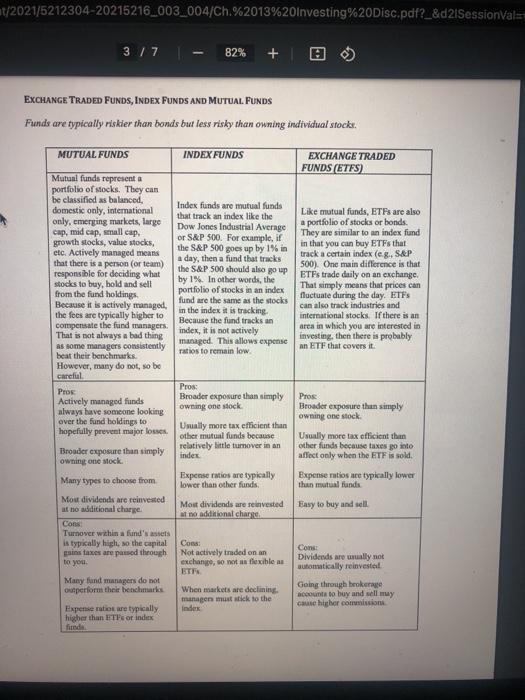
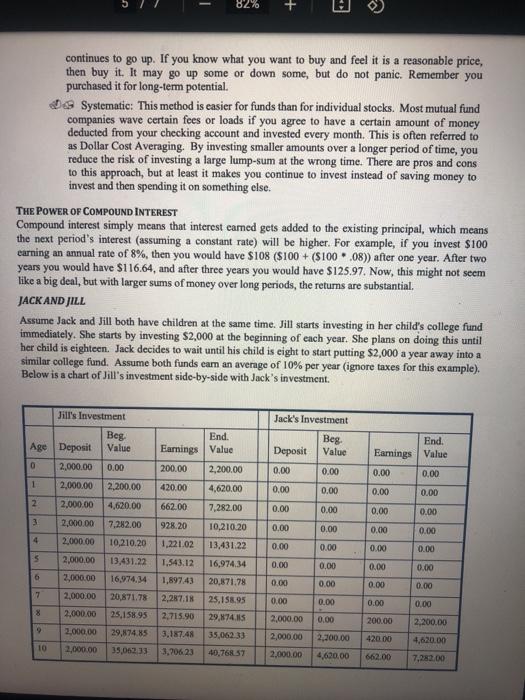
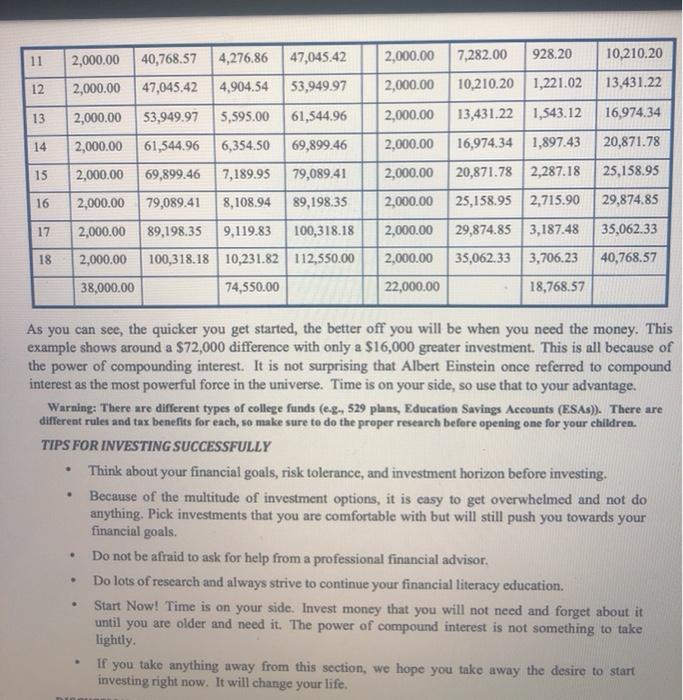
Financial Literacy Ch. 11: Investing Discussion MEET JACK AND JILL Throughout our module, we use an example of two people who illustrate good and poor financial choices. Their background information is as follows: Jack and Jill are best friends with a lot in common. They both graduated from college a couple of years ago with a degree in engineering. They both accepted a job with Water Pail Inc., making identical salaries. Jill is financially savvy; she is an avid reader of personal finance books and has specific financial goals she plans to accomplish. Jack has never been interested in personal finance; he does not puy much attention to his finances and has had some financial problems in the past. Jack and Jill have experiences which involve all of our financial literacy topics. Their successes and mistakes help provide a better understanding of the module topics. INVESTING WHAT INVESTMENT OPTIONS EXIST? Several different investment options are discussed below. This discussion is by no means all-inclusive; however, it provides a solid foundation for you to begin to understand the investment environment. Warming: This overview is intended to prowide basic knowledge of some investment options. Purther research should be done before deciding which investment is best for you. TREASURY BILLS, MONEY MARKET ACCOUNTS, AND CDS These investment options are generally thought of as the least risky investments. They earn low rates of return, but you probably will not lose your money. These investment options are preferred for money that you will need in the short-term (less than five years). TREASURY BILLS MONEY MARKET ACCOUNTS CERTIFTCATES OF DEPOSIT U-BILLS) (MMAS (CDS) Account that is similar to checking Account that is similar to savings account accounts. You can open one at most You can open one at most U.S. government backed bills banks. They typically pay a higher banks, however, with CDs, the deposit ully sold in $100 increments, interest rate than an interest earning has a fixed time period (six months, checking account but sometimes one year, five years, etc.). The longer require a higher minimum balance. you are willing to leave it deposited the higher interest rate it will carn Pros Pros Sale investment Safe investment Pros: Safe Investment backed by the U.S.gov. Little to no risk Little to no risk Little to no risk Easy to open and maintain Easy to open and maintain Inred by the FDIC Insured by the FDIC Com COM Con Rate of return is low and may not Rate of return is low and may not Rate of return is low and mwy nor outpace inflation outpace inflation outpace Inflation May not provide check-writing ability Can be pealized for early withdrawal ontent/2021/5212304-20215216_003_004/Ch.%2013%20Investing%20Disc.pdf?_&d2/SessionVal= 2 / 7 82% + | Financial Literacy Ch. 11. Investing Discussion BONDS Bonds are generally less risky than stocks and mutual funds, but they can lose their value if they fall out of favor with investors. Bonds wally pay periodic interest so they can represent a good source of cash flow. CORPORATE BONDS MUNICIPAL BONDS Bonds and by corporate entities Corporation issue bonds to raise money for a variety of items (c.g. expansion of facilities). Corporate bonds typically pay a higher interest rate the municipalities because there is a greater chance that the corporation will go bankrupt and not be able to fulfill its obligation Corporate bonds vary widely in terms of risk, from stable bonds in regulmed industries (eg, utilities) to unstable junk bonds. Bonds issued by local and state governments. Just like corporations, municipalities also issue bonds to borrow money for various projects (eg. a new library). They pay a lower interest rate the corporate bonds, but the interest reventie you com is not taxed on your federal tax retum Pros: Usually lower risk than stocks Provide steady stream of income through interest payment Rate of retumissily higher than short-term investments mentioned above Pros Lower risk the stocks and usually lower risk thun corporate bonds Provide seady stream of income through interest payments Rate ofretum is wally higher than short-term investments mentioned above. Interested is not able Com Pays lower interest than most corporate bonde Municipalities can also po bankrupe Cook Risk level can change alter you purchase, based on company performance and interest wie fluctuations Income is taxes ordinary income t/2021/5212304-20215216_003_004/Ch.