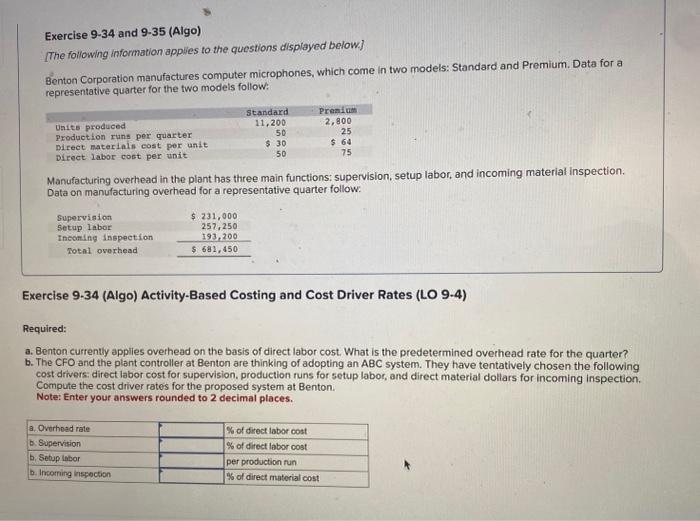
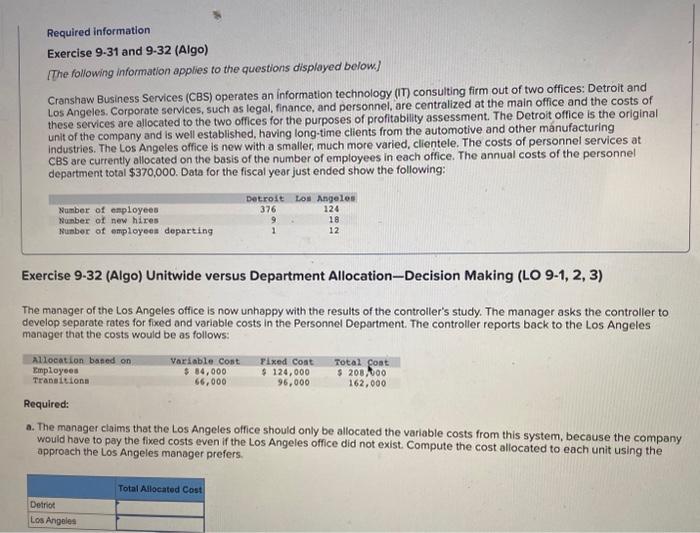
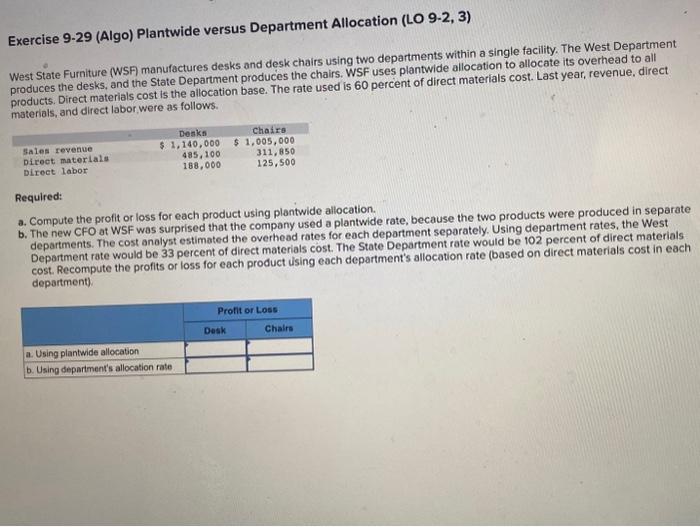
Exercise 9-34 and 9-35 (Algo) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below] Benton Corporation manufactures computer microphones, which come in two models: Standard and Premium. Data for a representative quarter for the two models follow: Manufacturing overhead in the plant has three main functions: supervision, setup labor, and incoming material inspection. Data on manufacturing overhead for a representative quarter follow. Exercise 9-34 (Algo) Activity-Based Costing and Cost Driver Rates (LO 9-4) Required: a. Benton currently applies overhead on the basis of direct labor cost. What is the predetermined overhead rate for the quarter? b. The CFO and the plant controller at Benton are thinking of adopting an ABC system. They have tentatively chosen the following cost drivers, direct labor cost for supervision, production runs for setup labor, and direct material dollars for incoming inspection. Compute the cost driver rates for the proposed system at Benton. Note: Enter your answers rounded to 2 decimal places. Exercise 9.31 and 9.32 (Algo) [The following information applies to the questions displayed below] Cranshaw Business Services (CBS) operates an information technology (iT) consulting firm out of two offices: Detroit and Los Angeles. Corporate services, such as legal, finance, and personnel, are centralized at the main office and the costs of these services are allocated to the two offices for the purposes of profitability assessment. The Detroit office is the original unit of the company and is well established, having long-time clients from the automotive and other manufacturing industries. The Los Angeles office is new with a smaller, much more varied, clientele. The costs of personnel services at CBS are currently allocated on the basis of the number of employees in each office. The annual costs of the personnel department total \$370,000. Data for the fiscal year just ended show the following: Exercise 9-32 (Algo) Unitwide versus Department Allocation-Decision Making (LO 9-1, 2, 3) The manager of the Los Angeles office is now unhappy with the results of the controller's study. The manager asks the controller to develop separate rates for fixed and variable costs in the Personnel Department. The controller reports back to the Los Angeles manager that the costs would be as follows: Required: a. The manager claims that the Los Angeles office should only be allocated the variable costs from this system, because the company would have to pay the fixed costs even if the Los Angeles office did not exist. Compute the cost allocated to each unit using the approach the Los Angeles manager prefers. Exercise 9-29 (Algo) Plantwide versus Department Allocation (LO 9-2,3) West State Furniture (WSF manufactures desks and desk chairs using two departments within a single facility. The West Department produces the desks, and the State Department produces the chairs. WSF uses plantwide allocation to allocate its overhead to all products. Direct materials cost is the allocation base. The rate used is 60 percent of direct materials cost. Last year, revenue, direct materials, and direct labor, were as follows. Required: a. Compute the profit or loss for each product using plantwide allocation. b. The new CFO at WSF was surprised that the company used a plantwide rate, because the two products were produced in separate departments. The cost analyst estimated the overhead rates for each department separately. Using department rates, the West Department rate would be 33 percent of direct materials cost. The State Department rate would be 102 percent of direct materials cost. Recompute the profits or loss for each product using each department's allocation rate (based on direct materials cost in each department)