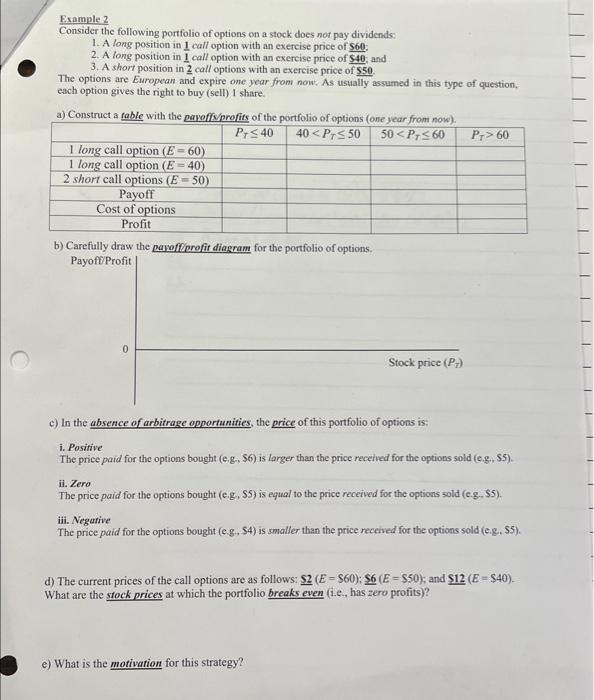
Example 2 Consider the following portfolio of options on a stock does nof pay dividends: 1. A long position in 1 call option with an exercise price of 560 ; 2. A long position in 1 call option with an exercise price of 540 ; and 3. A short position in 2 call options with an exercise price of $50. The options are European and expire one year from now: As usually assumed in this type of question, each option gives the right to buy (sell) 1 share. b) Carefully draw the payofforefit diagram for the portfolio of options. PayoftProfit c) In the absence of arbitrage opportunities, the price of this portfolio of options is: i. Positive The price paid for the options bought (e,g,$6) is larger than the price recetied for the options sold (e,g,, $5). ii. Zero The price puid for the options bought (e.g,$5) is equal to the price received for the options sold (e.g., \$5). iii. Negative The price paid for the options bought (e.g, \$4) is smaller than the price received for the options sold (e.g. \$5). d) The current prices of the call options are as follows: $2(E=$60);$6(E=$50); and $$12(E=$40). What are the stock prices at which the portfolio breaks even (1.e., has zero profits)? e) What is the motivation for this strategy? Example 2 Consider the following portfolio of options on a stock does nof pay dividends: 1. A long position in 1 call option with an exercise price of 560 ; 2. A long position in 1 call option with an exercise price of 540 ; and 3. A short position in 2 call options with an exercise price of $50. The options are European and expire one year from now: As usually assumed in this type of question, each option gives the right to buy (sell) 1 share. b) Carefully draw the payofforefit diagram for the portfolio of options. PayoftProfit c) In the absence of arbitrage opportunities, the price of this portfolio of options is: i. Positive The price paid for the options bought (e,g,$6) is larger than the price recetied for the options sold (e,g,, $5). ii. Zero The price puid for the options bought (e.g,$5) is equal to the price received for the options sold (e.g., \$5). iii. Negative The price paid for the options bought (e.g, \$4) is smaller than the price received for the options sold (e.g. \$5). d) The current prices of the call options are as follows: $2(E=$60);$6(E=$50); and $$12(E=$40). What are the stock prices at which the portfolio breaks even (1.e., has zero profits)? e) What is the motivation for this strategy