Question: Fixing the payment system at Alvalade XXI: a case on IT project risk management Ramon O'Callaghan Tilburg University, The Netherlands Correspondence: AO'Callaghan, School of Economics

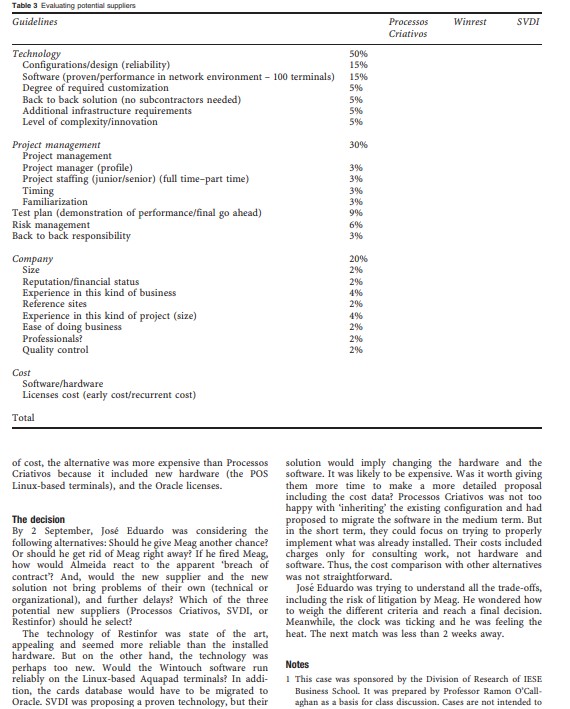








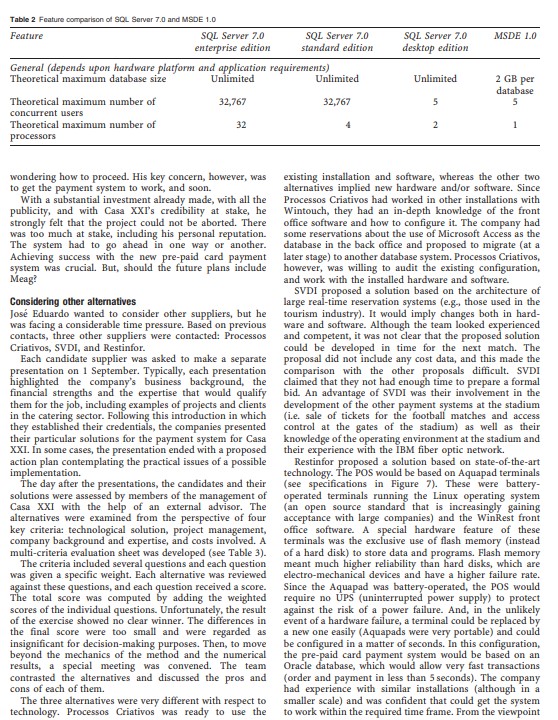

Fixing the payment system at Alvalade XXI: a case on IT project risk management Ramon O'Callaghan Tilburg University, The Netherlands Correspondence: AO'Callaghan, School of Economics and Business Administration, Warandelaan 2, Tilburg University, PO Box 90153, 5000 LE, Tilburg, The Netherlands. E-mail: r.ocallaghandust.ml Abstract This case describes the implementation and subsequent failure of an innovative system instaled in the bars of Alvalade XXI, the recently built football stadium in Lisbon, Portugal. Casa XXI. the company running the bars, had entrusted the project to an IT supplier who had limited experience with large systems. During the inauguration, the system failed spectacularly creating a chaotic situation. The fiasco meant not only a financial loss, but also a blow to the reputation of the company. The management blamed the supplier for the failure. The supplier, however, claimed that the problem was not technical but organizational, that is, poor planning of operations. Subsequent tests were inconclusive and failed to restore trust. At the and of the case, the CEO is considering the possibility to switch to an alternative supplier. He also wonders what they could have done to manage the project and the associated risks more effectively. The case highlights risk and project management issues in large systems implementations. The discussion can be structured around cost/benefit analysis, risk assessment, and project management. Relevant dimensions include: company operations, project scope, degree of innovation, technology used, system architecture, supplier selection, and project organization. In addition, the case raises governance questions: Who is responsible for the project? Even if the project is outsourced, how should the roles and responsibilities be apportioned between the company and the IT supplier(s)? What mechanisms should be used to plan and execute IT projects, and control their risks? journal of Information Technology (2007) 22, 399-409. doi: 10.1057/palgrave.jit.2000116 Keywords: risk management; project management; innovation adoption; systems implementation, governance; outsourcing Introduction n August 2003, while many Europeans were heading to image of innovation and modernity enhanced also by all the the beaches to mitigate the effects of the worst heat wave free publicity it received in recent newspapers articles on record, Jose Eduardo Sampaio, the CEO of Casa XXI. covering the inauguration. was faced with another kind of heat.' Cartao 21, the The failure of the system represented not only a innovative payment system of Casa XXI that he had significant financial loss for Casa XXI but also an personally conceived and subcontracted, had dramatically embarrassment for the Sporting Football Club as well as a failed on 6 August during the high-visibility inauguration of major blow to the reputation of Casa XXI and to the Alvalade XXI, the newly built football stadium of the credibility of Jose Eduardo, himself a former football Sporting Club of Portugal. player. Casa XXI had been granted the rights to exploit all the Jose Eduardo was quick to point the finger at Meag, bars and restaurants in the stadium. Based on pre-paid the company with whom he had contracted to design cards, the new payment system was supposed to make bar and implement the system. But Jose Almeida, Meag's operations more efficient by eliminating the use of cash. In manager, claimed that the system worked fine. In his addition, the system was supposed to give Casa XXI an opinion, the nature of the problem was organizational.Table 3 Evaluating potential suppliers Guidelines Processos Winrest SVDI Criativos Technology 50% Configurations/design (reliability) 15% Software (proven/performance in network environment - 100 terminals) 15% Degree of required customization 5% Back to back solution (no subcontractors needed) 5% Additional infrastructure requirements 50% Level of complexity/innovation 5% Project management Project management Project manager (profile) 3% Project staffing (junior/senior) (full time-part time) 3% Timing 3% Familiarization 3% Test plan (demonstration of performance/final go ahead) 9% Risk management 6% Back to back responsibility 3% Company 20% Size 206 Reputation/financial status 20% Experience in this kind of business Reference sites 2% Experience in this kind of project (size) 4% Ease of doing business 2% Professionals? 