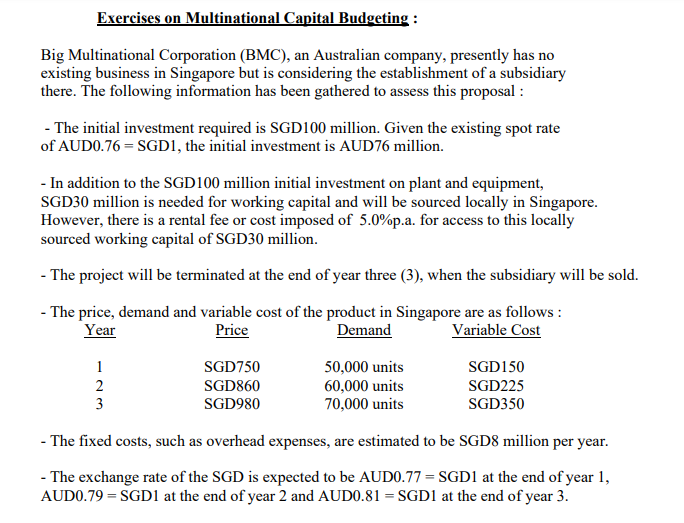


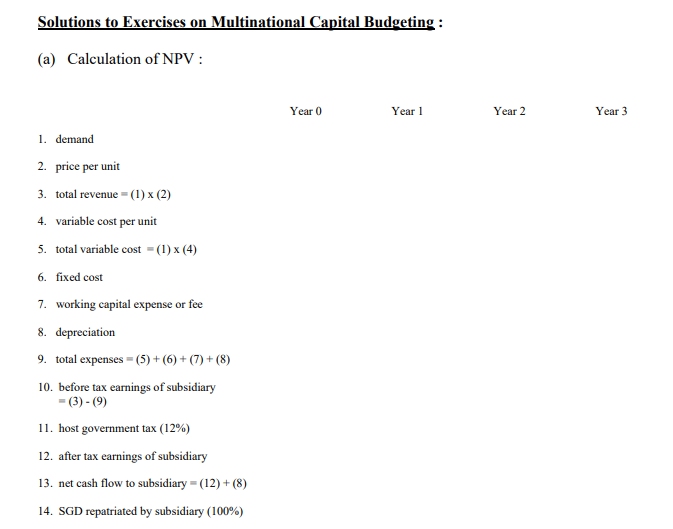



Exercises on Multinational Capital Budgeting : Big Multinational Corporation (BMC), an Australian company, presently has no existing business in Singapore but is considering the establishment of a subsidiary there. The following information has been gathered to assess this proposal : - The initial investment required is SGD100 million. Given the existing spot rate of AUDO.76 = SGD1, the initial investment is AUD76 million. - In addition to the SGD100 million initial investment on plant and equipment, SGD30 million is needed for working capital and will be sourced locally in Singapore. However, there is a rental fee or cost imposed of 5.0%p.a. for access to this locally sourced working capital of SGD30 million. - The project will be terminated at the end of year three (3), when the subsidiary will be sold. - The price, demand and variable cost of the product in Singapore are as follows: Year Price Demand Variable Cost 1 SGD750 50,000 units SGD150 2 SGD860 60,000 units SGD225 3 SGD980 70,000 units SGD350 - The fixed costs, such as overhead expenses, are estimated to be SGD8 million per year. - The exchange rate of the SGD is expected to be AUD0.77 = SGD1 at the end of year 1, AUDO.79 = SGD1 at the end of year 2 and AUD0.81 = SGD1 at the end of year 3. - The Singapore government will impose a corporate income tax of 12% p.a. on income earned by the Singapore subsidiary. In addition, it will impose a withholding tax of 2.5% p.a. on earnings repatriated by the subsidiary to the parent. - All cash flows received by the subsidiary are to be sent to the parent at the end of each year. The subsidiary uses its working capital to support ongoing operations. - The plant and equipment are depreciated fully over ten (10) years using the straight line depreciation method. Since the plant and equipment are initially valued at SGD100 million, the annual depreciation expense is SGD10 million. - In three (3) years, the subsidiary is to be sold. BMC plans to let the acquiring firm assume the existing Singapore local working capital arrangements. The working capital will not be liquidated, but will be used by the acquiring firm. BMC expects to receive SGD135 million when it sells the subsidiary. BMC requires a 10% p.a. return on this project. Required: (a) Calculate the net present value (NPV) of this project. Should BMC accept this project ? (b) Assume that BMC also considers an alternative investment arrangement in which it invests an additional AUD22.8 million itself to cover the working capital requirements and avoids the locally imposed rental fee for access to local currency working capital. If this arrangement is used the selling price of the subsidiary is expected to be SGD30 million higher. Is this alternative investment arrangement more feasible than the original proposed arrangement ? (re-calculate the NPV under this changed scenario) (c) Would the NPV of this project be more sensitive to exchange rate movements if BMC used Singapore local currency resources to cover working capital or invested more of its own parent currency funds to cover the working capital ? Briefly, but very clearly and explicitly explain. Solutions to Exercises on Multinational Capital Budgeting : (a) Calculation of NPV : Year 0 Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 1. demand 2. price per unit 3. total revenue - (1) (2) 4. variable cost per unit 5. total variable cost - (1) (4) 6. fixed cost 7. working capital expense or fee 8. depreciation 9. total expenses = (5) + (6) + (7) + (8) 10. before tax earnings of subsidiary - (3) - (9) 11. host government tax (12%) 12. after tax earnings of subsidiary 13. net cash flow to subsidiary = (12) + (8) 14. SGD repatriated by subsidiary (100%) 15. withholding tax imposed on repatriated funds (2.5%) 16. SGD repatriated after withholding taxes 17. sale value 18. exchange rate of SGDI 19. cash flows to parent 20. PV of parent cash flows (10% discount rate) 21. initial investment by parent 22. cumulative NPV of cash flows (b) The capital budgeting analysis is revised to incorporate the alternative investment changes. Year 0 Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 1. demand 2. price per unit 3. total revenue = (1)x (2) 4. variable cost per unit 5. total variable cost - (1) (4) 6. fixed cost 7. working capital expense or fee 8. depreciation 9. total expenses = (5) + (6) + (7) + (8) 10. before tax earnings of subsidiary -(3) - (9) 11. host government tax (12%) 12. after tax earnings of subsidiary 13. net cash flow to subsidiary - (12) + (8) 14. SGD repatriated by subsidiary (100%) 15. withholding tax imposed on repatriated funds (2.5%) 16. SGD repatriated after withholding taxes 17. sale value 18. exchange rate of SGDI 19. cash flows to parent 20. PV of parent cash flows (10% discount rate) 21. initial investment by parent 22. cumulative NPV of cash flows













