Exposure to air pollution is a risk factor for a variety of health outcomes. In particular, several studies have noted that exposure to elevated levels of air pollutants can increase a persons risk of respiratory infections, including influenza. Another recent study has suggested that exposure to elevated levels of air pollutants is also associated with an increased risk of Parkinsons Disease. Cocoros et al. did not collect information on air pollution for their investigation of the relationship between influenza and Parkinsons Disease. If they had collected this information, the investigators would have been able to account for confounding by air pollution. Based on the information provided, in what direction would you expect the observed odds ratio for the association between influenza infection >10 years ago (during any calendar time) and Parkinsons Disease to change if you were able to adjust for confounding for air pollution? Explain your answer.
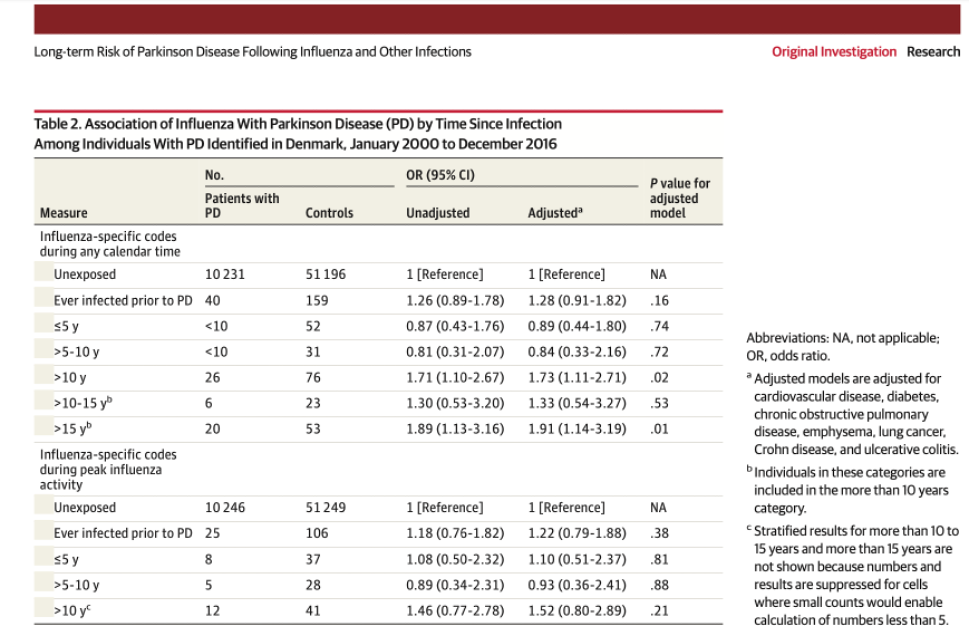
Long-term Risk of Parkinson Disease Following Influenza and Other Infections Original Investigation Research Table 2. Association of Influenza With Parkinson Disease (PD) by Time Since Infection Among Individuals with PD Identified in Denmark, January 2000 to December 2016 OR (95% CI) P value for adjusted model Controls Unadjusted Adjusted 51 196 NA 159 .16 52 .74 31 1 [Reference] 1.26 (0.89-1.78) 0.87 (0.43-1.76) 0.81 (0.31-2.07) 1.71 (1.10-2.67) 1.30 (0.53-3.20) 1.89 (1.13-3.16) 1 [Reference) 1.28 (0.91-1.82) 0.89 (0.44-1.80) 0.84 (0.33-2.16) 1.73 (1.11-2.71) 1.33 (0.54-3.27) 1.91 (1.14-3.19) .72 No. Patients with Measure PD Influenza-specific codes during any calendar time Unexposed 10 231 Ever infected prior to PD 40 s5 y 5-10 y 10 y 26 >10-15 y 6 > 15 y 20 Influenza-specific codes during peak influenza activity Unexposed 10 246 Ever infected prior to PD 25 55 y 8 >5-10 y 5 >10 y 12 76 .02 23 .53 53 .01 Abbreviations: NA, not applicable; OR, odds ratio. * Adjusted models are adjusted for cardiovascular disease, diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, emphysema, lung cancer, Crohn disease, and ulcerative colitis. Individuals in these categories are included in the more than 10 years category. Stratified results for more than 10 to 15 years and more than 15 years are not shown because numbers and results are suppressed for cells where small counts would enable calculation of numbers less than 5. 51 249 NA 106 38 37 1 [Reference) 1.18 (0.76-1.82) 1.08 (0.50-2.32) 0.89 (0.34-2.31) 1.46 (0.77-2.78) 1 [Reference) 1.22 (0.79-1.88) 1.10 (0.51-2.37) 0.93 (0.36-2.41) 1.52 (0.80-2.89) .81 28 .88 41 .21 Long-term Risk of Parkinson Disease Following Influenza and Other Infections Original Investigation Research Table 2. Association of Influenza With Parkinson Disease (PD) by Time Since Infection Among Individuals with PD Identified in Denmark, January 2000 to December 2016 OR (95% CI) P value for adjusted model Controls Unadjusted Adjusted 51 196 NA 159 .16 52 .74 31 1 [Reference] 1.26 (0.89-1.78) 0.87 (0.43-1.76) 0.81 (0.31-2.07) 1.71 (1.10-2.67) 1.30 (0.53-3.20) 1.89 (1.13-3.16) 1 [Reference) 1.28 (0.91-1.82) 0.89 (0.44-1.80) 0.84 (0.33-2.16) 1.73 (1.11-2.71) 1.33 (0.54-3.27) 1.91 (1.14-3.19) .72 No. Patients with Measure PD Influenza-specific codes during any calendar time Unexposed 10 231 Ever infected prior to PD 40 s5 y 5-10 y 10 y 26 >10-15 y 6 > 15 y 20 Influenza-specific codes during peak influenza activity Unexposed 10 246 Ever infected prior to PD 25 55 y 8 >5-10 y 5 >10 y 12 76 .02 23 .53 53 .01 Abbreviations: NA, not applicable; OR, odds ratio. * Adjusted models are adjusted for cardiovascular disease, diabetes, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, emphysema, lung cancer, Crohn disease, and ulcerative colitis. Individuals in these categories are included in the more than 10 years category. Stratified results for more than 10 to 15 years and more than 15 years are not shown because numbers and results are suppressed for cells where small counts would enable calculation of numbers less than 5. 51 249 NA 106 38 37 1 [Reference) 1.18 (0.76-1.82) 1.08 (0.50-2.32) 0.89 (0.34-2.31) 1.46 (0.77-2.78) 1 [Reference) 1.22 (0.79-1.88) 1.10 (0.51-2.37) 0.93 (0.36-2.41) 1.52 (0.80-2.89) .81 28 .88 41 .21







