Financial Modeling Assignment
The exercise 5 has to be modeled as the example provided in excel.


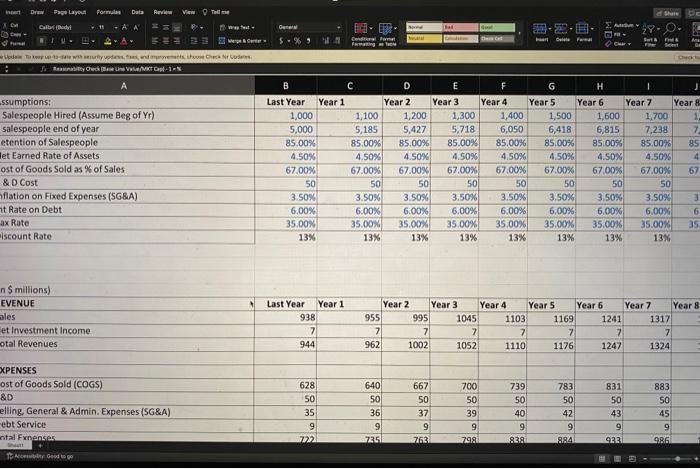
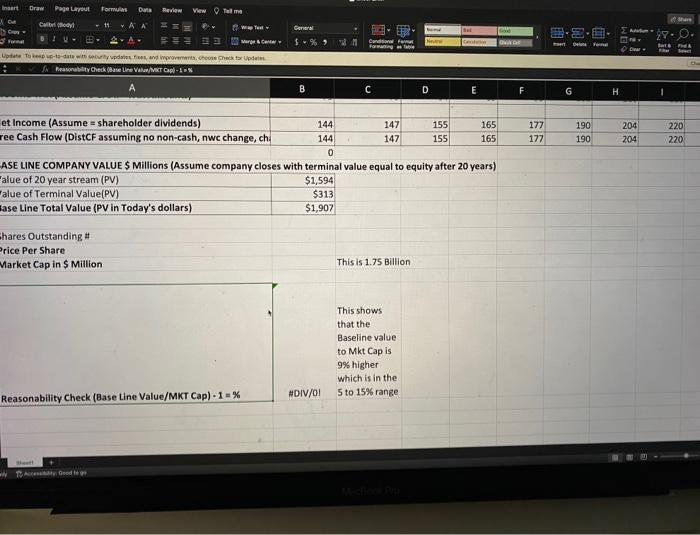
Pear, Inc, a competitor to Apple in the handheld electronic device market, manufactures 5 martPhones and similar devices, and sells them through retall outlets in the United States. It hopes to expand operations into Canada, someday, but has no specific plans as of yet. Pear's main competitive advantage is a service called infinityG, which allows for better reception and faster data transfer rates than its competitors. Pear's advertising also claims that InfinityG is much better at protecting customer data through enhanced encryption on data transfers, and other proprietary techniques. At the end of last year, Pear had 1,000 salespeople, producing an average of $187,500 in annual sales per salesperson, based on a $250 purchase price per unit, which in the past has just kept pace with inflation, Pear tends to lose 15% of its salespeople each year. Last year, Pear hired an additional 200 new salespeople; starting this year, Pear plans to increase the number of additional new salespeople hired by 100 each year (i.e., 300 this year, 400 next year, etc.). Other revenues last year included net investment income of 4.5% net earned rate on assets of $133,971,292. Other assets of $30,000,000 are non-depreciating and non-income generating. Other liabilities are a constant $50,000,000. Last year, expenses were: - Cost of goods sold (CGS): $135,750,000 (variable costs) (costs are variable directly with sales) - Selling General \& Administrative (SG\&A): \$18,347,826 (fixed costs) - Research \& Development (R\&D) 5% of revenues (semi-variable costs) There is a $100,000,000 debt on which Pear pays debt service of 6.00% annually. There are no plans to pay down the debt, and the debt is expected to be renewed indefinitely at the same rate. Going forward, Pear expects inflation of 3.5%. Income taxes are generally 35% of Earnings Before income Tax (EBT). Management uses 12% as a hurdle rate to estimate returns expected by shareholders. There are 88 million shares outstanding. The stock price is $7.50 per share. Assume: - GAP = TAX basis for taxes - Net income = shareholder dividends - There are no non-cash items (distributable cash flow = net income) - Company value = present value of distributable cash flow through 20 vears, plus the discounted value of remaining equity at the end of year 20 . First study the baseline valuation provided in the spreadsheet and then perform the exercise below. a) Perform revised baseline valuation for the case below, starting with the baseline valuation provided and revising it for the new strategy below b) Quantify the execution risk of not achieving the additional growth expected (DO NOT USE THE "SHOCK" AREA / IT WILL BE EASIER TO MAKE CHANGES DIRECTLY TO BASEUINE AREA) After a contentious strategic planning meeting, management revised its strategic plan, and you are asked to construct the revised baseline valuation. You are also asked to quantify the risk of not achieving the growth portion of the revised strategy, in terms of the potential impact on company value. Pear's revised strategic plan Growth Portion Pear's new growth strategy consists of three elements: Increase the additional number of salespeople hired each year from 100 to 125 (i.e, 