%2013%20Investing%20Disc.pdf?_&d2/Sessionals 377 82% + 0 EXCHANGE TRADED FUNDS, INDEX FUNDS AND MUTUAL FUNDS Funds are typically riskier than bonds but less risky than owning individual stocke. MUTUAL FUNDS INDEX FUNDS EXCHANGE TRADED FUNDS (ETFS) Like mutual funds, ETFs are also a portfolio of stocks or bonds. They are similar to an index fund in that you can buy ETFs that track a certain index (eg., S&P 500). One main difference is that ETFs trade daily on an exchange. That simply means that prices can fluctuate during the day. ETFs can also track industries and international stocks. If there is an area in which you are interested in investing, then there is probably an ETF that covers it Mutual funds representa portfolio of stocks. They can be classified as balanced, Index funds are mutual funds domestic only, international only, emerging markets, large that track an index like the Dow Jones Industrial Average cap, mid cap, small cap, growth stocks, value stocks, or S&P 500. For example, if etc. Actively managed means the S&P 500 goes up by 1% in that there is a person (or team) a day, then a fund that tracks responsible for deciding what the S&P 500 should also go up by 1%. In other words, the stocks to buy, bold and sell from the fund holdings portfolio of stocks in an index Because it is actively managed, fund are the same as the stocks the focs are typically higher to in the index it is tracking. Because the fund tracks an compensate the fund managers. That is not always a bad thing index, it is not actively as some managers consistently managed. This allows expense beat their benchmarks. ratios to remain low However, many do not, so be careful Pro Pros Actively managed funds Broader exposure than simply always have someone looking owning one stock over the fund holdings to Usually more tax efficient than hopefully prevent major losses other mutual funds because relatively little turnover in an Broader exposure than simply index owning one stock Many types to choose from Expense ratios are typically lower than other funds Mou dividends are reinvested at no additional charge Most dividends are reinvested at no additional charge Cons Turnover within a funds assets is typically high, so the capital Cons: psins taxes are passed through Not actively traded on an to you exchange, so not a flexible as Many fund managers do not outperform their benchmarks When markets are declining, managen must stick to the Expense ratios are typically Index higher than the or index find Pros Broader exposure then simply owning one stock Usually more tax officient than other funds because taxes go into affect only when the ETF is sold, Expense ratios are typically lower than mutual funds Easy to buy and sell Cons: Dividends are wally not automatically reinvestet Going through brokerage account to buy and sell my cause higher commission 4 / 7 82% + 0 STOCKS Stocks represent ownership in a company. Stocks are traded on exchanges with the three most common being the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), NASDAQ, and the American Stock Exchange (AMEX). Typically, all that is needed to buy and sell stock is an account with a brokerage company. Several on- line brokers are available today. They all offer varying services and charge varying commissions, Stocks are typically viewed as riskier than funds because the probability of any one stock losing value is higher than an entire portfolio of stocks. However, within the category of stocks, there are still varying