Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Explain about the case scenario of FIGURE 13-7 Price discovery by hill climbing: structure and key components.? And about Modeling decision Making.? Kindly take reference
Explain about the case scenario of FIGURE 13-7 Price discovery by hill climbing: structure and key components.?
And about Modeling decision Making.?
Kindly take reference from below and chapter 13 from John D Sterman - Business Dynamics Systems Thinking and Modeling for a Complex World-McGraw-Hill Higher Education (2000)
?
?
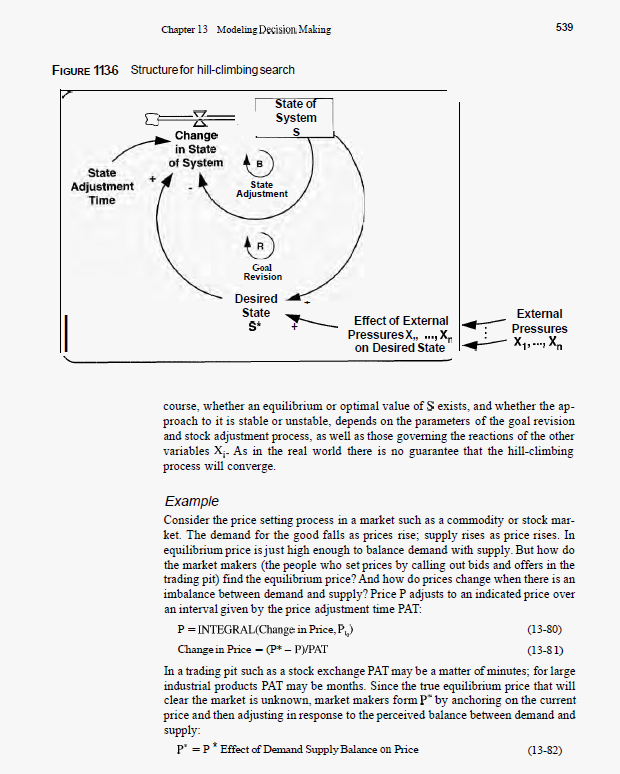

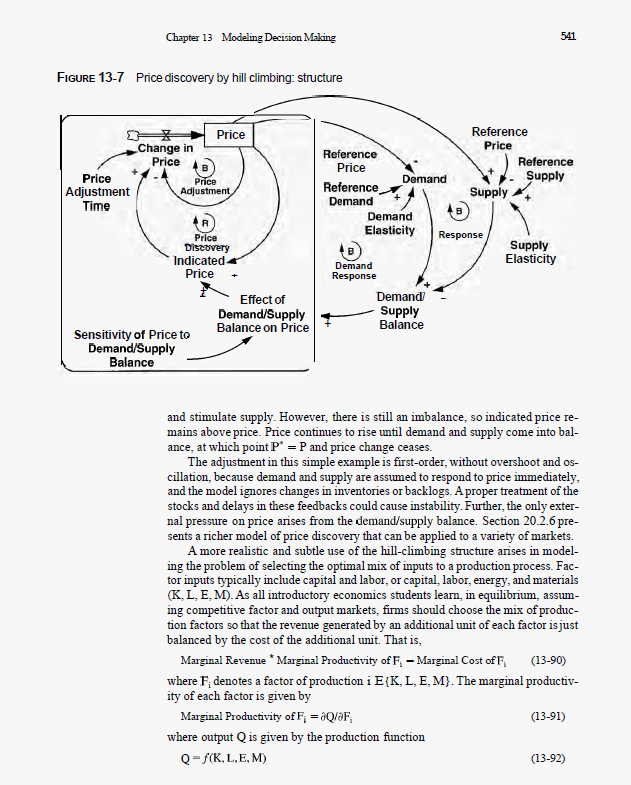
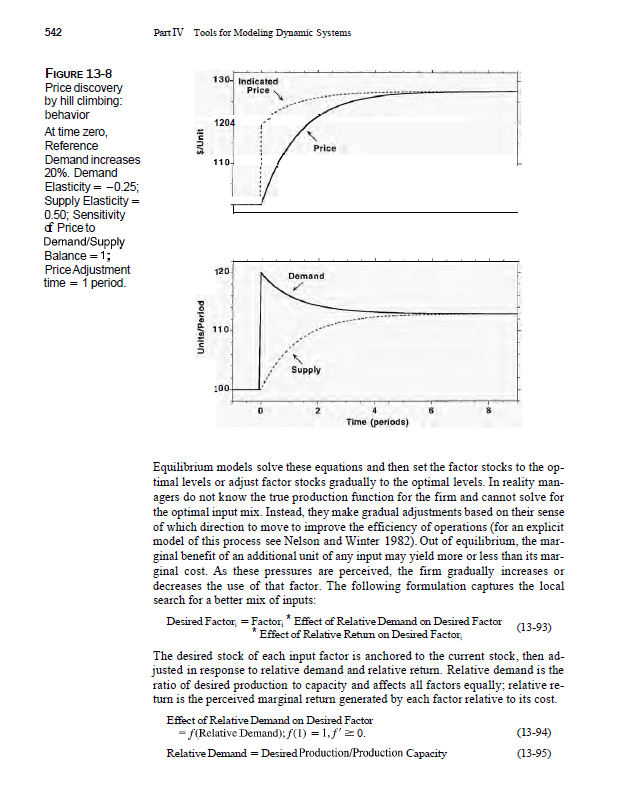
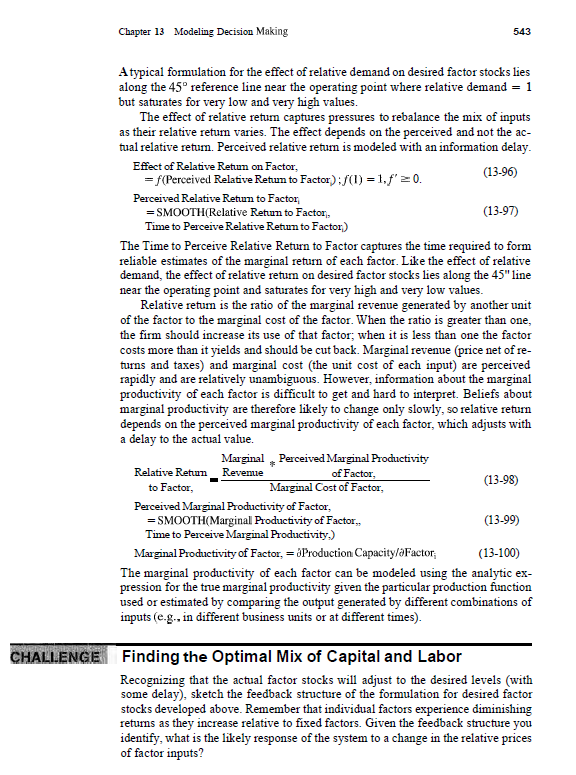








Chapter 13 Modeling Decision Making FIGURE 1136 Structure for hill-climbing search State Adjustment Time Change in State of System State of System S State Adjustment Goal Revision Desired State S* Effect of External Pressures X.,., ..., X on Desired State 539 External Pressures X X course, whether an equilibrium or optimal value of S exists, and whether the ap- proach to it is stable or unstable, depends on the parameters of the goal revision and stock adjustment process, as well as those governing the reactions of the other variables X. As in the real world there is no guarantee that the hill-climbing process will converge. Example Consider the price setting process in a market such as a commodity or stock mar- ket. The demand for the good falls as prices rise; supply rises as price rises. In equilibrium price is just high enough to balance demand with supply. But how do the market makers (the people who set prices by calling out bids and offers in the trading pit) find the equilibrium price? And how do prices change when there is an imbalance between demand and supply? Price P adjusts to an indicated price over an interval given by the price adjustment time PAT: P = INTEGRAL(Change in Price, P.) Change in Price - (P* -P)/PAT (13-80) (13-81) In a trading pit such as a stock exchange PAT may be a matter of minutes; for large industrial products PAT may be months. Since the true equilibrium price