
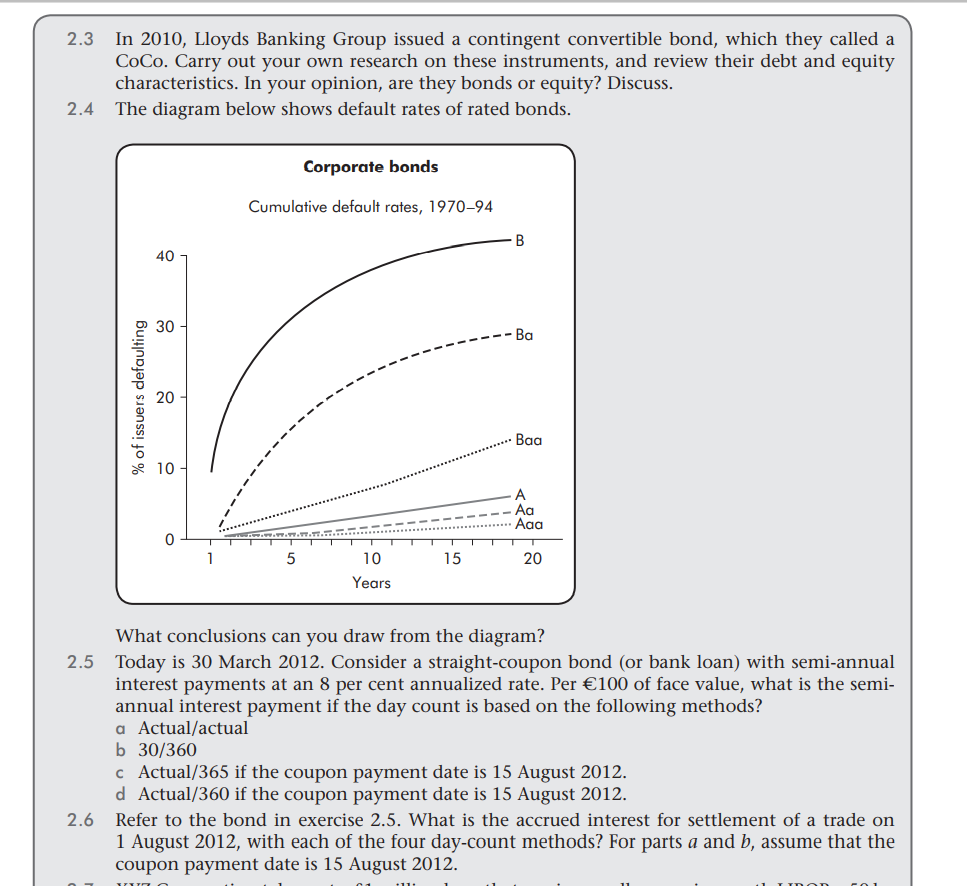

Exercises 2.1 Critics of rating agencies argue that because the firm pays rating agencies to rate the firm's debt, the rating agencies have the wrong incentives. What do you think of this argument? Can you think of ways to assess its validity? 2.2 Credit rating agencies experienced substantial criticism from the regulatory authorities for not predicting the global financial crisis in 2008. Why do you think this happened, and how did the agencies defend themselves? 2.3 In 2010, Lloyds Banking Group issued a contingent convertible bond, which they called a CoCo. Carry out your own research on these instruments, and review their debt and equity characteristics. In your opinion, are they bonds or equity? Discuss. The diagram below shows default rates of rated bonds. 2.4 Corporate bonds Cumulative default rates, 1970-94 B 40 30 -Ba % of issuers defaulting 20 10 A Aaa 0 5 15 20 10 Years What conclusions can you draw from the diagram? 2.5 Today is 30 March 2012. Consider a straight-coupon bond (or bank loan) with semi-annual interest payments at an 8 per cent annualized rate. Per 100 of face value, what is the semi- annual interest payment if the day count is based on the following methods? a Actual/actual b 30/360 c Actual/365 if the coupon payment date is 15 August 2012. d Actual/360 if the coupon payment date is 15 August 2012. 2.6 Refer to the bond in exercise 2.5. What is the accrued interest for settlement of a trade on 1 August 2012, with each of the four day-count methods? For parts a and b, assume that the coupon payment date is 15 August 2012. 2.7 XYZ Corporation takes out a 1 million loan that semi-annually pays six-month LIBOR + 50 bp on 5 March 2012. Assume that LIBOR is at 7 per cent on 5 March 2012, 6.75 per cent on 5 September 2012, and 7.125 per cent on 5 March 2013. What are the first three interest payments on the loan? When are they paid? (Hint: LIBOR-based loans typically use the modified following business day convention for payment dates and interest accrued to the payment date. For the 'actual' in the actual/360 day count, this means that if the payment date (say six months from now) falls on a Saturday, the payment date is the next business day.)* * An exception occurs when the next business day falls in the subsequent month, in which case the prior business day to that Saturday would be the payment date. 2.8 A 5 per cent corporate bond maturing 14 November 2020 (originally a 25-year bond at issue) has a yield to maturity of 6 per cent (a 3 per cent discount rate per six-month period for each of its semi-annual payments) for the settlement date, 9 June 2012. What are the flat price, full price and accrued interest of the bond on 9 June 2012? 