levels of risk, from stable blue-chip companies to risky start-ups with little cash flow. Before investing in stocks, fimiliarize yourself with the following: Da Brokerage accounts - full service company (Merrill Lynch, Charles Schwab, etc.) or on line discount company (Soottrade, Etrade, etc.) G Market jargon used when valuing a company - PE ratios, PEG ratios, dividend yields, forward P/E ratios, free cash flow, etc.; Types of stocks you are interested in buying - specific companies (e.g., Apple or Best Buy), types (eg value, growth, or large cap), certain industries (0.8. energy or financials), or regions (e.g.domestic or international): Risk tolerance -- see discussion below. INFORMATION YOU SHOULD KNOW Risk TOLERANCE, ASSET ALLOCATION, AND INVESTMENT HORIZON Investing, in a sense, is like gambling. There exists the risk that you can lose all your investment, but there is also the potential for extremely large gains. There is an investment option for everyone based on their risk tolerance. Your risk tolerance and investment horizon often determines asset allocation Because you are young, your risk tolerance for all long-term investments should be high because you can afford to wait out the ups and downs of the market. A couple of bad months or even a bad year will probably not affect your long-term earning potential. This does not mean choosing crazy investments that you are not sure about, but it does mean you have time on your side. If you are a short-term investor (you plan to use the money in less than five years), then your risk tolerance is low. For example if you are saving for a down payment on a car, a relatively ride-free investment like a MMA might be a good choice. AMMA is easy to access, you can continue adding to it, and its rate of return will hopefully keep up with or outpace inflation. You will not get rich, but your down payment will be secure and your purchasing power should not be diminished D As you get older and move closer to retirement, your risk tolerance should gradually get lower and you should start shifting your risker assets into less risky funds or bonds WHEN IS THE RIGHT TIME TO INVENT? The time tirtis now, but different approaches exist for investing. You can try to pick and choose the time of your investments or you can set up an automatic system that consistently deducts money from your checking account to invest Pick and choose There is no way to perfectly forecast peaks and valleys in the stock market. If you can then you do not need to read any more because you are already rich Waiting for a stock to dip in price may become an expensive part-time if the stock - 82% + continues to go up. If you know what you want to buy and feel it is a reasonable price, then buy it. It may go up some or down some, but do not panic. Remember you purchased it for long-term potential. O Systematic: This method is easier for funds than for individual stocks. Most mutual fund companies wave certain fees or loads if you agree to have a certain amount of money deducted from your checking account and invested every month. This is often referred to as Dollar Cost Averaging. By investing smaller amounts over a longer period of time, you reduce the risk of investing a large lump-sum at the wrong time. There are pros and cons to this approach, but at least it makes you continue to invest instead of saving money to invest and then spending it on something else. THE POWER OF COMPOUND INTEREST Compound interest simply means that interest camed gets added to the existing principal, which means the next period's interest (assuming a constant rate) will be higher. For example, if you invest $100 earning an annual rate of 8%, then you would have $108 ($100 + ($100.08)) after one year. After two years you would have $116.64, and after three years you would have $125.97. Now, this might not seem like a big deal, but with larger sums of money over long periods, the returns are substantial. JACK AND JILL Assume Jack and Jill both have children at the same time. Jill starts investing