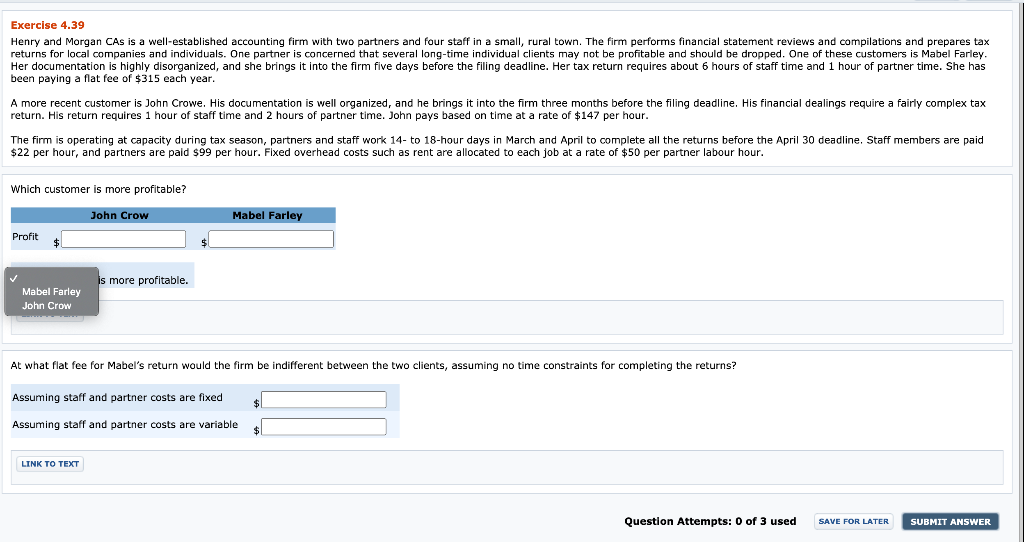
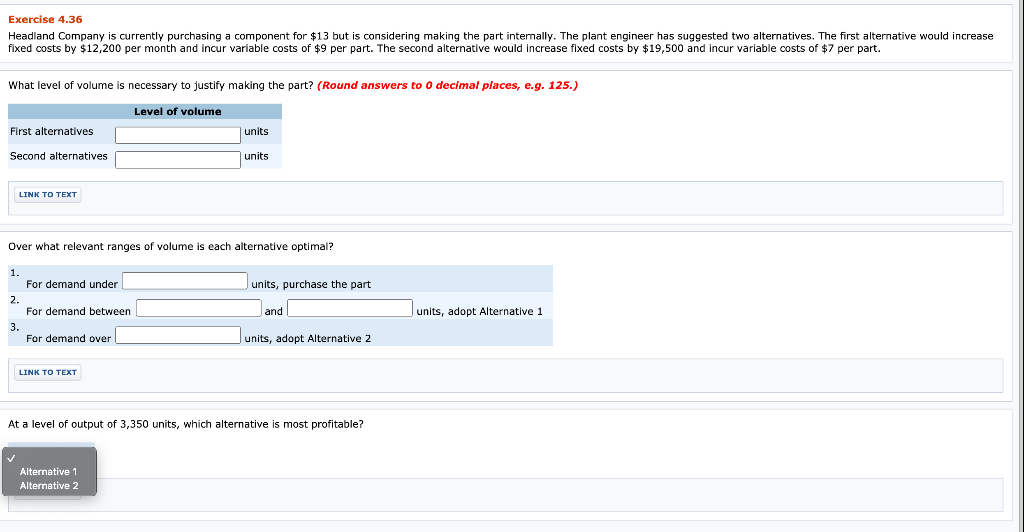
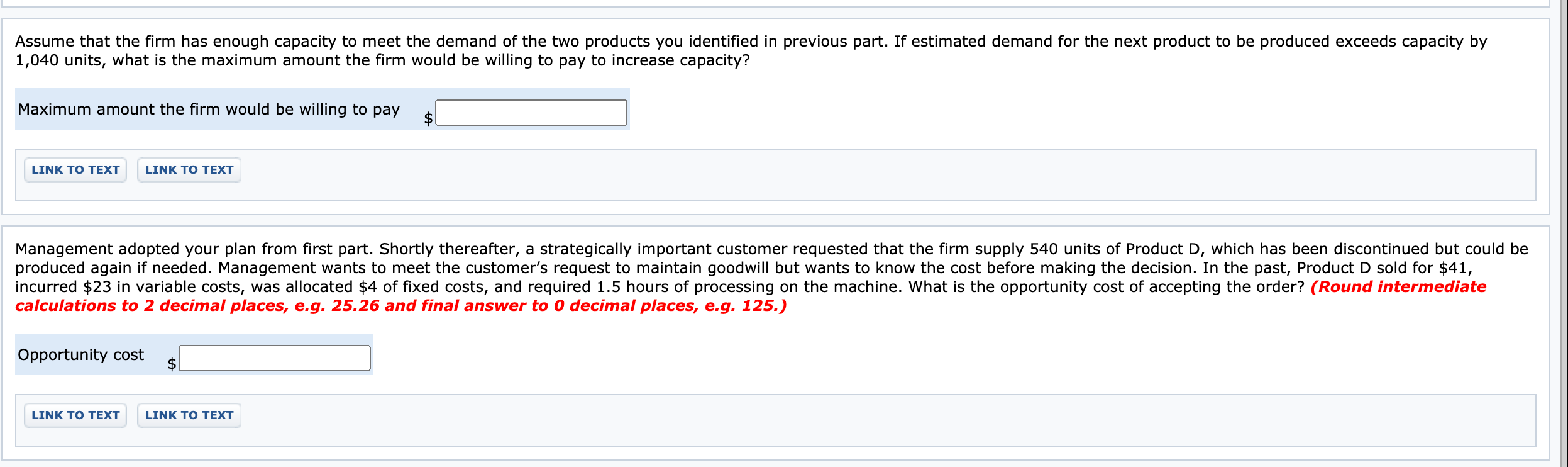
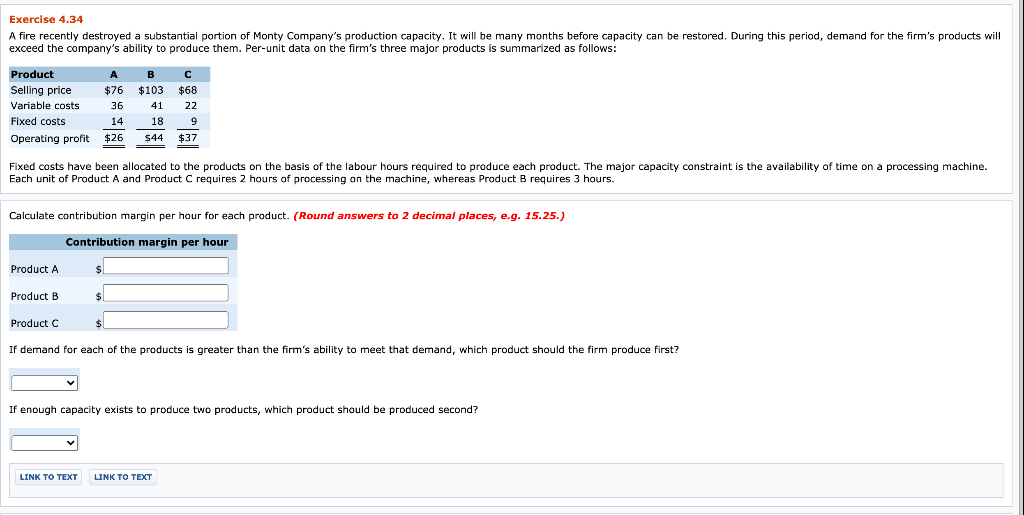
Exercise 4.39 Henry and Morgan CAS is a well-established accounting firm with two partners and four staff in a small, rural town. The firm performs financial statement reviews and compilations and prepares tax returns for local companies and individuals. One partner is concerned that several long-time individual clients may not be profitable and should be dropped. One of these customers is Mabel Farley. Her documentation is highly disorganized, and she brings it into the firm five days before the filing deadline. Her tax return requires about 6 hours of staff time and 1 hour of partner time. She has been paying a flat fee of $315 each year. A more recent customer is John Crowe. His documentation is well organized, and he brings it into the firm three months before the filing deadline. His financial dealings require a fairly complex tax return. His return requires 1 hour of staff time and 2 hours of partner time. John pays based on time at a rate of $147 per hour. The firm is operating at capacity during tax season, partners and staff work 14- to 18-hour days in March and April to complete all the returns before the April 30 deadline. Staff members are paid $22 per hour, and partners are paid $99 per hour. Fixed overhead costs such as rent are allocated to each job at a rate of $50 per partner labour hour. Which customer is more profitable? John Crow Mabel Farley Profit more profitable. Mabel Farley John Crow At what flat fee for Mabel's return would the firm be indifferent between the two clients, assuming no time constraints for completing the returns? Assuming staff and partner costs are fixed Assuming staff and partner costs are variable LINK TO TEXT Question Attempts: 0 of 3 used SAVE FOR LATER SUBMIT ANSWER Exercise 4.36 Headland Company is currently purchasing a component for $13 but is considering making the part internally. The plant engineer