325 this year, 450 next year, etc.). - Increase the retention of salespeople, over the three-year strategic plan period, by 100 basis points (1.00%) each year, remaining flat thereafter - Increase average production per salesperson as follows: To achieve this, Pear must launch a program that will increase SG\&A expenses this year to $24,000,000. Whether or not the growth is actually achieved, the shift to a more aggressive growth plan has increased the company's riskiness, and management would like to reflect this in the valuation by increasing the discount rate to 13% Non-Growth Portion - Outstanding debt will be refinanced on the first day of this year, at a new debt service rate: 5.5% - R\&D costs increase to 6% of revenues TEAM MEMBERS: a) Baseline company value = b) Revised baseline company value = c) Quantification of execution risk = Copripht o Simfirid. All rehes recened. \begin{tabular}{|l|r|r|r|r|r|r|r|r|} \hline A & B & C & D & E & F & G & H \\ \hline & & & & & & & & \\ \hline \\ \hline et Income (Assume = shareholder dividends) & 144 & 147 & 155 & 165 & 177 & 190 & 204 & 220 \\ \hline ree Cash Flow (DistCF assuming no non-Cash, nwe change, ch: & 144 & 147 & 155 & 165 & 177 & 190 & 204 & 220 \\ \hline \end{tabular} ASE UNE COMPANY VALUE $ Millions (Assume company closes with terminal value equal to equity after 20 years) \begin{tabular}{l|r} 'alue of 20 year stream (PV) & $1,594 \\ \hline talue of Terminal Value(PV) & $313 \\ \hline lase Line Total Value (PV in Today's dollars) & $1,907 \\ \hline \end{tabular} Thares Outstanding \# Price Per Share Market Cap in \$ Million This is 1.75 Billion This shows that the Baseline value to Mkt Cap is 9\% higher which is in the Reasonability Check (Base Line Value/MKT Cap) - 1=% \#DIV/01 5 to 15% range Pear, Inc, a competitor to Apple in the handheld electronic device market, manufactures 5 martPhones and similar devices, and sells them through retall outlets in the United States. It hopes to expand operations into Canada, someday, but has no specific plans as of yet. Pear's main competitive advantage is a service called infinityG, which allows for better reception and faster data transfer rates than its competitors. Pear's advertising also claims that InfinityG is much better at protecting customer data through enhanced encryption on data transfers, and other proprietary techniques. At the end of last year, Pear had 1,000 salespeople, producing an average of $187,500 in annual sales per salesperson, based on a $250 purchase price per unit, which in the past has just kept pace with inflation, Pear tends to lose 15% of its salespeople each year. Last year, Pear hired an additional 200 new salespeople; starting this year, Pear plans to increase the number of additional new salespeople hired by 100 each year (i.e., 300 this year, 400 next year, etc.). Other revenues last year included net investment income of 4.5% net earned rate on assets of $133,971,292. Other assets of $30,000,000 are non-depreciating and non-income generating. Other liabilities are a constant $50,000,000. Last year, expenses were: - Cost of goods sold (CGS): $135,750,000 (variable costs) (costs are variable directly with sales) - Selling General \& Administrative (SG\&A): \$18,347,826 (fixed costs) - Research \& Development (R\&D) 5% of revenues (semi-variable costs) There is a $100,000,000 debt on which Pear pays debt