in her child's college fund immediately. She starts by investing $2,000 at the beginning of each year. She plans on doing this until her child is eighteen. Jack decides to wait until his child is eight to start putting $2,000 a year away into a similar college fund. Assume both funds cum an average of 10% per year (ignore taxes for this example). Below is a chart of Jill's investment side-by-side with Jack's investment. Jill's Investment Age Deposit Beg Value Jack's Investment Beg Deposit Value 0.00 0.00 End. Earnings Value 0.00 0.00 0 2,000.00 0.00 2,200.00 1 0.00 0.00 2,000.00 2,000.00 0.00 0.00 2 4,620.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 3 7.282.00 0.00 End. Earnings Value 200.00 2,200.00 420.00 4,620.00 662.00 7.282.00 928.20 10,210.20 1,221.02 13,431.22 1.543.12 16,974.34 1.897.43 20,871.78 2.287.18 25,158.95 2.715.90 29,874.5 0.00 0.00 0.00 4 0.00 0.00 10,210.20 13,431.22 0.00 0.00 5 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 6 16,974.34 2,000.00 2,000.00 2,000.00 2,000.00 2,000.00 2,000.00 2.000,00 2,000.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 7 20.871.78 0.00 0.00 0.00 8 0.00 2,200.00 200.00 25,158.95 29,874.85 35,062 33 0.00 2,100.00 3.187.48 2.000.00 2,000.00 2,000.00 35,062 33 420.00 10 40.76857 4,690.00 4,620.00 7.282.00 662.00 11 4,276.86 47,045.42 2,000.00 7,282.00 10,210.20 928.20 2,000.00 2,000.00 40,768.57 47,045.42 12 4,904.54 53,949.97 2,000.00 10,210.20 1,221.02 13.431.22 13 2,000.00 53,949.97 5,595.00 61,544.96 13,431.22 1,543.12 16,974.34 2,000.00 2,000.00 14 2,000.00 61,544.96 6,354.50 16,974.34 1,897.43 20,871.78 69,899.46 79,089.41 15 2,000.00 69,899.46 7,189.95 2,000.00 20,871.78 2,287.18 25,158.95 16 2,000.00 79,089.41 8,108.94 89,198.35 25,158.95 2,715.90 29,874.85 17 29,874.85 3,187.48 35,062.33 2,000.00 2,000.00 2,000.00 22,000.00 2,000.00 89,198.35 9,119.83 100,318.18 2,000.00 100,318.18 10,231.82 112,550.00 38,000.00 74,550.00 18 40,768.57 35,062.33 3,706.23 18,768.57 As you can see, the quicker you get started, the better off you will be when you need the money. This example shows around a $72,000 difference with only a $16,000 greater investment. This is all because of the power of compounding interest. It is not surprising that Albert Einstein once referred to compound interest as the most powerful force in the universe. Time is on your side, so use that to your advantage. Warning: There are different types of college funds (e-g- 529 plans, Education Savings Accounts (ESAs)). There are different rules and tax benefits for each, so make sure to do the proper research before opening one for your children. TIPS FOR INVESTING SUCCESSFULLY Think about your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon before investing Because of the multitude of investment options, it is easy to get overwhelmed and not do anything. Pick investments that you are comfortable with but will still push you towards your financial goals. Do not be afraid to ask for help from a professional financial advisor. Do lots of research and always strive to continue your financial literacy education. Start Now! Time is on your side. Invest money that you will not need and forget about it until you are older and need it. The power of compound interest is not something to take lightly If you take anything away from this section, we hope you take away the desire to start investing right now. It will change your life. . . DISCUSSION QUESTIONS 1. Why is understanding your investment time horizon (long vs. short term) so important when deciding where to put your money? 2. Discuss the meaning and importance of the power of compound interest". 3. Discuss the approach that helps you continue to invest smaller amounts over a longer period of time? Is it easier to use this approach for mutual funds rather than stocks, and why? 4. In the case of Jack and Jill, how much have they both invested and what is the ending value of their investments, at Age 10? At Age 18? 