has suggested two alternatives. The first alternative would increase fixed costs by $12,200 per month and incur variable costs of $9 per part. The second alternative would increase fixed costs by $19,500 and incur variable costs of $7 per part. What level of volume necessary to justify making the part? (Round answers to O decimal places, e.g. 125.) Level of volume First alternatives units Second alternatives units LINK TO TEXT Over what relevant ranges of volume each alternative optimal? 1. For demand under units, purchase the part 2 For demand between and units, adopt Alternative 1 3. For demand over units, adopt Alternative 2 LINK TO TEXT At a level of output of 3,350 units, which alternative is most profitable? Alternative 1 Alternative 2 Assume that the firm has enough capacity to meet the demand of the two products you identified in previous part. If estimated demand for the next product to be produced exceeds capacity by 1,040 units, what is the maximum amount the firm would be willing to pay to increase capacity? Maximum amount the firm would be willing to pay LINK TO TEXT LINK TO TEXT Management adopted your plan from first part. Shortly thereafter, a strategically important customer requested that the firm supply 540 units of Product D, which has been discontinued but could be produced again if needed. Management wants to meet the customer's request to maintain goodwill but wants to know the cost before making the decision. In the past, Product D sold for $41, incurred $23 in variable costs, was allocated $4 of fixed costs, and required 1.5 hours of processing on the machine. What is the opportunity cost of accepting the order? (Round intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places, e.g. 25.26 and final answer to 0 decimal places, e.g. 125.) Opportunity cost LINK TO TEXT LINK TO TEXT Exercise 4.34 A fire recently destroyed a substantial portion of Monty Company's production capacity. It will be many months before capacity can be restored. During this period, demand for the firm's products