2% Quality control 206 Cost Software/hardware Licenses cost (early cost/recurrent cost) Total of cost, the alternative was more expensive than Processos solution would imply changing the hardware and the Criativos because it included new hardware (the POS software. It was likely to be expensive. Was it worth giving Linux-based terminals), and the Oracle licenses. them more time to make a more detailed proposal including the cost data? Processos Criativos was not too happy with 'inheriting' the existing configuration and had The decision proposed to migrate the software in the medium term. But By 2 September, Jose Eduardo was considering the in the short term, they could focus on trying to properly following alternatives: Should he give Meag another chance? implement what was already installed. Their costs included Or should he get rid of Meag right away? If he fired Meag. charges only for consulting work, not hardware and how would Almeida react to the apparent 'breach of software. Thus, the cost comparison with other alternatives contract"? And, would the new supplier and the new was not straightforward. solution not bring problems of their own (technical or Jose Eduardo was trying to understand all the trade-offs, organizational), and further delays? Which of the three including the risk of litigation by Meag. He wondered how potential new suppliers (Processos Criativos, SVDI, or to weigh the different criteria and reach a final decision. Restinfor) should he select? Meanwhile, the clock was ticking and he was feeling the The technology of Restinfor was state of the art, heat. The next match was less than 2 weeks away. appealing and seemed more reliable than the installed hardware. But on the other hand, the technology was perhaps too new. Would the Wintouch software run Notes reliably on the Linux-based Aquapad terminals? In addi- 1 This case was sponsored by the Division of Research of IESE tion, the cards database would have to be migrated to Business School. It was prepared by Professor Ramon O'Call- Oracle. SVDI was proposing a proven technology, but their aghan as a basis for class discussion. Cases are not intended toFeatures & Specs FIC AquaPad: WLAN connected wutpad based on a SOOMHa Cruson processor and Midori Linux 08 Features: TM5400 500MHz Crusoe 8.4" TFT 800830 display 3200mAh Lithium battery Built-in InDA, speaker, mic 3.0 hours badary Ro Magnesium enclosure Technical Specs: 128MB BODIMM SORAM ix PCMCIA bay 2x USB ports 1x Compact Flash Bay Midori Linux 03 Dimensions: 274x164127mm The 2.5lb AquaPad is a medium sized portable device centered Weight: around an 800x600 pixel TFT touch sensitive screen. The device 253 Lba is larger than a PDA, but smaller than a laptop. The smooth blue and silver AquaPad has several ports for SUMMARY expansion cards, but not much else, and fits easily into the left The FIC Aqua Pad is hand. The unit is encased in a Magnesium alloy shell that is mobile Internet acc lightweight and sturdy. device connected by a wireless PCMCIA card. The operating system is designed especially for low-power mobile Battery Wa isabout 3 devices and works off of a RAM based file system that can reside hours and the unit in everyday memory. Under the terms of GNU General Public boasts an BOOK600 TFT License, Midori Linux has been open sourced, so it is an ever touch sensitive screen. evolving free operating system which Transmeta indirectly supports. FIC website Figure 7 FIC Midori Linux AquaPad. serve as endorsements, sources of data, or illustrations of and innovation management, project implementation and effective or ineffective management. risk management. His recent academic recognitions include UEFA - the Union of European Football Associations - is the the best paper award in the Knowledge Management track governing body of football (soccer) on the continent of Europe. at the Hawaii International Conference on Information Its mission is to safeguard the development of European Sciences (HICSS) and