5. What do you think it means to be diversified in your investments? How would you go about making your investment portfolio diversified? Financial Literacy Ch. 11: Investing Discussion MEET JACK AND JILL Throughout our module, we use an example of two people who illustrate good and poor financial choices. Their background information is as follows: Jack and Jill are best friends with a lot in common. They both graduated from college a couple of years ago with a degree in engineering. They both accepted a job with Water Pail Inc., making identical salaries. Jill is financially savvy; she is an avid reader of personal finance books and has specific financial goals she plans to accomplish. Jack has never been interested in personal finance; he does not puy much attention to his finances and has had some financial problems in the past. Jack and Jill have experiences which involve all of our financial literacy topics. Their successes and mistakes help provide a better understanding of the module topics. INVESTING WHAT INVESTMENT OPTIONS EXIST? Several different investment options are discussed below. This discussion is by no means all-inclusive; however, it provides a solid foundation for you to begin to understand the investment environment. Warming: This overview is intended to prowide basic knowledge of some investment options. Purther research should be done before deciding which investment is best for you. TREASURY BILLS, MONEY MARKET ACCOUNTS, AND CDS These investment options are generally thought of as the least risky investments. They earn low rates of return, but you probably will not lose your money. These investment options are preferred for money that you will need in the short-term (less than five years). TREASURY BILLS MONEY MARKET ACCOUNTS CERTIFTCATES OF DEPOSIT U-BILLS) (MMAS (CDS) Account that is similar to checking Account that is similar to savings account accounts. You can open one at most You can open one at most U.S. government backed bills banks. They typically pay a higher banks, however, with CDs, the deposit ully sold in $100 increments, interest rate than an interest earning has a fixed time period (six months, checking account but sometimes one year, five years, etc.). The longer require a higher minimum balance. you are willing to leave it deposited the higher interest rate it will carn Pros Pros Sale investment Safe investment Pros: Safe Investment backed by the U.S.gov. Little to no risk Little to no risk Little to no risk Easy to open and maintain Easy to open and maintain Inred by the FDIC Insured by the FDIC Com COM Con Rate of return is low and may not Rate of return is low and may not Rate of return is low and mwy nor outpace inflation outpace inflation outpace Inflation May not provide check-writing ability Can be pealized for early withdrawal ontent/2021/5212304-20215216_003_004/Ch.%2013%20Investing%20Disc.pdf?_&d2/SessionVal= 2 / 7 82% + | Financial Literacy Ch. 11. Investing Discussion BONDS Bonds are generally less risky than stocks and mutual funds, but they can lose their value if they fall out of favor with investors. Bonds wally pay periodic interest so they can represent a good source of cash flow. CORPORATE BONDS MUNICIPAL BONDS Bonds and by corporate entities Corporation issue bonds to raise money for a variety of items (c.g. expansion of facilities). Corporate bonds typically pay a higher interest rate the municipalities because there is a greater chance that the corporation will go bankrupt and not be able to fulfill its obligation Corporate bonds vary widely in terms of risk, from stable bonds in regulmed industries (eg, utilities) to unstable junk bonds. Bonds issued by local and state governments. Just like corporations, municipalities also issue bonds to borrow money for various projects (eg. a new library). They pay a lower interest rate the corporate bonds, but the interest reventie you com is not taxed on your federal tax retum Pros: Usually lower risk than stocks Provide steady stream of income through interest payment Rate of retumissily higher than short-term investments mentioned above Pros Lower risk the stocks and usually lower risk thun corporate bonds Provide seady stream of income through interest payments Rate ofretum is wally higher than short-term investments mentioned above. Interested is not able Com Pays lower interest than most corporate bonde Municipalities can also po bankrupe Cook Risk level can change alter you purchase, based on company performance and interest wie fluctuations Income is taxes ordinary income t/2021/5212304-20215216_003_004/Ch.