Question
Fill in blanks. See drop down menu (in photo) for options Text from photo: Smart Ltd is a business selling small electronic gadgets to the
Fill in blanks.
See drop down menu (in photo) for options
Text from photo:
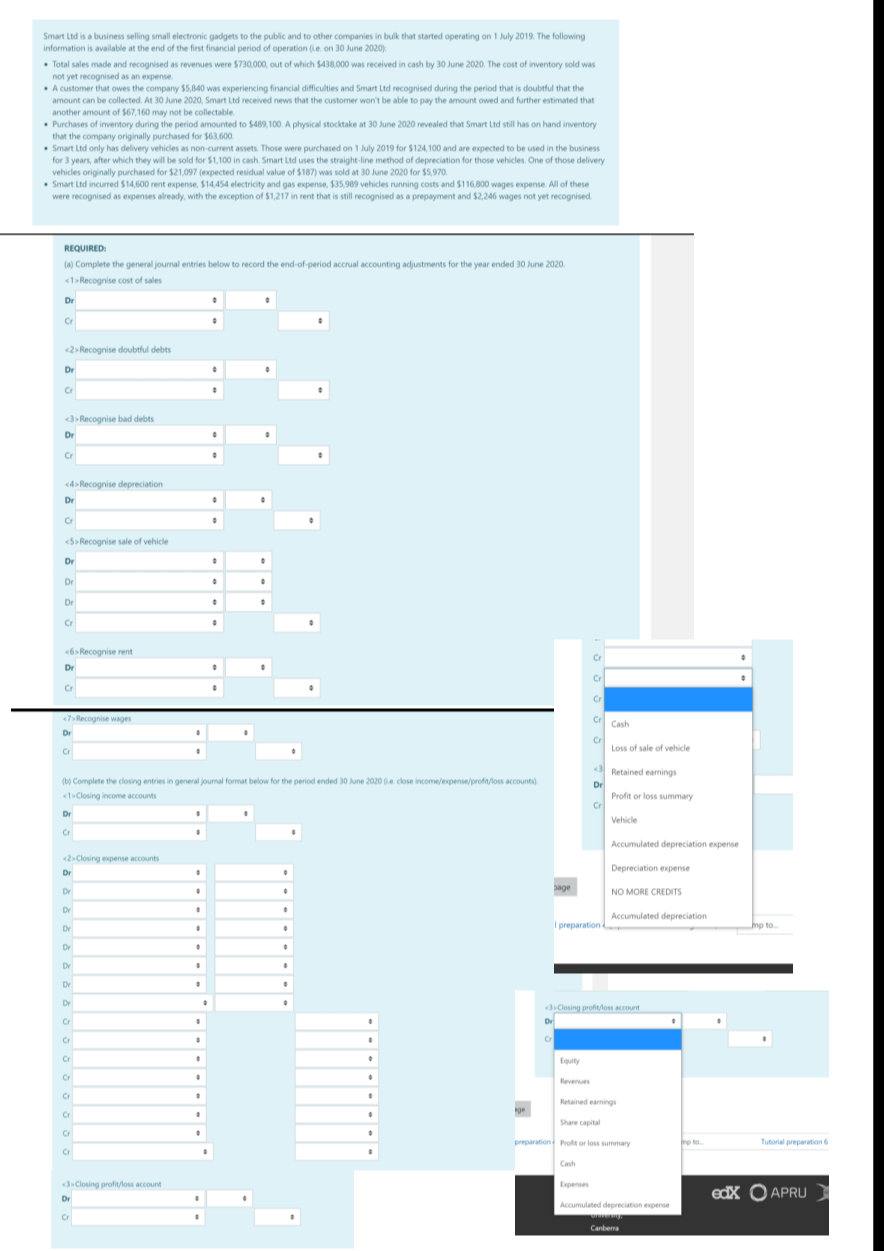
Smart Ltd is a business selling small electronic gadgets to the public and to other companies in bulk that started operating on 1 July 2019. The following information is available at the end of the first financial period of operation (i.e. on 30 June 2020):
- Total sales made and recognised as revenues were $730,000, out of which $438,000 was received in cash by 30 June 2020. The cost of inventory sold was not yet recognised as an expense.
- A customer that owes the company $5,840 was experiencing financial difficulties and Smart Ltd recognised during the period that is doubtful that the amount can be collected. At 30 June 2020, Smart Ltd received news that the customer wont be able to pay the amount owed and further estimated that another amount of $67,160 may not be collectable.
- Purchases of inventory during the period amounted to $489,100. A physical stocktake at 30 June 2020 revealed that Smart Ltd still has on hand inventory that the company originally purchased for $63,600.
- Smart Ltd only has delivery vehicles as non-current assets. Those were purchased on 1 July 2019 for $124,100 and are expected to be used in the business for 3 years, after which they will be sold for $1,100 in cash. Smart Ltd uses the straight-line method of depreciation for those vehicles. One of those delivery vehicles originally purchased for $21,097 (expected residual value of $187) was sold at 30 June 2020 for $5,970.
- Smart Ltd incurred $14,600 rent expense, $14,454 electricity and gas expense, $35,989 vehicles running costs and $116,800 wages expense. All of these were recognised as expenses already, with the exception of $1,217 in rent that is still recognised as a prepayment and $2,246 wages not yet recognised.
REQUIRED:
(a) Complete the general journal entries below to record the end-of-period accrual accounting adjustments for the year ended 30 June 2020.
From photo you can see the boxes. Each one you have to choose name of account and then the amount debited and credited (see photo to see the number of boxes)
part b:
Complete the closing entries in general journal format below for the period ended 30 June 2020 (i.e. close income/expense/profit/loss accounts).
Closing income accounts
Closing expense accounts
Closing profit/loss account
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