the best teaching case award at the football at every level of the game and to promote the principles International Conference on Information Systems (ICIS). of unity and solidarity. His work has been published in books, refereed journals and conference proceedings, for example the Journal of Marketing, European Journal of IS, Journal of IT, ECIS, ICIS, About the author HICSS. He is an editorial board member of the Journal of Ramon O'Callaghan is Professor in the Department of Strategic Information Systems. He holds the degrees of Information Systems and Management at Tilburg Univer- Doctor of Business Administration from Harvard Business sity (the Netherlands); and extraordinary professor at IESE School; MBA from IESE Business School; M.Sc. and B.Sc. in Business School (Spain). His current research/teaching Electrical Engineering from UPC, the Technical University interests include strategic management of IT, knowledge of Catalunya.400 He believed the mishap had to with the late activation and distribution of the cards, as well as the lack of training of the bar staff, and these were responsibilities of Casa XXI, not his. But it was difficult to know what went wrong and whom to blame. In reality, the system had never been fully deployed and tested before the event. The construction of the stadium had been completed just a few days before the inauguration, and neither Casa XXI nor Meag had prior access to the stadium. Thus, nobody knew whether the installed configuration actually worked. With such uncer- tainty and the next match just days away, Jose Eduardo demanded a comprehensive system test. By the end of August, Meag conducted such a test in the presence of Casa XXI's management team. The results were discouraging: the Figure 1 Jose Alvalade stadium, Lisbon. system failed to operate properly. Casa XXI lost faith in both the system and the supplier. Then Jose Eduardo began considering the possibility of Sporting Club de Portugal, Alvalade XXI was a first-class switching to another IT supplier. But, he was also stadium that would host five matches of the Euro 2004 pondering whether a new supplier and a new system would championship. It was designed by architect Tomas Taveira not bring new problems, and additional delays. Should he who also worked on other Euro 2004 stadiums in Portugal. give Meag another chance or should he drop them? He The vibrant colors (mainly green and yellow) and wave-like knew he would have to weigh the risk of litigation by Meag roof are features of the new stadium (as seen in Figure 1). against the relative advantage and costs of a potential new The stadium seated 52,000 spectators. Its modern design supplier. He then approached other suppliers and requested included full covering for all seats. The stadium was part of new proposals. Three suppliers were selected and invited to a larger complex, which included restaurants and bars, a present their solution to Casa XXI's management team. cinema multiplex and bowling alley, as well as a medical By 2 September Jose Eduardo was reviewing these new center and a health club. Located in an urban zone adjacent proposals and trying to understand the costs, benefits, and to the current stadium, the new project was integrated risks associated with each alternative. He had to make a within a larger complex with sports and residential decision and wondered what criteria he had to use. He components, the latter including housing, shops and could not afford to make another mistake. He was also services. reflecting on the factors that led to the present situation. He wondered if there was something that Casa XXI should have done differently to identify and manage the risks in a more effective manner. Jose Eduardo knew that he was running Casa Vinte e Um (Casa XXI) out of time: the date of the next match was fast The restaurants and bars of the new Alvalade stadium were approaching. run by Casa XXI, a company of the group Casa do Marques S.A., the largest catering company in Portugal specialized in banquets for corporations, governments, or large private Background parties (Figures 1 and 2). In 2003 Portugal had been frantically building 10 new Casa do Marques was founded in 1989 by Jose Eduardo football stadiums for Euro 2004, the European football Sampaio, Fernanda Seijo and Florbela Bem. Jose Eduardo championship