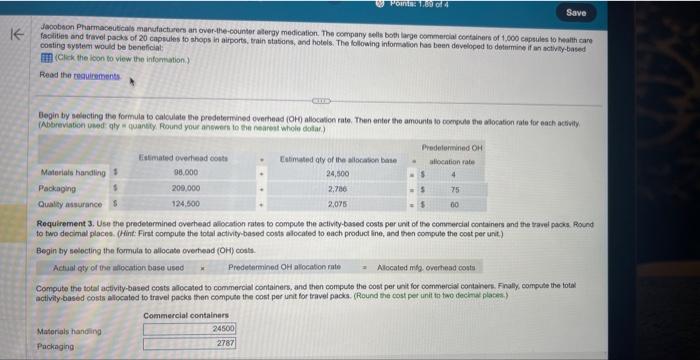
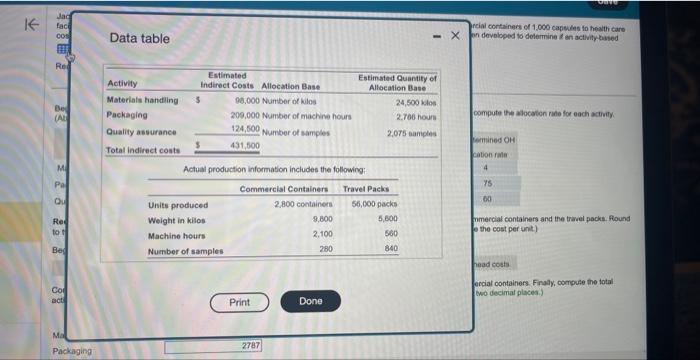
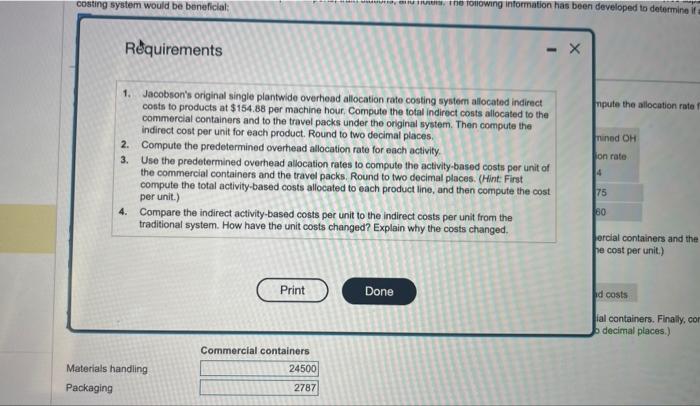
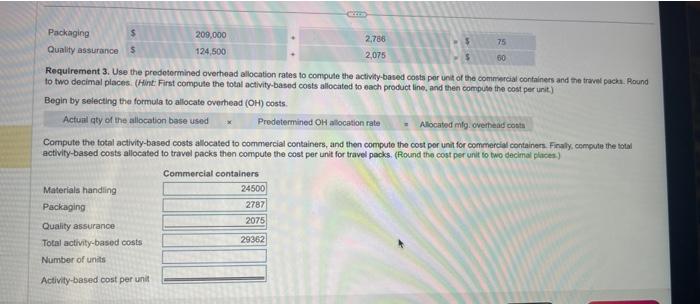
factities and trevol packs of 20 capsules to ahops it airports, train statons, and hotels. The folowing information has been develioped to detnrmine if an metivity-based costing wystem would be beneficiat: IA (Clitk the ison to view the infortation.) (Abbreviaberi ucod qly = quanky. Found your anewert to the fearest whole dotar.) Requirement 3. Use the predetermined ovechead aliocation rates to compute the activity-based costs per unt of the commercial containers and the travei pacas Round to two decimal pilaces. (Hint: Firat corrpute the total activity based costs alocated to each product line, and then coepule the cost per unit) Begin ty selecting the formula to allocate overtead (OH1) costa. Compute the total activity-based costs aliccated to commercial containers, and then compute the cost per unit for coenmeicis containert. Finally, compule the totai activity based costs allocaled to travel packs then compute the cost per unit for travel packs. (Round the cost pet unit tn tao decitux plates.) Data table reial containers of 1,000 capedhe io hesith care Actual production information includes the following: inmercial containers and the tracel packs. flound ethe cost per unit) arcial containers. Finaly, compute the total two decimal placea.) Rquirements 1. Jacobson's original single plantwide overheed allocation rate costing system allocated indirect conts to products at $154.88 per machine hour. Compute the total indirect costs allocated to the commercial containers and to the travel packs under the original system. Then compute the indirect cost per unit for each product. Round to two decimal places. 2. Compute the predetermined overhead allocation rate for each activity. 3. Use the predetermined overhead allocation rates to compute the activity-based costs per unit of the commercial containers and the travel packs. Round to two decimal places. (Hint: First compute the total activity-based costs allocated to each product line, and then compute the cost per unit.) 4. Compare the indirect activity-based costs per unit to the indirect costs per unit from the traditional system. How have the unit costs changed? Explain why the costs changed. ercial containers and the ve cost per unit.) fal containers. Finally, cor o decimal places.) Requirement 3. Use the predetormined overhead allocation rates to compute the activity-based costa per unit of the cominsercial containers and the trainl pach. Round to two decimal places. (Hint: First compute the total activity-based costs allocitod to each product line, and then compute the cost per unit) Begin by selecting the formula to allocate overhead (OH) costs. Actunt qty of the allocation base used : x. Predetermined OH allocation rate Compute the total activity-based costs allocated to commercial containers, and then compute the cost por unit for commercial containers. Firaly, compute the stal activity-based costs allocated to travel packs then compute the cost per unit for travel pocks. (flound the cost per unit to two decimal places.)