Question
/*---------------------------------------------------- File: bisectionSearchSoln.c Description: Applies bisection root finding method. ------------------------------------------------------*/ #include #include #include gng1106plplot.h #define N 100 // number of points #define TRUE 1 #define

/*----------------------------------------------------
File: bisectionSearchSoln.c
Description: Applies bisection root finding method.
------------------------------------------------------*/
#include
#include
#include "gng1106plplot.h"
#define N 100 // number of points
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define EPSILON 1e-10
// Function Prototypes
void findInterval(double *, double *);
int findRoot(double, double, double *);
void plotFunc(double, double, int, double []);
double func(double);
void plot(int, double[], double[], int, double[], double[]);
double getMin(double *, int );
double getMax(double *, int );
/*--------------------------------------------------------
Function: main()
---------------------------------------------------------*/
int main()
{
double start, end;
double root;
int n; // number of roots found
// Get intervals from user
findInterval(&start, &end);
printf("Finding root for interval between %.4f and %.4f ",
start, end);
if(findRoot(start, end, &root))
{
printf("Found root at: %.8f (f(x) = %.8f) ",root, func(root));
n = 1;
}
else
{
printf("Did not find root in interval.");
n = 0;
}
plotFunc(start, end, n, &root);
return 0;
}
/*----------------------------------------------------------
Function: findRoot
Parameters
lower, upper: lower and upper values of x for the interval
n - number of coefficients
coeffs - reference to array of coefficients
root - pointer to array for saving roots
Returns: TRUE if a root was found (store in root), and FALSE
if no root exists in interval.
Description: Find the root between the interval for the
function using the bisection
method.
---------------------------------------------------------------*/
int findRoot(double lower, double upper, double *root)
{
// Complete this function
}
/*----------------------------------------------------------
Function: func
Parameters:
x - x value function f(x)
Returns: value y of function f(x)
Description: Plots the value of the function:
f(x) = 50 - x^2 |cos(sqrt(x)| , x must be positive, if x
negative return 0.
-----------------------------------------------------------*/
double func(double x)
{
}
/*----------------------------------------------------------
Function: findInterval
Parameters:
begin, end: pointers to double variables for storing selected
begin and end values of x for the desired interval
Description: Repeatedly plot the graph of the function for the
intervals given by the user until the user
has made a selection of the interval for root
finding.
---------------------------------------------------------------*/
void findInterval(double *begin, double *end)
{
//Variables declarations
char answer; // sentinal
do
{
printf("Please give start and end values for plotting: ");
fflush(stdin);
scanf("%lf %lf",begin,end);
plotFunc(*begin, *end, 0, NULL);
printf("Are you happy with this interval: ");
fflush(stdin);
scanf("%c",&answer);
}
while(answer != 'y');
}
/*----------------------------------------------------------
Function: plotFunc
Parameters:
begin, end: beginning and end of interval (x values) to plot
flag - set to TRUE when root was found and needs to be plotted
root - value of root when flag is TRUE.
Description: Plot the function on the
interval between begin and end. Plots an x at the roots
if nRoots > 0.
---------------------------------------------------------------*/
void plotFunc(double begin, double end, int nRoots, double roots[])
{
double x[N];
double y[N];
double inc; // increment for incrementing x
double yRoots[nRoots];
int ix;
// Calculate function points
inc = (end - begin)/N;
x[0] = begin;
y[0] = func(x[0]); // Compute first point
for(ix = 1; ix
{
x[ix] = x[ix -1] + inc;
y[ix] = func(x[ix]);
}
// Calculate y points at the root
for(ix = 0; ix
{
yRoots[ix] = func(roots[ix]);
}
// Plot
plot(N, x, y, nRoots, roots, yRoots);
}
/*-------------------------------------------------
Function: plot()
Parameters:
n: number of points in the arrays
xPtr: pointer to x values (horizontal axis).
yPtr: pointer to y values (vertical axis).
Return value: none.
Description: Initialises the plot. The following values
in the referenced structure are used to setup
the plot:
x[0], x[n-1] - assume that x values are sequential
miny, maxy - vertical axis range (add 10% to min/max value)
Sets up white background and black forground
colors.
Then plots the curve accessed using xPtr and yPtr.
