Question
find an optimal loop count for your system to force CPU scheduling to kick-in. System call fork() is used to create processes. It takes no

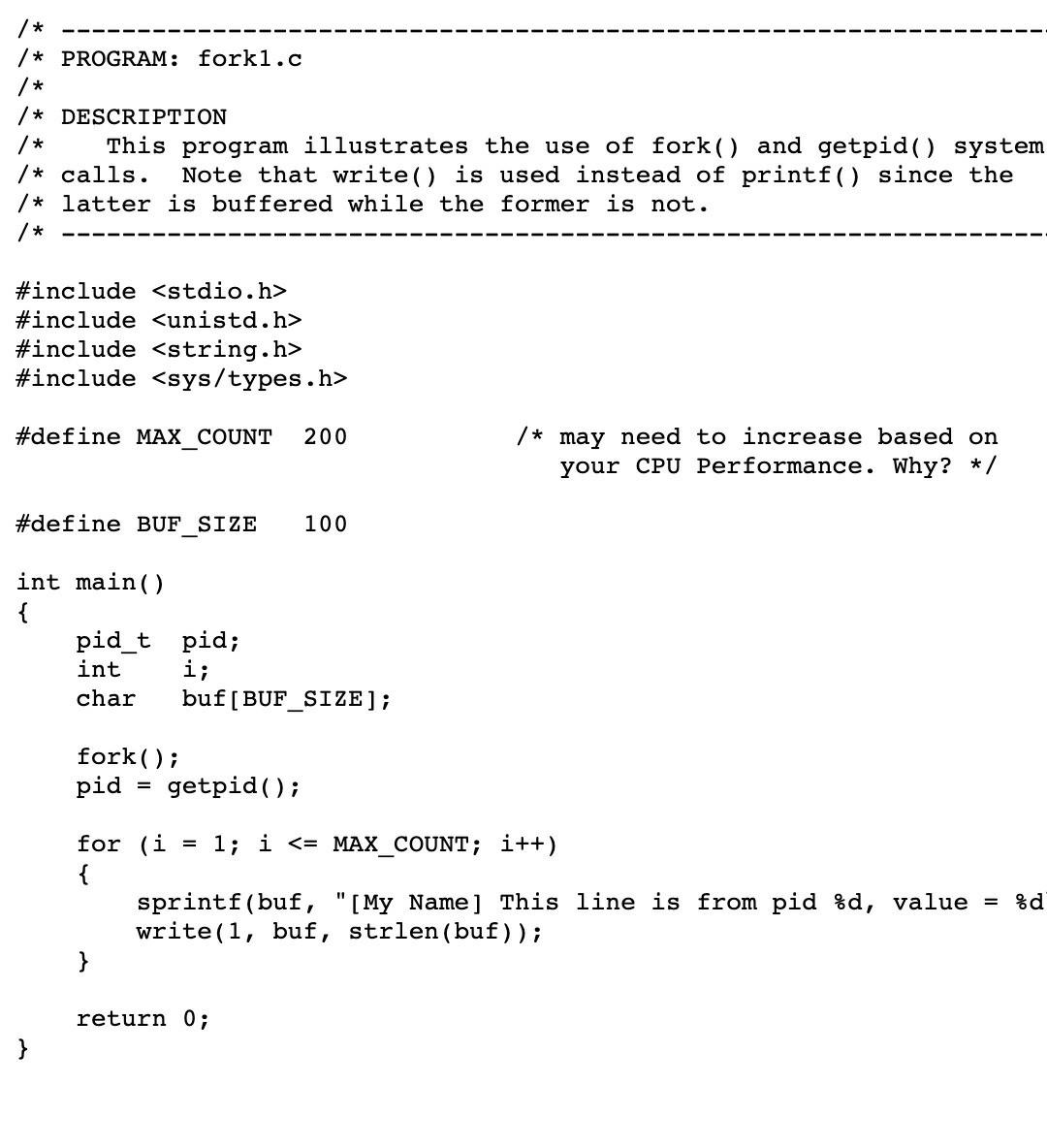
find an optimal loop count for your system to force CPU scheduling to kick-in.
System call fork() is used to create processes. It takes no arguments and returns a process ID. The purpose of fork() is to create a new process, which becomes the child process of the caller. After a new child process is created, both processes will execute the next instruction following the fork() system call.
Experiment with how fork can create a process and how the parent and child will get scheduled to run in modern concurrent and multi-tasking operating system.
Modify each c fork to display your name where it says "My Name".
Then compile them with the following command:
gcc -o fork1 fork1.c
gcc -o fork2 fork2.c
Now run each as follows:
First, by having the output to the console:
./fork1
./fork2
Second, by directing the output to a file:
./fork1 > fork1.out
./fork2 > fork2.out
Examine the outputs of these, and create a Word document and describe your understanding of this assignment as follows:
When fork1.c and fork2.c are run, what happens inside the kernel with respect to how the kernel works with its internal algorithms, and scheduling and switching the tasks to run. The computer speed has something to do with this, so you would need to adjust max count and see how these two source code will behave. Note that, the computer speed is irreverent and it is only a byproduct.
/* /* PROGRAM: fork2.c /* DESCRIPTION /* This program runs two processes, a parent and a child. Both of /* them run the same loop printing some messages. Note that printf() /* is used in this program. */ +/ #includeStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