service of 6.00% annually. There are no plans to pay down the debt, and the debt is expected to be renewed indefinitely at the same rate. Going forward, Pear expects inflation of 3.5%. Income taxes are generally 35% of Earnings Before income Tax (EBT). Management uses 12% as a hurdle rate to estimate returns expected by shareholders. There are 88 million shares outstanding. The stock price is $7.50 per share. Assume: - GAP = TAX basis for taxes - Net income = shareholder dividends - There are no non-cash items (distributable cash flow = net income) - Company value = present value of distributable cash flow through 20 vears, plus the discounted value of remaining equity at the end of year 20 . First study the baseline valuation provided in the spreadsheet and then perform the exercise below. a) Perform revised baseline valuation for the case below, starting with the baseline valuation provided and revising it for the new strategy below b) Quantify the execution risk of not achieving the additional growth expected (DO NOT USE THE "SHOCK" AREA / IT WILL BE EASIER TO MAKE CHANGES DIRECTLY TO BASEUINE AREA) After a contentious strategic planning meeting, management revised its strategic plan, and you are asked to construct the revised baseline valuation. You are also asked to quantify the risk of not achieving the growth portion of the revised strategy, in terms of the potential impact on company value. Pear's revised strategic plan Growth Portion Pear's new growth strategy consists of three elements: Increase the additional number of salespeople hired each year from 100 to 125 (i.e, 325 this year, 450 next year, etc.). - Increase the retention of salespeople, over the three-year strategic plan period, by 100 basis points (1.00%) each year, remaining flat thereafter - Increase average production per salesperson as follows: To achieve this, Pear must launch a program that will increase SG\&A expenses this year to $24,000,000. Whether or not the growth is actually achieved, the shift to a more aggressive growth plan has increased the company's riskiness, and management would like to reflect this in the valuation by increasing the discount rate to 13% Non-Growth Portion - Outstanding debt will be refinanced on the first day of this year, at a new debt service rate: 5.5% - R\&D costs increase to 6% of revenues TEAM MEMBERS: a) Baseline company value = b) Revised baseline company value = c) Quantification of execution risk = Copripht o Simfirid. All rehes recened. \begin{tabular}{|l|r|r|r|r|r|r|r|r|} \hline A & B & C & D & E & F & G & H \\ \hline & & & & & & & & \\ \hline \\ \hline et Income (Assume = shareholder dividends) & 144 & 147 & 155 & 165 & 177 & 190 & 204 & 220 \\ \hline ree Cash Flow (DistCF assuming no non-Cash, nwe change, ch: & 144 & 147 & 155 & 165 & 177 & 190 & 204 & 220 \\ \hline \end{tabular} ASE UNE COMPANY VALUE $ Millions (Assume company closes with terminal value equal to equity after 20 years) \begin{tabular}{l|r} 'alue of 20 year stream (PV) & $1,594 \\ \hline talue of Terminal Value(PV) & $313 \\ \hline lase Line Total Value (PV in Today's dollars) & $1,907 \\ \hline \end{tabular} Thares Outstanding \# Price Per Share Market Cap in \$ Million This is 1.75 Billion This shows that the Baseline value to Mkt Cap is 9\% higher which is in the Reasonability Check (Base Line Value/MKT Cap) - 1=% \#DIV/01 5 to 15% range