-------------------------------------------------*/
void plot(int n, double *xPtr, double *yPtr, int nRoots, double *xRoots, double *yRoots)
{
double miny, maxy;
double range; // range of vertical axix
// Setup plot configuration
plsdev("wingcc"); // Sets device to wingcc - CodeBlocks compiler
// Initialise the plot
plinit();
// Configure the axis and labels
plwidth(3); // select the width of the pen
// Find range for axis
miny = getMin(yPtr, n);
maxy = getMax(yPtr, n);
range = maxy - miny; // the width of the range
maxy = maxy + 0.1*range;
miny = miny - 0.1*range;
plenv0(xPtr[0], xPtr[n-1], miny, maxy,
0, 1);
plcol0(GREEN); // Select color for labels
pllab("x", "f(x)", "Function");
// Plot the velocity.
plcol0(BLUE); // Color for plotting curve
plline(n, xPtr, yPtr);
// Plot the points
if(nRoots > 0)
{
plcol0(RED);
plpoin(nRoots,xRoots, yRoots, 'x');
}
plend();
}
/*----------------------------------------------------------
Function: getMin
Parameters:
array - reference to an array with double values
n - number of elements in the array
Returns
min: the minimum value found in the array
Description: Traverses the array to find its minimum value.
----------------------------------------------------------------*/
double getMin(double *array, int n)
{
int ix;
double min = array[0];
for(ix = 1; ix
if(min > array[ix]) min = array[ix];
return(min);
}
/*----------------------------------------------------------
Function: getMax
Parameters:
array - reference to an array with double values
n - number of elements in the array
Returns
max: the maximum value found in the array
Description: Traverses the array to find its maximum value.
----------------------------------------------------------------*/
double getMax(double *array, int n)
{
int ix;
double max = array[0];
for(ix = 1; ix
if(max
return(max);
}
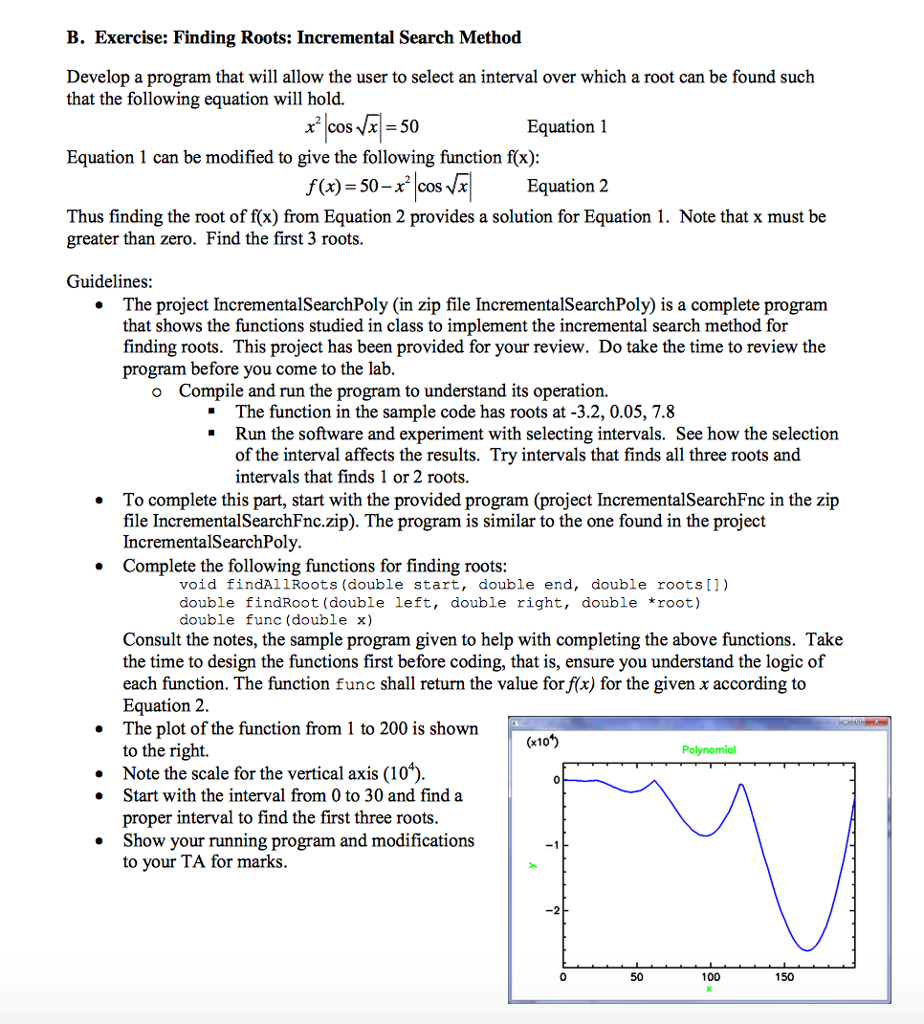
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


