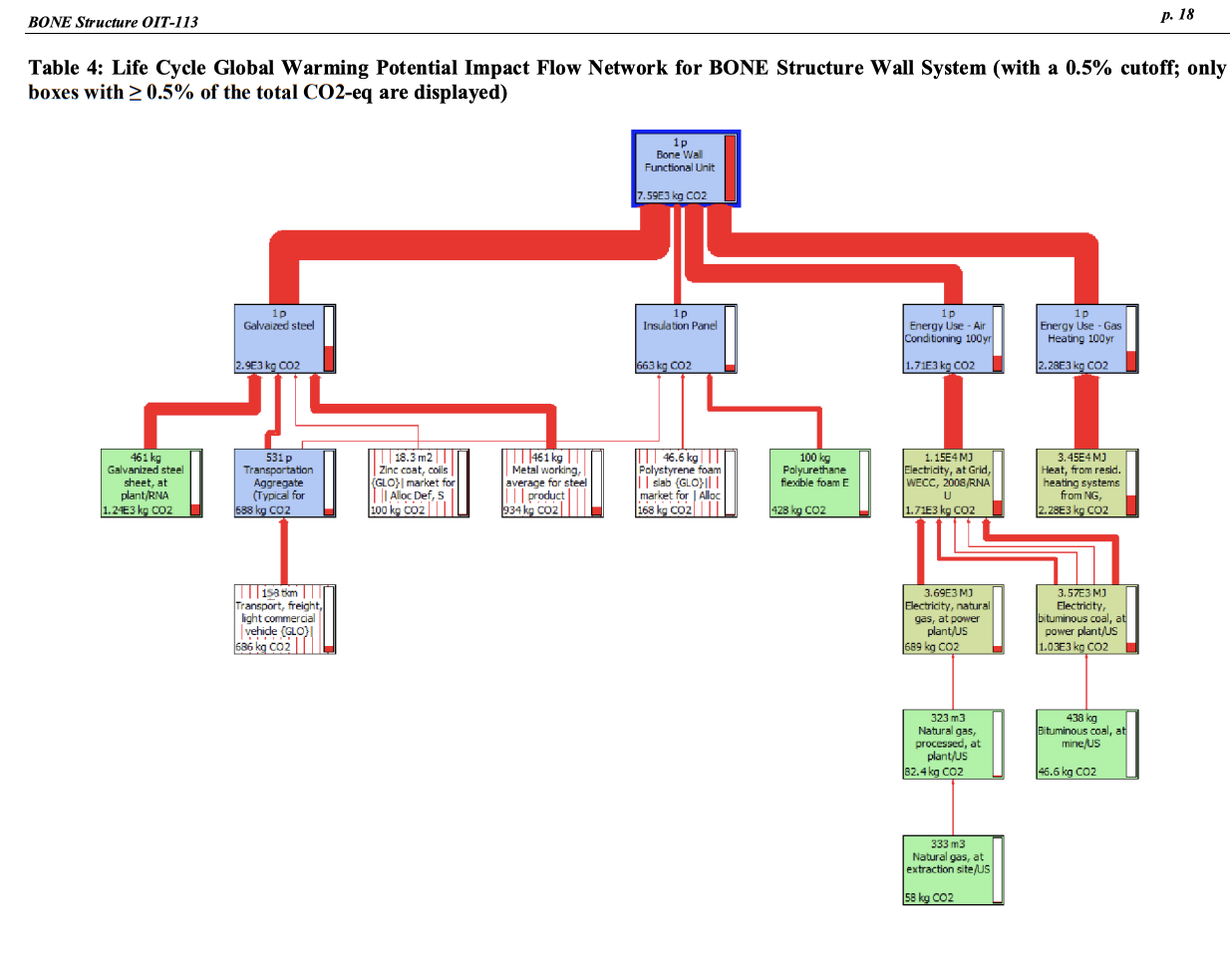
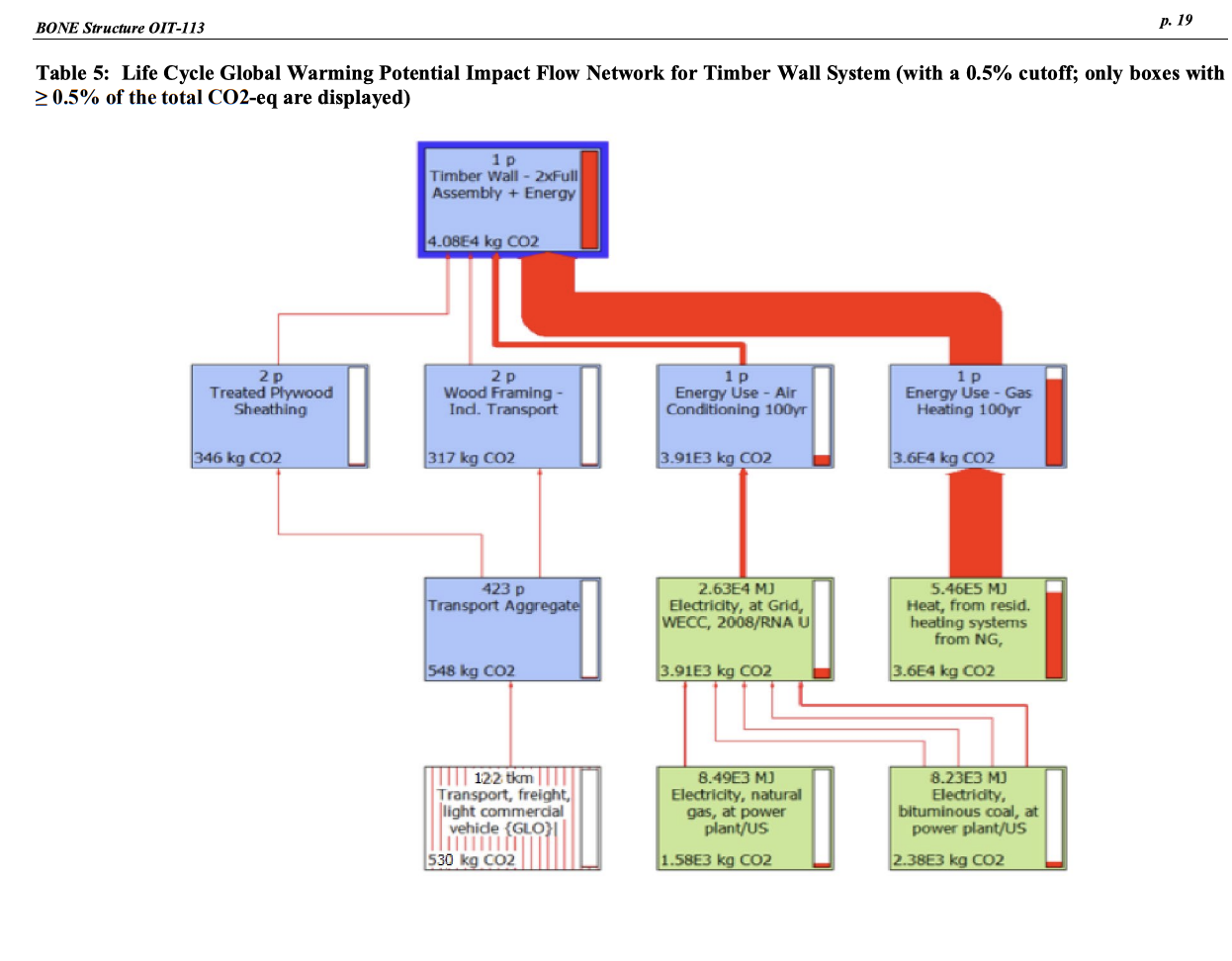
Exhibit 6 Life Cycle Assessment of BONE Structure Class Project, School of Engineering, Stanford University Goal and Scope of Analysis The purpose of this analysis is to assess the life cycle impacts of a BONE Structure wall relative timber wall system provides an R-value of 13 and 3.0 air changes per hour at a pressure of 50Pa2929 In contrast, the BONE Structure wall system provides an R-value of 28.5 and 0.8 air changes per hour at a pressure of 50Pa. The functional unit for this study is a wall unit of 25 feet by 10 feet ( 7.62 meters by 3.05 meters) with 15 percent of window space over 100 years. The boundaries of the analysis include fabrication and transportation of building materials, construction (including construction waste), and use. The lifetime of a BONE structure is assumed to be 100 years whereas lifetime of a conventional timber structure is 50 years, and the analysis accounts for impacts associated with replacement of the timber wall after 50 years. The analysis does not account for carbon sequestered during timber growth. End-of-life management and waste streams are not included because of associated high levels of uncertainty. Maintenance, renovation, and repair are not included. Assumptions and Life Cycle Inventory Analysis We have assumed that transportation distances for the components of the Bone Structure system are the same as for the timber system, 250km. Furthermore, the transport is by commercial truck, which produces 0.00435kgCO2 per kg cargo per km travel. Construction waste is zero for the BONE Structure system. A waste factor of 15 percent in cutting wood on the construction