Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Filename: main.cpp // Purpose: To practice using overloaded functions and operators #include Date.h #include using namespace std; int main() { Date date1; int month, day,




Filename: main.cpp
// Purpose: To practice using overloaded functions and operators
#include "Date.h"
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
Date date1;
int month, day, year;
cout
cout
cin >> month >> day >> year;
date1.setMonth(month);
date1.setDay(day);
date1.setYear(year);
cout
cin >> month >> day >> year;
//Calling constructor with three arguments
Date date2(month, day, year);
/*----------------------------------------------------------*/
/*-PART 1 Change this code to the comments indicated beside-*/
/*----------------------------------------------------------*/
date1.printDate(); //cout
date2.printDate(); //
if (date1.sameMonth(date2)) //if (date1 == date2)
cout
else
cout
//++date1;
//++date2;
//cout
//cout
/*----------------------------------------------------------*/
/*-PART 2 Uncomment these lines */
/*----------------------------------------------------------*/
/*
Date date3, date4;
date3 = date1 + 82;
date4 = 6 + date2;
cout
cout using namespace std; int main() { Date date1; int month, day, year; cout > month >> day >> year; date 1.setMonth(month); date1.setDay(day); date 1.setYear(year); cout > month >> day >> year; //Calling constructor with three arguments Date date2(month, day, year); 1 /*-PART 1 Change this code to the comments indicated beside-*1 I */ date1.printDate(); //cout
*/
return 0;
}
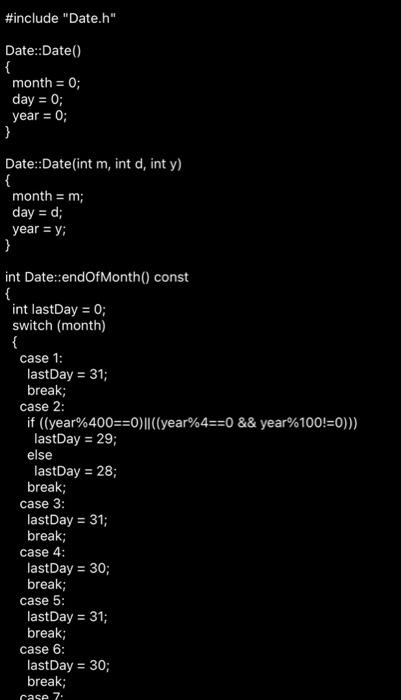
filename: Date.cpp
#include "Date.h"
Date::Date()
{
month = 0;
day = 0;
year = 0;
}
Date::Date(int m, int d, int y)
{
month = m;
day = d;
year = y;
}
int Date::endOfMonth() const
{
int lastDay = 0;
switch (month)
{
case 1:
lastDay = 31;
break;
case 2:
if ((year%400==0)||((year%4==0 && year%100!=0)))
lastDay = 29;
else
lastDay = 28;
break;
case 3:
lastDay = 31;
break;
case 4:
lastDay = 30;
break;
case 5:
lastDay = 31;
break;
case 6:
lastDay = 30;
break;
case 7:
lastDay = 31;
break;
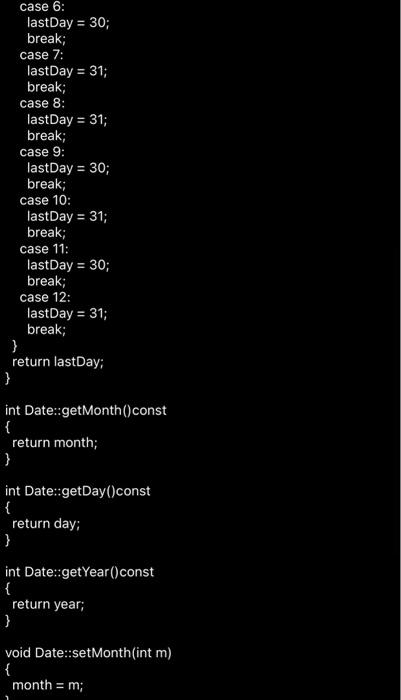
case 8:
lastDay = 31;
break;
case 9:
lastDay = 30;
break;
case 10:
lastDay = 31;
break;
case 11:
lastDay = 30;
break;
case 12:
lastDay = 31;
break;
}
return lastDay;
}
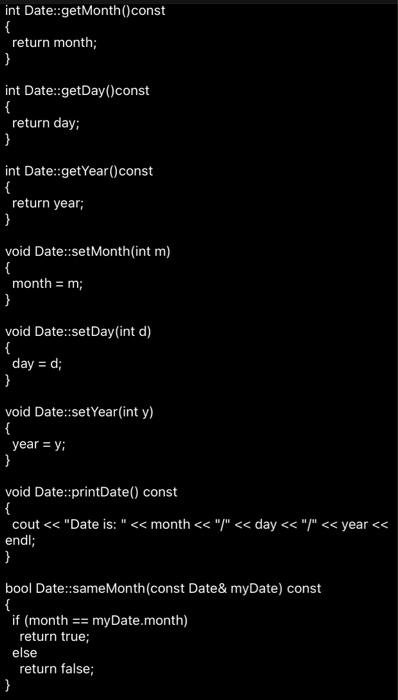
int Date::getMonth()const
{
return month;
}
int Date::getDay()const
{
return day;
}
int Date::getYear()const
{
return year;
}
void Date::setMonth(int m)
{
month = m;
}
void Date::setDay(int d)
{
day = d;
}
void Date::setYear(int y)
{
year = y;
}
void Date::printDate() const
{
cout
4. Lab Exercise -- Overloading Part 1 1. Change the sameMonth function into a overloaded == operator. This will be a member function as demonstrated in the notes. Remember that you will want to compare the month, day, and year. 2. Add an overloaded ++ operator (as a member function, shown in the notes) 3. Just for fun, change the printDate function into an overloaded using namespace std; class Date { private: int month; int day; int year; public: Date(); Date(int m, int d, int y); int endOfMonth() const; int getMonth() const; int getDay() const; int getYear() const; void setMonth(int m); void setDay (int d); void setYear(int y); void printDate() const; bool sameMonth(const Date& myDate) const; }; // Filename: main.cpp // Purpose: To practice using overloaded functions and operators #include "Date.h" #include }
bool Date::sameMonth(const Date& myDate) const
{
if (month == myDate.month)
return true;
else
return false;
}
filename: date.h
#include
using namespace std;
class Date
{
private:
int month;
int day;
int year;
public:
Date();
Date(int m, int d, int y);
int endOfMonth() const;
int getMonth() const;
int getDay() const;
int getYear() const;
void setMonth(int m);
void setDay(int d);
void setYear(int y);
void printDate() const;
bool sameMonth(const Date& myDate) const;
};
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