%2013%20Investing%20Disc.pdf?_&d2/Sessionals 377 82% + 0 EXCHANGE TRADED FUNDS, INDEX FUNDS AND MUTUAL FUNDS Funds are typically riskier than bonds but less risky than owning individual stocke. MUTUAL FUNDS INDEX FUNDS EXCHANGE TRADED FUNDS (ETFS) Like mutual funds, ETFs are also a portfolio of stocks or bonds. They are similar to an index fund in that you can buy ETFs that track a certain index (eg., S&P 500). One main difference is that ETFs trade daily on an exchange. That simply means that prices can fluctuate during the day. ETFs can also track industries and international stocks. If there is an area in which you are interested in investing, then there is probably an ETF that covers it Mutual funds representa portfolio of stocks. They can be classified as balanced, Index funds are mutual funds domestic only, international only, emerging markets, large that track an index like the Dow Jones Industrial Average cap, mid cap, small cap, growth stocks, value stocks, or S&P 500. For example, if etc. Actively managed means the S&P 500 goes up by 1% in that there is a person (or team) a day, then a fund that tracks responsible for deciding what the S&P 500 should also go up by 1%. In other words, the stocks to buy, bold and sell from the fund holdings portfolio of stocks in an index Because it is actively managed, fund are the same as the stocks the focs are typically higher to in the index it is tracking. Because the fund tracks an compensate the fund managers. That is not always a bad thing index, it is not actively as some managers consistently managed. This allows expense beat their benchmarks. ratios to remain low However, many do not, so be careful Pro Pros Actively managed funds Broader exposure than simply always have someone looking owning one stock over the fund holdings to Usually more tax efficient than hopefully prevent major losses other mutual funds because relatively little turnover in an Broader exposure than simply index owning one stock Many types to choose from Expense ratios are typically lower than other funds Mou dividends are reinvested at no additional charge Most dividends are reinvested at no additional charge Cons Turnover within a funds assets is typically high, so the capital Cons: psins taxes are passed through Not actively traded on an to you exchange, so not a flexible as Many fund managers do not outperform their benchmarks When markets are declining, managen must stick to the Expense ratios are typically Index higher than the or index find Pros Broader exposure then simply owning one stock Usually more tax officient than other funds because taxes go into affect only when the ETF is sold, Expense ratios are typically lower than mutual funds Easy to buy and sell Cons: Dividends are wally not automatically reinvestet Going through brokerage account to buy and sell my cause higher commission 4 / 7 82% + 0 STOCKS Stocks represent ownership in a company. Stocks are traded on exchanges with the three most common being the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), NASDAQ, and the American Stock Exchange (AMEX). Typically, all that is needed to buy and sell stock is an account with a brokerage company. Several on- line brokers are available today. They all offer varying services and charge varying commissions, Stocks are typically viewed as riskier than funds because the probability of any one stock losing value is higher than an entire portfolio of stocks. However, within the category of stocks, there are still varying levels of risk, from stable blue-chip companies to risky