organized by UEFA.' The Portuguese Foot- was a well-known former player of Sporting and had many ball Federation had to ensure that 10 football stadiums contacts in the sports world. Fernanda Seijo had been would be available to host the final round matches of Euro associated with the restaurant business all her life. She came 2004. The renovation of five existing arenas and the from a family of caterers. Her father had the largest catering building of five new stadiums were being carried out with company in Portugal during the 1980s. The three knew each the support of the government. In total, the overall cost was other from the time they worked together in the business of estimated to be 500 million euros. The government and the Fernanda's father. football federation had formed a joint venture to oversee Casa do Marques was run by three of them. Fernanda the preparations. Along with the stadiums, the projects oversaw the production, decoration and logistics of the included motorways, revamping airports, new urban and events; Florbela was responsible for sales; and Jose Eduardo regional railways and upgrading ports. The airports was the general director (CEO) of the group. authority spent 350 million euros upgrading terminals at The company reached a partnership agreement with the Lisbon, second city Porto and Faro in the Algarve area. Sporting Club to become the exclusive operator of catering Hosting of Euro 2004 was bringing many other benefits to services and special events at the Alvalade stadium for a the country. New investments were being attracted to period of 15 years. The result was the creation of a new Portugal, many monuments were being restored, and new company, Casa XXI, which was established for the hotels were being constructed. exploitation of the business at the Alvalade complex. The One of the new arenas was the new Jose Alvalade stadium agreement with the Sporting Club granted Casa XXI the in Lisbon, also known as Alvalade XXI. Home of the rights to exploit the following areas:401 258 25 E 256 Figure 3 Example of the early card design. Figure 2 Examples of banquets provided by Casa do Marques. . Prestige - 1000m space that includes a restaurant for 800 persons Corporate Club - 400 m space for 126 persons Sport 21 - 500 m space, split into two floors, includes a Figure 4 Point-of-sale (POS) terminal. restaurant for 400 persons . Restaurant Casa XXI - 250 m space with capacity for 150 persons, open daily, an upscale alternative for employees value of all the cards. The communications between the of companies in the area point-of-sale terminals (POSs) and the central server (the Cafeteria - located at the entrance of the stadium card database) used a fiber-optic network. This network Refeitorio - canteen for the employees of Sporting had been installed by IBM as part of the stadium's Camarotes - loges for Sporting group companies and infrastructure and was being used by other applications, other partner companies for example sales of tickets for football matches. When a Kiosks - 15 kiosks associated with brands client made a payment with a given card, the POS scanned . Bars - 26 bars scattered all over the stadium in different the code of the card, the system then checked the "amount sectors of cash' left in the card, and debited the card according to Venta ambulante ('moving' sales) - 50 waking sales- cost of the item ordered. persons The overall system architecture comprised two modules: the front office and the back office. The front office supported the sales process and client interaction including Carto 21: an innovative payment system the Cartao 21 payment system. The back office supported An important aspect of the operations at the bars and other food and beverage operations (inventory management and points of sale was the use of an innovative payment system purchasing). The data corresponding to all the transactions based on pre-paid cards ("Cartao 21'). Each card was worth (sales, purchases, inventory) were recorded and sent to an a given cash value (ie. 206, 156, 106, 56 or 2.56) and had a external accounting application. unique serial number (the bar code) that identified it. A The software was a standard application provided by scanner was used to read the code, check the money left on Wintouch, that is, wSIR (Sistema Integrado de Restau- the