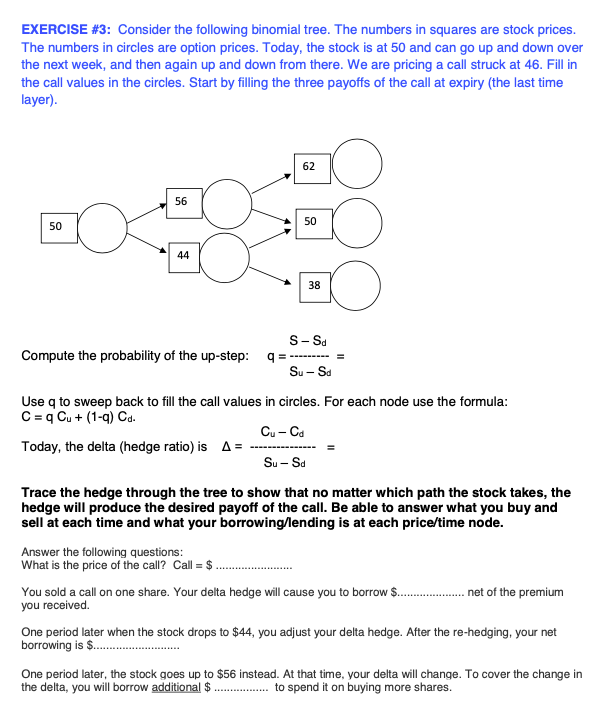
EXERCISE #3: Consider the following binomial tree. The numbers in squares are stock prices. The numbers in circles are option prices. Today, the stock is at 50 and can go up and down over the next week, and then again up and down from there. We are pricing a call struck at 46. Fill in the call values in the circles. Start by filling the three payoffs of the call at expiry (the last time layer). 62 56 50 50 44 38 Compute the probability of the up-step: S-Sd q= Su - Sd Use q to sweep back to fill the call values in circles. For each node use the formula: C = q Cu + (1-9) Cd. Cu-Cd Today, the delta (hedge ratio) is A = Su - Sa Trace the hedge through the tree to show that no matter which path the stock takes, the hedge will produce the desired payoff of the call. Be able to answer what you buy and sell at each time and what your borrowing/lending is at each price/time node. Answer the following questions: What is the price of the call? Call = $. You sold a call on one share. Your delta hedge will cause you to borrow $... .net of the premium you received. One period later when the stock drops to $44, you adjust your delta hedge. After the re-hedging, your net borrowing is $..... One period later, the stock goes up to $56 instead. At that time, your delta will change. To cover the change in the delta, you will borrow additional $ ..... to spend it on buying more shares. EXERCISE #3: Consider the following binomial tree. The numbers in squares are stock prices. The numbers in circles are option prices. Today, the stock is at 50 and can go up and down over the next week, and then again up and down from there. We are pricing a call struck at 46. Fill in the call values in the circles. Start by filling the three payoffs of the call at expiry (the last time layer). 62 56 50 50 44 38 Compute the probability of the up-step: S-Sd q= Su - Sd Use q to sweep back to fill the call values in circles. For each node use the formula: C = q Cu + (1-9) Cd. Cu-Cd Today, the delta (hedge ratio) is A = Su - Sa Trace the hedge through the tree to show that no matter which path the stock takes, the hedge will produce the desired payoff of the call. Be able to answer what you buy and sell at each time and what your borrowing/lending is at each price/time node. Answer the following questions: What is the price of the call? Call = $. You sold a call on one share. Your delta hedge will cause you to borrow $... .net of the premium you received. One period later when the stock drops to $44, you adjust your delta hedge. After the re-hedging, your net borrowing is $..... One period later, the stock goes up to $56 instead. At that time, your delta will change. To cover the change in the delta, you will borrow additional $ ..... to spend it on buying more shares