start-ups with little cash flow. Before investing in stocks, fimiliarize yourself with the following: Da Brokerage accounts - full service company (Merrill Lynch, Charles Schwab, etc.) or on line discount company (Soottrade, Etrade, etc.) G Market jargon used when valuing a company - PE ratios, PEG ratios, dividend yields, forward P/E ratios, free cash flow, etc.; Types of stocks you are interested in buying - specific companies (e.g., Apple or Best Buy), types (eg value, growth, or large cap), certain industries (0.8. energy or financials), or regions (e.g.domestic or international): Risk tolerance -- see discussion below. INFORMATION YOU SHOULD KNOW Risk TOLERANCE, ASSET ALLOCATION, AND INVESTMENT HORIZON Investing, in a sense, is like gambling. There exists the risk that you can lose all your investment, but there is also the potential for extremely large gains. There is an investment option for everyone based on their risk tolerance. Your risk tolerance and investment horizon often determines asset allocation Because you are young, your risk tolerance for all long-term investments should be high because you can afford to wait out the ups and downs of the market. A couple of bad months or even a bad year will probably not affect your long-term earning potential. This does not mean choosing crazy investments that you are not sure about, but it does mean you have time on your side. If you are a short-term investor (you plan to use the money in less than five years), then your risk tolerance is low. For example if you are saving for a down payment on a car, a relatively ride-free investment like a MMA might be a good choice. AMMA is easy to access, you can continue adding to it, and its rate of return will hopefully keep up with or outpace inflation. You will not get rich, but your down payment will be secure and your purchasing power should not be diminished D As you get older and move closer to retirement, your risk tolerance should gradually get lower and you should start shifting your risker assets into less risky funds or bonds WHEN IS THE RIGHT TIME TO INVENT? The time tirtis now, but different approaches exist for investing. You can try to pick and choose the time of your investments or you can set up an automatic system that consistently deducts money from your checking account to invest Pick and choose There is no way to perfectly forecast peaks and valleys in the stock market. If you can then you do not need to read any more because you are already rich Waiting for a stock to dip in price may become an expensive part-time if the stock - 82% + continues to go up. If you know what you want to buy and feel it is a reasonable price, then buy it. It may go up some or down some, but do not panic. Remember you purchased it for long-term potential. O Systematic: This method is easier for funds than for individual stocks. Most mutual fund companies wave certain fees or loads if you agree to have a certain amount of money deducted from your checking account and invested every month. This is often referred to as Dollar Cost Averaging. By investing smaller amounts over a longer period of time, you reduce the risk of investing a large lump-sum at the wrong time. There are pros and cons to this approach, but at least it makes you continue to invest instead of saving money to invest and then spending it on something else. THE POWER OF COMPOUND INTEREST Compound interest simply means that interest camed gets added to the existing principal, which means the next period's interest (assuming a constant rate) will be higher. For example, if you invest $100 earning an annual rate of 8%, then you would have $108 ($100 + ($100.08)) after one year. After two years you would have $116.64, and after three years you would have $125.97. Now, this might not seem like a big deal, but with larger sums of money over long periods, the returns are substantial. JACK AND JILL Assume Jack and Jill both have children at the same time. Jill starts investing in her child's college fund immediately. She starts by investing $2,000 at the beginning of each year. She plans on doing this until her child is eighteen. Jack decides to wait until his child is eight to start putting $2,000 a year away into a similar college fund. Assume both funds cum an average of 10% per year (ignore taxes for this example). Below is a chart of Jill's investment side-by-side with Jack's investment. Jill's Investment Age Deposit Beg Value Jack's Investment Beg Deposit Value 0.00 0.00 End. Earnings Value 0.00 0.00 0 2,000.00 0.00 2,200.00 1 0.00 0.00 2,000.00 2,000.00 0.00 0.00 2 4,620.