Question
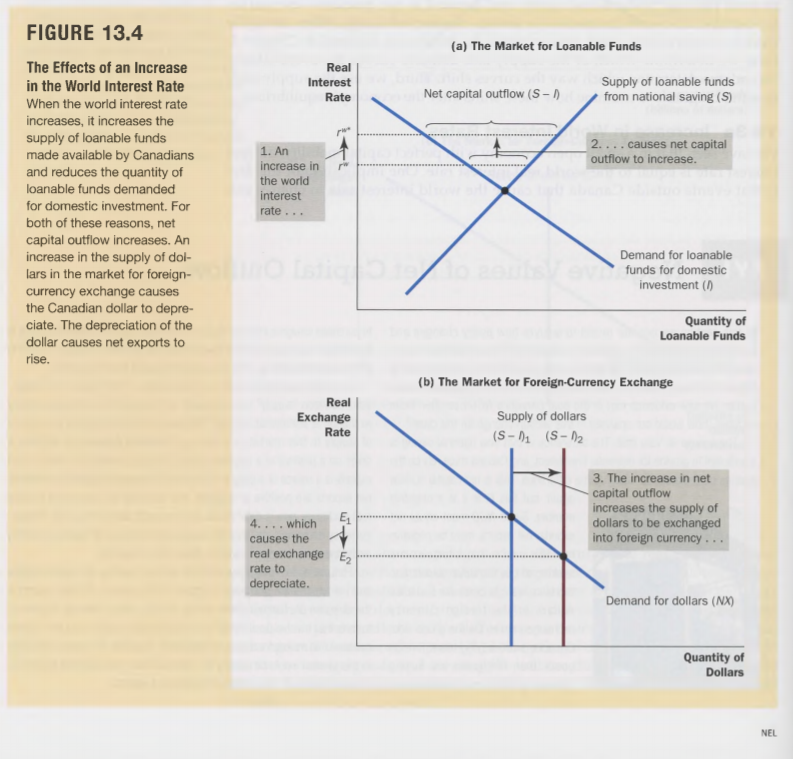
Figure 13.4 shows the effect of an increase in the world interest rate on a small open economy with perfect capital mobility. We assumed there
Figure 13.4 shows the effect of an increase in the world interest rate on a small open economy with perfect capital mobility. We assumed there that the Net Capital Outflow (NCO) was positive. For most of the past 40 years, however, Canada's NCO has been negative.
a.Redraw the two panels of figure 13.4, but this time assume that NCO is negative at the world interest rate. Now suppose that the world interest rate increases. What happens to national saving (S)? What happens to domestic Investment (I)? What happens to NCO and the real exchange rate? Carefully label both diagrams and explain step by step what happens starting from the initial equilibrium in both markets. Make sure to include all the relevant details step by step or you will lose marks.
b.Does the conclusion we reached in figure 13.4 (that an increase in world interest rates causes the Canadian dollar to depreciate and net exports to increase) still hold? Explain why or why not.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