that will clear the market is unknown, market makers form P" by anchoring on the current price and then adjusting in response to the perceived balance between demand and supply: P" =P* Effect of Demand Supply Balance on Price (13-82) Chapter 13 Modeling Decision Making FIGURE 1136 Structure for hill-climbing search State Adjustment Time Change in State of System State of System S State Adjustment Goal Revision Desired State S* Effect of External Pressures X.,., ..., X on Desired State 539 External Pressures X X course, whether an equilibrium or optimal value of S exists, and whether the ap- proach to it is stable or unstable, depends on the parameters of the goal revision and stock adjustment process, as well as those governing the reactions of the other variables X. As in the real world there is no guarantee that the hill-climbing process will converge. Example Consider the price setting process in a market such as a commodity or stock mar- ket. The demand for the good falls as prices rise; supply rises as price rises. In equilibrium price is just high enough to balance demand with supply. But how do the market makers (the people who set prices by calling out bids and offers in the trading pit) find the equilibrium price? And how do prices change when there is an imbalance between demand and supply? Price P adjusts to an indicated price over an interval given by the price adjustment time PAT: P = INTEGRAL(Change in Price,P,) Change in Price - (P* -P)/PAT (13-80) (13-81) In a trading pit such as a stock exchange PAT may be a matter of minutes; for large industrial products PAT may be months. Since the true equilibrium price that will clear the market is unknown, market makers form P" by anchoring on the current price and then adjusting in response to the perceived balance between demand and supply: P" =P* Effect of Demand Supply Balance on Price (13-82)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Here are the key details from the case study The price discovery process described is an example of hill climbing decision making where the desired st...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


