explain clearly please

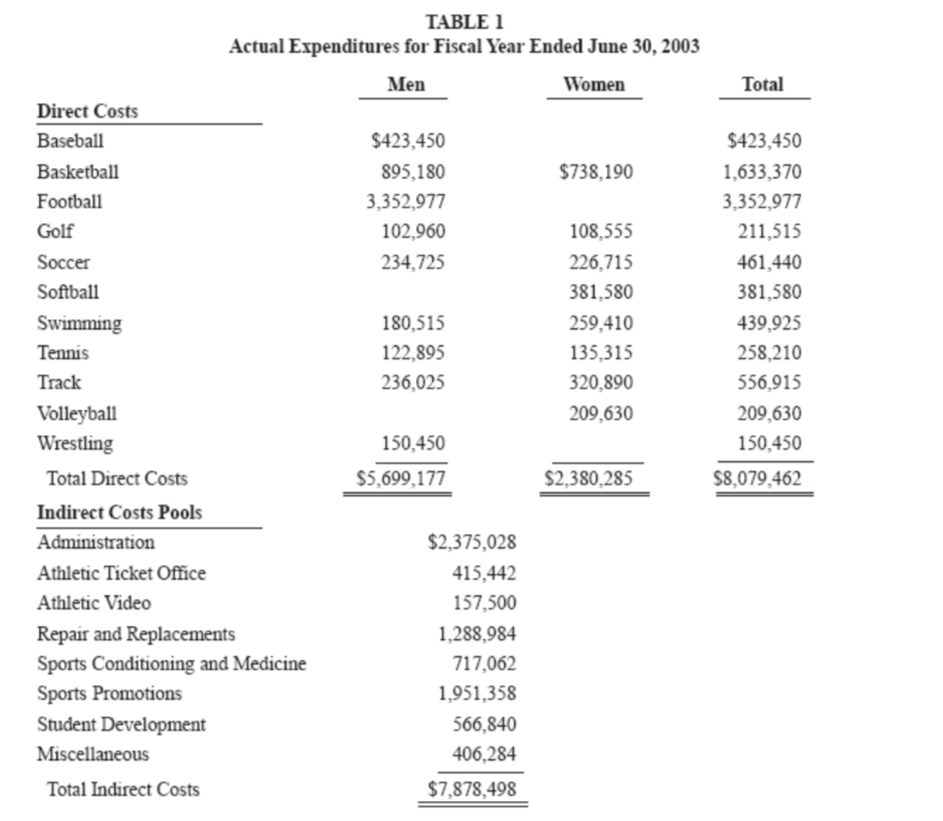
Title IX is a comprehensive federal law that states, "No person in the United States shall, on the basis of sex, be excluded from participation in, be denied the benefits of, or be subjected to discrimination under any education program or activity receiving Federal financial assistance" (United States Code 1972, 20 U.S.C. 1681). This case focuses on a single Title IX issue, gender equality in collegiate athletics, which specifically requires the effective accommodation of athletic interests and abilities of men and women necessary for providing equal athletic opportunities. One way to comply with this aspect of Title IX is for a university to demonstrate continuing progress in the expansion of programs for the underrepresented gender (i.e., women). Assume you are a staff accountant at the athletic department of Kingston State University (KSU), which competes in Division 1-A sports. Your task is to help the athletic director document KSU's compliance with Title IX using the information that follows. Table 1 provides the actual costs incurred by the athletic department for the most recent fiscal year. Table 2 presents summary information by sport. KSU considers only football and men's basketball as revenue sports, in which revenues generated exceed the costs of those teams.2 All other sports teams are deemed nonrevenue teams (i.e., earns revenue via ticket sales and other means, but their revenues do not cover the team's costs). Table 3 shows the Internal Audit Department's calculation of the amount spent per student athlete during the year. Table 4 describes the various cost categories. The athletic director wants to find a way to be in compliance with Title IX without resorting to actions he considered drastic reducing the number of existing male student-athletes and incurring additional costs to start new women's programs; although to be fair, he felt he needed to look at all options. He was aware that the allocation of indirect costs, because indirect costs are not directly traceable to any particular team, contains a degree of arbitrariness and the reallocation of indirect costs might be beneficial to KSU in terms of compliance with Title IX. The athletic director has asked you to prepare an internal memo and provide your cost analysis as follows: Part 1: Discuss the pros and cons of the current system of allocating indirect costs in terms of: a. allocating all of the cost pools under "Total Indirect Costs'; b. choosing 'number of athletes' as the cost driver (i.e., the basis to allocate the indirect costs); c. satisfying the Title IX compliance issue above (i.e., gender equality in collegiate athletics); and d. satisfying key stakeholders (i.e., in addition to the athletic director and current student-athletes). 1. TABLE 1 Actual Expenditures for Fiscal Year Ended June 30, 2003 Men Women Total Direct Costs $423,450 $423,450 Baseball Basketball $738,190 895,180 1,633,370 3,352,977 Football 3,352,977 Golf 102,960 108,555 211,515 Soccer 234,725 226,715 461,440 Softball 381,580 381,580 Swimming 180,515 259,410 439,925 135,315 258,210 Tennis 122,895 Track 236,025 320,890 556,915 Volleyball 209,630 209,630 Wrestling 150,450 150,450 $5,699,177 Total Direct Costs $2,380,285 $8,079,462 Indirect Costs Pools Administration $2,375,028 415,442 Athletic Ticket Office Athletic Video 157,500 Repair and Replacements 1,288,984 Sports Conditioning and Medicine Sports Promotions 717,062 1,951,358 Student Development 566,840 406,284 Miscellaneous Total