Firstly, i need this code to be in java and please do not copy and paste from others!
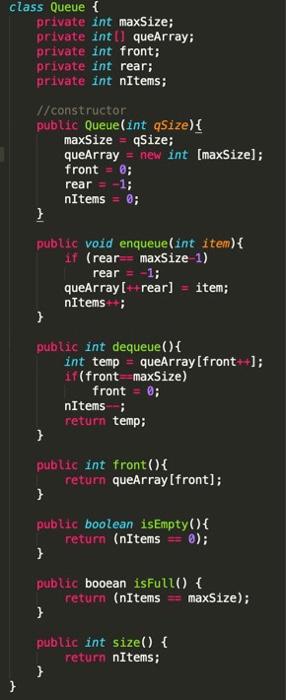
Secondly, you cant use library, so please use the queue implementation that has been given to you shown in the second image
Thirdly, there has to be an input where user can enter how many minutes (eg. 30) and i need the output to be almost similar to the sample output shown in the first image.
Lastly, there are some guidelinesyou need to follow which you can find the third image.
Lastly, do provide me a ss of our output. thanks!
Part B: (70.0 marks) Your task for this assignment is to investigate some of the properties of queues. Queues are commonly used in network systems. For example, e-mail is placed in queues while it is waiting to be sent and after it arrives at the recipient's mailbox. A problem occurs, however, if the outgoing mail processor cannot send one or more of the messages in the queue. For example, a message might not be sent because the recipient's system is not available. Write an e-mail simulator that processes mail at an average of 30 messages per minute. As messages are received, they are placed in a queue. For the simulation, assume that the messages arrive at an average rate of 30 messages per minute. Remember, the messages must arrive randomly, so you will need to use a random number generator to determine when messages are received. Each minute, you can dequeue up to 30 messages and send them. Assume that 25% of the messages in the queue cannot be sent in any processing cycle. Again, you will need to use a random number to determine whether a given message can be sent. If it cannot be sent, put it back at the end of the queue or enqueue it. Run the simulator for 15 minutes, tracking the number of times each message had to be requeued. At the end of the simulation, print the statistics that show: 1 The total messages processed. 2 The average arrival rate, that is, the average number of messages arriving per minute. 3 The average number of messages sent per minute. 4 The average number of messages in the queue in a minute. 5 The number of messages sent on the first attempt, the number of messages sent on the second attempt, and so forth. 6 The average number of times messages had to be requeued (do not include the messages sent the first time in this average.) NOTE: Since the question is to assess your understanding of the concept of Queue, you are NOT allowed to use the library of the language that implement queue. You need to write the codes (Implementation) of Queue for this exercise. (See point (1).) Sample Output: (Note: Since this exercise is a simulation exercise and involves random numbers, the output shown here are for your reference only. You may not necessarily be able to obtain the same output shown here.) Please enter the total minutes to run: 30 Total number of messages processed 818 Average arrival rate : 29.03 Average number of messages sent per minute 19.97 Average number of messages in the queue per minute : 122.77 Number of messages sent on 1st attempt : 491 Number of messages sent on 2nd attempt : 87 Number of messages sent on 3rd attempt : 18 Number of messages sent on 4th attempt Number of messages sent on 5th attempt 32 Average number of times messages had to be requeued : 1.30 :1 class Queue { private int maxSize; private int[queArray; private int front; private int rear; private int nItems; //constructor public Queue (int qSize) { maxSize = qsize; queArray = new int [maxSize]; front = 0; rear -1; nItems = %; } public void enqueue(int item) { if (rear-maxSize 1) rear = -1; queArray ( +rear] = item; nItems; } public int dequeue(){ int temp = queArray (front); if (front maxSize) front = 0; nItems; return temp; } public int front() { return queArray (front); } public boolean isEmpty(){ return (nItems == 0); } public booean isFull() { return (nItems = maxSize); } public int size() { return nItems; } } Email arriving: 1. Need to generate a random number (between 0 and 60, or 10 and 50, or 20 and 40... to determine the number of emails coming in (arriving) in one minute. 2. add the x number of emails to the queue. E.g. if in step 1, the random generator generates 50, then you need to add 50 emails to the queue Process the email: 3. Need to generate a random number between 0 and 30 to determine the number of emails to be sent to the respective email inbox, let's say x = 20. 4. About 25% of these 20 emails cannot be sent out. Hence, need to be requeue to the queue again. Note: 25% of 20 emails equals to about 5 emails. The question now is which 5 emails cannot be sent out? In this exercise, we just have to simulate it by generating a number between 0 and 1 for each of the 20 emails . A normalize random generator should generate number randomly and hence have a normal distribution Hence, what we can do is that after dequeue a particular email from the queue, I generate a random number between 0 and 1. If the number generated is less than 0.25, then I will enqueue back that email, otherwise, I will send out that email