Explain clearly
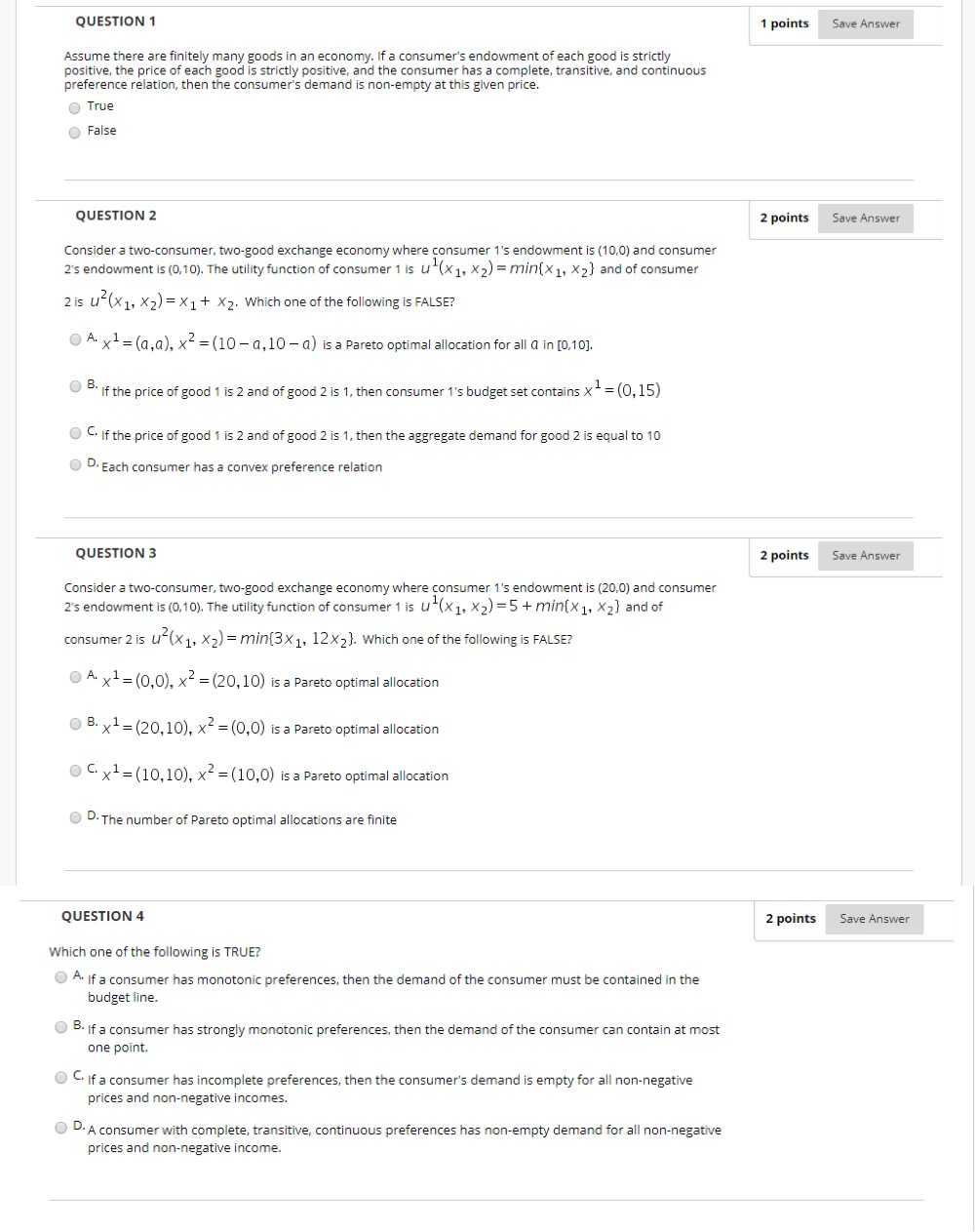
QUESTION 1 1 points Save Answer Assume there are finitely many goods in an economy. If a consumer's endowment of each good is strictly positive, the price of each good is strictly positive, and the consumer has a complete, transitive, and continuous preference relation, then the consumer's demand is non-empty at this given price. O True False QUESTION 2 2 points Save Answer Consider a two-consumer, two-good exchange economy where consumer 1's endowment is (10.0) and consumer 2's endowment is (0,10). The utility function of consumer 1 is u(X1. X2) = min{x1, X2) and of consumer 2is u"(X1, X2) = X1+ X2. Which one of the following is FALSE? O A. x1 = (a,a), x2 = (10 -a,10 -a) is a Pareto optimal allocation for all a in [0,10]. O B. If the price of good 1 is 2 and of good 2 is 1, then consumer 1's budget set contains x - = (0, 15) O C. If the price of good 1 is 2 and of good 2 is 1, then the aggregate demand for good 2 is equal to 10 O D. Each consumer has a convex preference relation QUESTION 3 2 points Save Answer Consider a two-consumer, two-good exchange economy where consumer 1's endowment is (20,0) and consumer 2's endowment is (0,10). The utility function of consumer 1 is u(X1, X2) =5 + min(x1, X2) and of consumer 2 is u"(X1, X2) = min(3X1, 12x2]. Which one of the following is FALSE? O A. x1 = (0,0), x2 =(20,10) is a Pareto optimal allocation O B. x1 = (20,10), x2 = (0,0) is a Pareto optimal allocation " x1 =(10,10), x2 = (10,0) is a Pareto optimal allocation O D. The number of Pareto optimal allocations are finite QUESTION 4 2 points Save Answer Which one of the following is TRUE? O A. If a consumer has monotonic preferences, then the demand of the consumer must be contained in the budget line. O B. If a consumer has strongly monotonic preferences, then the demand of the consumer can contain at most one point. O " If a consumer has incomplete preferences, then the consumer's demand is empty for all non-negative prices and non-negative incomes. O D. A consumer with complete, transitive, continuous preferences has non-empty demand for all non-negative prices and non-negative income