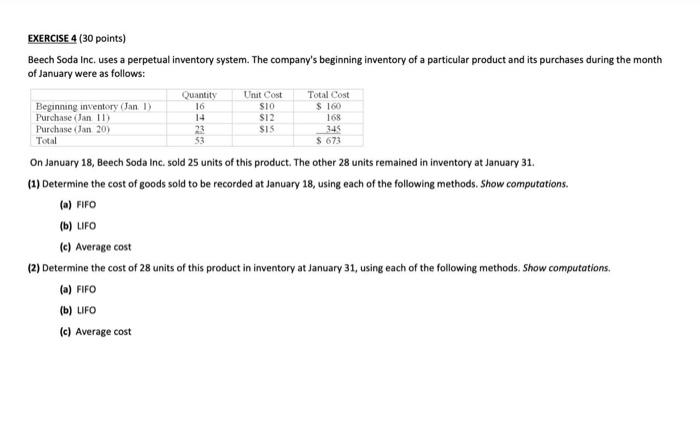
EXERCISE 1 (20 points) On September 1, 2019, Dental Equipment Corporation sold equipment priced at 350,000 in exchange for a six-month note receivable with an annual interest rate of 12%, all due at maturity. (a) Prepare the entry on 1 September 2019 made by Dental to record the receipt of this note receivable. (b) Prepare the December 31, 2019 (fiscal year-end), adjusting entry made by Dental with regard to this note receivable. (c) Prepare the entry made by Dental on March 1, 2020 (maturity date of note), to record collection of note and interest. General Journal Account Titles and Explanation Debit Credit Date (6) TC) EXERCISE 2 (20 points) (1) The general ledger controlling account for Accounts Receivable has a balance of 120,500 at year-end before adjustment. The company uses the balance sheet approach to estimate uncollectible accounts. By aging the individual customers' accounts, it was determined that the doubtful accounts amounted to 5,020. Prepare the year-end adjusting entry for uncollectible accounts under each of the following independent assumptions: (a) Allowance for Doubtful Accounts has a credit balance of 2,850. (b) Allowance for Doubtful Accounts has a debit balance of C925. General Journal Account Titles and Explanation Debit Credit Date (a) (6) (2) As of December 31, 2015, Valley Company has $16,920 cash in its current bank account, as well as several other items listed below: Bank credit card slips signed by customers. S 1.400 Money market fund balance.... $10,000 Investment in US Treasury bills.mature within 90 days $40,000 Checks received from customers, but not yet deposited in the bank $1,800 Investment in ATT 10%. bonds, maturing June 2016 560.000 What amount should be shown in Valley's December 31, 2015, balance sheet as "Cash and cash equivalents"? EXERCISE 3 (30 points) (1) Miracle Corporation had gross sales revenue of 1,700,000; cost of goods sold of 950,000; sales returns of 52,500; and sales discounts of 30,000 Compute for the year: (a) What is the net sales? (b) What is the gross profit? (c) What is the gross profit rate? (2) Your store sells computers and software. The average computer sells for 1,350, but the customer buying a computer also buys an average of 750 in software. You earn only 10% gross profit rate on sales of computers, but you make a 40% gross profit rate on software. You currently are selling 150 computers per month. What is the total amount of your monthly gross profit? (3) Indicate whether you would expect each of the following businesses to maintain a perpetual or a periodic inventory system. Explain the reasoning behind your answers: (a) A jewelry store (b) A roadside vegetable stand. Quantity 16 14 SIO SI2 $ 160 168 EXERCISE 4 (30 points) Beech Soda Inc. uses a perpetual inventory system. The company's beginning inventory of a particular product and its purchases during the month of January were as follows: Unit Cost Total Cost Beginning inventory (Jan 1) Purchase Jan 11 Purchase Jan 20) 23 SIS 345 Total $ 673 On January 18, Beech Soda Inc. sold 25 units of this product. The other 28 units remained in inventory at January 31. (1) Determine the cost of goods sold to be recorded at January 18, using each of the following methods. Show computations. (a) FIFO (b) LIFO (c) Average cost (2) Determine the cost of 28 units of this product in inventory at January 31, using each of the following methods. Show computations. (a) FIFO (b) LIFO (c) Average cost