site is applied for the timber wall system, based on the industry average in conventional timber construction. All in-wall MEP (mechanical, electrical, plumbing) systems are assumed equal. All window assemblies are assumed identical. All exterior siding on both units is assumed equal. Thus, only structural elements and insulation materials differentiate the two walls. The BONE Structure wall section is comprised of steel structural elements, plywood window framing, polystyrene insulation panels, and a polyurethane insulation spray. The component quantities and fabrication processes are summarized in Table 1. The timber wall section is comprised of Douglas Fir lumber, unfaced glass wool insulation, and an exterior plywood sheathing barrier. The component quantities and fabrication processes are summarized in Table 2. Table 2: Timber Wall System Component Quantities and Fabrication Processes Life Cycle Impact Assessment A comparison of life cycle environmental impacts, including global warming potential, acidification potential, eutrophication potential, and carcinogens is provided in Table 3 . The life cycle global warming potential impact flow networks for the BONE Structure wall system and timber wall system are shown in Table 4 and Table 5, respectively. The life cycle global warming potential comparison is broken down further in Table 6. Table 3: Life Cycle Environmental Impact Metrics for BONE Structure and Timber Wall Systems Table 4: Life Cycle Global Warming Potential Impact Flow Network for BONE Structure Wall System (with a 0.5\% cutoff; only Table 5: Life Cycle Global Warming Potential Impact Flow Network for Timber Wall System (with a 0.5\% cutoff; only boxes with 0