Indirect Costs $7,878,498 Title IX is a comprehensive federal law that states, "No person in the United States shall, on the basis of sex, be excluded from participation in, be denied the benefits of, or be subjected to discrimination under any education program or activity receiving Federal financial assistance" (United States Code 1972, 20 U.S.C. 1681). This case focuses on a single Title IX issue, gender equality in collegiate athletics, which specifically requires the effective accommodation of athletic interests and abilities of men and women necessary for providing equal athletic opportunities. One way to comply with this aspect of Title IX is for a university to demonstrate continuing progress in the expansion of programs for the underrepresented gender (i.e., women). Assume you are a staff accountant at the athletic department of Kingston State University (KSU), which competes in Division 1-A sports. Your task is to help the athletic director document KSU's compliance with Title IX using the information that follows. Table 1 provides the actual costs incurred by the athletic department for the most recent fiscal year. Table 2 presents summary information by sport. KSU considers only football and men's basketball as revenue sports, in which revenues generated exceed the costs of those teams.2 All other sports teams are deemed nonrevenue teams (i.e., earns revenue via ticket sales and other means, but their revenues do not cover the team's costs). Table 3 shows the Internal Audit Department's calculation of the amount spent per student athlete during the year. Table 4 describes the various cost categories. The athletic director wants to find a way to be in compliance with Title IX without resorting to actions he considered drastic reducing the number of existing male student-athletes and incurring additional costs to start new women's programs; although to be fair, he felt he needed to look at all options. He was aware that the allocation of indirect costs, because indirect costs are not directly traceable to any particular team, contains a degree of arbitrariness and the reallocation of indirect costs might be beneficial to KSU in terms of compliance with Title IX. The athletic director has asked you to prepare an internal memo and provide your cost analysis as follows: Part 1: Discuss the pros and cons of the current system of allocating indirect costs in terms of: a. allocating all of the cost pools under "Total Indirect Costs'; b. choosing 'number of athletes' as the cost driver (i.e., the basis to allocate the indirect costs); c. satisfying the Title IX compliance issue above (i.e., gender equality in collegiate athletics); and d. satisfying key stakeholders (i.e., in addition to the athletic director and current student-athletes). 1. TABLE 1 Actual Expenditures for Fiscal Year Ended June 30, 2003 Men Women Total Direct Costs $423,450 $423,450 Baseball Basketball $738,190 895,180 1,633,370 3,352,977 Football 3,352,977 Golf 102,960 108,555 211,515 Soccer 234,725 226,715 461,440 Softball 381,580 381,580 Swimming 180,515 259,410 439,925 135,315 258,210 Tennis 122,895 Track 236,025 320,890 556,915 Volleyball 209,630 209,630 Wrestling 150,450 150,450 $5,699,177 Total Direct Costs $2,380,285 $8,079,462 Indirect Costs Pools Administration $2,375,028 415,442 Athletic Ticket Office Athletic Video 157,500 Repair and Replacements 1,288,984 Sports Conditioning and Medicine Sports Promotions 717,062 1,951,358 Student Development 566,840 406,284 Miscellaneous Total Indirect Costs $7,878,498