will exceed the company's ability to produce them. Per-unit data on the firm's three major products is summarized as follows: Product Selling price Variable costs Fixed costs Operating profit A $76 36 $103 41 18 $44 $68 22 9 $37 14 $26 Fixed costs have been allocated to the products on the basis of the labour hours required to produce each product. The major capacity constraint is the availability of time on a processing machine. Each unit of Product A and Product C requires 2 hours of processing on the machine, whereas Product B requires 3 hours. Calculate contribution margin per hour for each product. (Round answers to 2 decimal places, e.g. 15.25.) Contribution margin per hour Product A $ Product B $ Product C If demand for each of the products is greater than the firm's ability to meet that demand, which product should the firm produce first? If enough capacity exists to produce two products, which product should be produced second? LINK TO TEXT LINK TO TEXT Exercise 4.31 The Crane packages and distributes three grades of animal feed. The material cost per tonne and estimated annual sales for each of the products are listed here: Material Estimated Product Cost Sales Super Premium $ 10.75 2,000 tonnes Premium 9.00 2,800 tonnes Economy 8.00 5,000 tonnes The fixed cost of operating the machinery used to package all three products is $10,100 per year. In the past, prices have been set by allocating the fixed operating cost to products on the basis of estimated sales in tonnes. The resulting full costs (material costs plus allocated fixed operating cost) are then marked up 100%. The Crane has received an offer from a foreign firm for 900 tonnes of the premium-grade feed. Sales to the foreign firm would not affect domestic sales but would require a $1,800 increase in fixed production costs. (c) Using only quantitative information, what is the minimum price that the Crane's managers should be willing to accept from the foreign firm? Price for order: LINK TO TEXT LINK TO TEXT Question Attempts: 0 of 3 used











