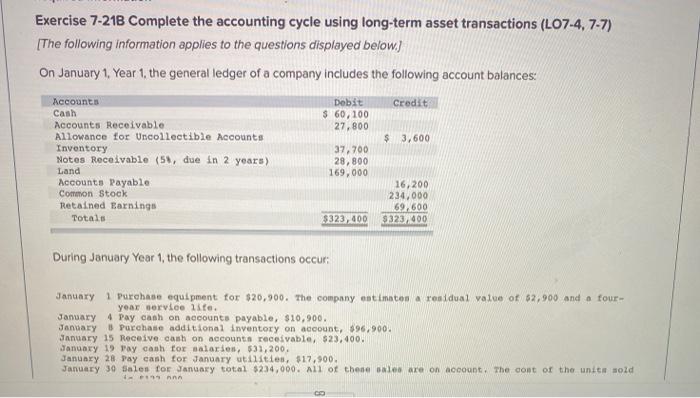
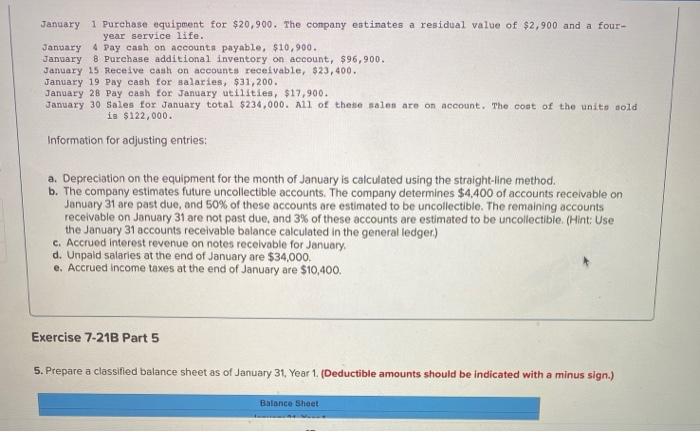
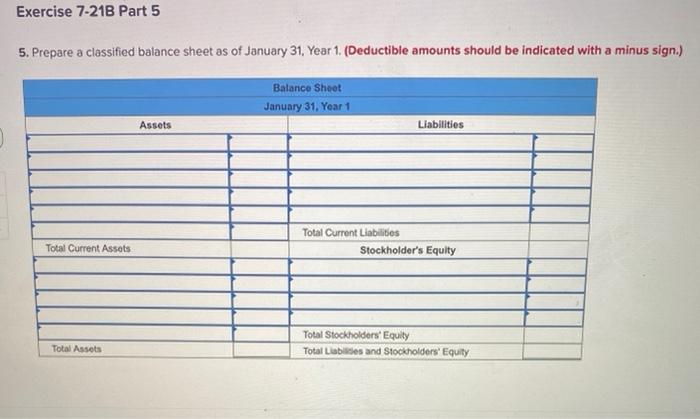
Exercise 7-218 Complete the accounting cycle using long-term asset transactions (L07-4, 7-7) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below) On January 1, Year 1. the general ledger of a company includes the following account balances: Credit Dobit $ 60, 100 27,800 $3,600 Accounts Cash Accounts Receivable Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts Inventory Notes Receivable (5#, due in 2 years) Land Accounts Payable Common Stock Retained Earnings Totals 37,700 28,800 169,000 16,200 234,000 59,600 $323,400 $323,400 During January Year 1, the following transactions occur January 1 Purchase equipment for $20,900. The company estimaton a residual value of 62,900 and a four- year service life. January 4 Pay canh on accounts payable, $10,900. January Purchase additional inventory on account, 96,900. January 15 Receive cash on accounts receivable, $23,400. January 19 Pay cash for salaries,531,200. January 28 Pay cash for January utilities, $17,900. January 30 Sales for January total $234,000. All of these sales are on account. The cont of the units sold 1- January 1 Purchase equipment for $20,900. The company estimates a residual value of $2,900 and a four- year service life. January 4 Pay cash on accounts payable, $10,900. January 8 Purchase additional inventory on account, $96,900. January 15 Receive cash on accounts receivable, $23,400. January 19 Day cash for salaries, $31,200. January 28 Pay cash for January utilities, $17,900. January 30 Sales for January total $234,000. All of these sales are on account. The cost of the unito sold is $122,000. Information for adjusting entries: a. Depreciation on the equipment for the month of January is calculated using the straight-line method. b. The company estimates future uncollectible accounts. The company determines $4,400 of accounts receivable on January 31 are past due, and 50% of these accounts are estimated to be uncollectible. The remaining accounts receivable on January 31 are not past due, and 3% of these accounts are estimated to be uncollectible. (Hint: Use the January 31 accounts receivable balance calculated in the general ledger) c. Accrued interest revenue on notes receivable for January d. Unpaid salaries at the end of January are $34,000. e. Accrued Income taxes at the end of January are $10,400. Exercise 7-21B Part 5 5. Prepare a classified balance sheet as of January 31 Year 1. (Deductible amounts should be indicated with a minus sign.) Balance Sheet Exercise 7-21B Part 5 5. Prepare a classified balance sheet as of January 31, Year 1 (Deductible amounts should be indicated with a minus sign.) Balance Sheet January 31, Year 1 Assets Liabilities Total Current Assets Total Current Liabilities Stockholder's Equity Total Stockholders' Equity Total Liabides and Stockholders' Equity Total Assets