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 3 7.282.00 0.00 End. Earnings Value 200.00 2,200.00 420.00 4,620.00 662.00 7.282.00 928.20 10,210.20 1,221.02 13,431.22 1.543.12 16,974.34 1.897.43 20,871.78 2.287.18 25,158.95 2.715.90 29,874.5 0.00 0.00 0.00 4 0.00 0.00 10,210.20 13,431.22 0.00 0.00 5 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 6 16,974.34 2,000.00 2,000.00 2,000.00 2,000.00 2,000.00 2,000.00 2.000,00 2,000.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 7 20.871.78 0.00 0.00 0.00 8 0.00 2,200.00 200.00 25,158.95 29,874.85 35,062 33 0.00 2,100.00 3.187.48 2.000.00 2,000.00 2,000.00 35,062 33 420.00 10 40.76857 4,690.00 4,620.00 7.282.00 662.00 11 4,276.86 47,045.42 2,000.00 7,282.00 10,210.20 928.20 2,000.00 2,000.00 40,768.57 47,045.42 12 4,904.54 53,949.97 2,000.00 10,210.20 1,221.02 13.431.22 13 2,000.00 53,949.97 5,595.00 61,544.96 13,431.22 1,543.12 16,974.34 2,000.00 2,000.00 14 2,000.00 61,544.96 6,354.50 16,974.34 1,897.43 20,871.78 69,899.46 79,089.41 15 2,000.00 69,899.46 7,189.95 2,000.00 20,871.78 2,287.18 25,158.95 16 2,000.00 79,089.41 8,108.94 89,198.35 25,158.95 2,715.90 29,874.85 17 29,874.85 3,187.48 35,062.33 2,000.00 2,000.00 2,000.00 22,000.00 2,000.00 89,198.35 9,119.83 100,318.18 2,000.00 100,318.18 10,231.82 112,550.00 38,000.00 74,550.00 18 40,768.57 35,062.33 3,706.23 18,768.57 As you can see, the quicker you get started, the better off you will be when you need the money. This example shows around a $72,000 difference with only a $16,000 greater investment. This is all because of the power of compounding interest. It is not surprising that Albert Einstein once referred to compound interest as the most powerful force in the universe. Time is on your side, so use that to your advantage. Warning: There are different types of college funds (e-g- 529 plans, Education Savings Accounts (ESAs)). There are different rules and tax benefits for each, so make sure to do the proper research before opening one for your children. TIPS FOR INVESTING SUCCESSFULLY Think about your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon before investing Because of the multitude of investment options, it is easy to get overwhelmed and not do anything. Pick investments that you are comfortable with but will still push you towards your financial goals. Do not be afraid to ask for help from a professional financial advisor. Do lots of research and always strive to continue your financial literacy education. Start Now! Time is on your side. Invest money that you will not need and forget about it until you are older and need it. The power of compound interest is not something to take lightly If you take anything away from this section, we hope you take away the desire to start investing right now. It will change your life. . . DISCUSSION QUESTIONS 1. Why is understanding your investment time horizon (long vs. short term) so important when deciding where to put your money? 2. Discuss the meaning and importance of the power of compound interest". 3. Discuss the approach that helps you continue to invest smaller amounts over a longer period of time? Is it easier to use this approach for mutual funds rather than stocks, and why? 4. In the case of Jack and Jill, how much have they both invested and what is the ending value of their investments, at Age 10? At Age 18? 5. What do you think it means to be diversified in your investments? How would you go about making your investment portfolio diversified