Question
% Example of the use of Zero. % REQUIRES Zero.m and Xzerof.m. global nfeval % Assign bracket and error tolerances. b = 1; c =

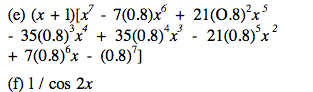
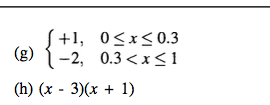
% Example of the use of Zero.
% REQUIRES Zero.m and Xzerof.m.
global nfeval
% Assign bracket and error tolerances.
b = 1;
c = 0;
abserr = 1e-8;
relerr = 1e-6;
nfeval = 0; % global variable to count function evaluations.
% Use Zero to find a root.
[b,c,residual,flag] = Zero('Xzerof',b,c,abserr,relerr);
% Check flag and print results.
fprintf('flag = %i ',flag)
if flag == 0
fprintf('Computed a root b = %e ',b);
fprintf('%i evaluations of f were required. ',nfeval);
elseif flag == 1
fprintf('Too much work: nfeval = %i ',nfeval);
fprintf('There is a root in [b,c] with ');
fprintf('b = %e, c = %e ',b,c);
elseif flag == 2
fprintf('Computed a pole b = %e ',b);
end
fprintf('The residual f(b) = %e ',residual);
4.10 Use the code Zero with an initial bracket of [0, 1] to find the roots of the equation F(x) = 0, where F(x) is given by each of the following. 4.10 Use the code Zero with an initial bracket of [0, 1] to find the roots of the equation F(x) = 0, where F(x) is given by each of the following
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