2.9 A bank loan to the Knowledge Company has a 50 basis point spread to LIBOR. If LIBOR is at 6 per cent, what is the rate of interest on the bank loan? Exercises 2.1 Critics of rating agencies argue that because the firm pays rating agencies to rate the firm's debt, the rating agencies have the wrong incentives. What do you think of this argument? Can you think of ways to assess its validity? 2.2 Credit rating agencies experienced substantial criticism from the regulatory authorities for not predicting the global financial crisis in 2008. Why do you think this happened, and how did the agencies defend themselves? 2.3 In 2010, Lloyds Banking Group issued a contingent convertible bond, which they called a CoCo. Carry out your own research on these instruments, and review their debt and equity characteristics. In your opinion, are they bonds or equity? Discuss. The diagram below shows default rates of rated bonds. 2.4 Corporate bonds Cumulative default rates, 1970-94 B 40 30 -Ba % of issuers defaulting 20 10 A Aaa 0 5 15 20 10 Years What conclusions can you draw from the diagram? 2.5 Today is 30 March 2012. Consider a straight-coupon bond (or bank loan) with semi-annual interest payments at an 8 per cent annualized rate. Per 100 of face value, what is the semi- annual interest payment if the day count is based on the following methods? a Actual/actual b 30/360 c Actual/365 if the coupon payment date is 15 August 2012. d Actual/360 if the coupon payment date is 15 August 2012. 2.6 Refer to the bond in exercise 2.5. What is the accrued interest for settlement of a trade on 1 August 2012, with each of the four day-count methods? For parts a and b, assume that the coupon payment date is 15 August 2012. 2.7 XYZ Corporation takes out a 1 million loan that semi-annually pays six-month LIBOR + 50 bp on 5 March 2012. Assume that LIBOR is at 7 per cent on 5 March 2012, 6.75 per cent on 5 September 2012, and 7.125 per cent on 5 March 2013. What are the first three interest payments on the loan? When are they paid? (Hint: LIBOR-based loans typically use the modified following business day convention for payment dates and interest accrued to the payment date. For the 'actual' in the actual/360 day count, this means that if the payment date (say six months from now) falls on a Saturday, the payment date is the next business day.)* * An exception occurs when the next business day falls in the subsequent month, in which case the prior business day to that Saturday would be the payment date. 2.8 A 5 per cent corporate bond maturing 14 November 2020 (originally a 25-year bond at issue) has a yield to maturity of 6 per cent (a 3 per cent discount rate per six-month period for each of its semi-annual payments) for the settlement date, 9 June 2012. What are the flat price, full price and accrued interest of the bond on 9 June 2012? 2.9 A bank loan to the Knowledge Company has a 50 basis point spread to LIBOR. If LIBOR is at 6 per cent, what is the rate of interest on the bank loan