card, and debit the value of the card according to cost of racao), which had been installed in many other companies the sale. The cards were sold at special kiosks inside the in the restaurant business. It ran in a decentralized way, stadium and by special sales staff walking about the bars. that is, every bar had two or more POSs connected to a local The cards could be used during several matches, and their server with the software running on it in order to manage validity was 2 years. and record all the transactions. The system was meant to avoid the use of cash thereby The front office software supported the work of the shortening the time it took to execute payment transac- sales staff in the restaurants and bars (Figure 4). A client tions. For clients, this meant shorter queues at the bars. For wanting to buy an item at a bar, had to go firstly to the Casa XXI, it meant more productivity of their bar bartender at a POS, tell what he/she wanted to order personnel, faster turnaround, and more sales at peak times. and give his/her Cartao 21. The bartender then clicked In addition, it reduced the need for controlling cash the order on the tactile screen and would slide the card registers and bartenders (Figure 3). through the bar code reader for the payment. Then the The cards had pictures of famous sportsmen (e-g. legends POS printed a ticket (receipt/order confirmation) that the of Sporting's history). Many people would want to buy and client subsequently had to show to collect the ordered collect them because of their historic value. In fact, the item from another staff member (normally in the central publicity and the articles in the press referred to the cards section of the bar). Thus, in busy moments, customers had as items to 'collect history" ('Cartoes para coleccionar to queue a second time to get the items they had ordered historia'). (see Figure 5). The payment transaction was executed through a real- The front office also supported the 'vendedores ambu- time connection to a central database that kept track of the lantes' (walking salespeople) in the spectator areas of theTable 1 Mong's proposal (April 2003) Points of Sale (PQSs) 54 POS - SNS 3030 premium touch E 67.500,00 54 Ticket printers Epson TM &8 III E 20.520,00 54 Cash registers RJ11 ELT ML E 3.672,00 54 Displays LCD 2 x 20 FG23 E 7.506,00 54 Bar code readers Laser BI E 10.260,00 Workstations 7 Workstations (Warehouse) E 5,600,00 3 Workstation (Administration) E 3.600,00 Racks E 3.216,00 Servers E 4.000,00 Equipment for walking salesmen Antennas E 2.402,20 15 Terminals X54 XRT503 Laser E 15.797,25 Software Wintouch WSIR back Office (SQL) OLP E 2.500,00 Wintouch WSIR front Office (SQL) OLP E 15.000,00 Wintouch WebCOM (FTP) OLP E 250,00 Installation and configuration E 1.500,00 Figure 5 Bars in operation. Total (exclusive VAT) E 163.323,45 The inauguration The inauguration of the stadium on the 6th of August 2003 was an important event not only for the Sporting Football Club, but also for Portugal. The spectacle included a laser show, the Sporting anthem sung by the popular Portuguese singer Dulce Pontes and the official opening by the President of the Republic, Jorge Sampaio. The jubilation Figure 6 'vendedor ambulante' or walking seller. was taken down a notch with a minute's silence before the kick-off, in remembrance of those who had lost their lives in the recent spate of forest fires in the country. A friendly stadium (terraces, stands) (Figure 6). These walking sellers match between Sporting and Manchester United followed carried a transparent plastic tray with a limited assortment the official inauguration. of products. They used hand-held wireless terminals But it was not all jubilation at the stadium that day. Casa running a customized version of the software to record XXI was "inaugurating' Cartao 21, its innovative payment sales and accept Cartao 21 payments 'on the move'. system, and the experience turned out to be a nightmare. A The Cartao 21 system had been conceived by Casa XXI, couple of football fans recalled the incidents: but the design and implementation had been subcon- tracted. Several international IT services companies re- We were not allowed to enter the stadium until 30 sponded to the call for tender, but the project was awarded minutes before the match. We had been waiting outside to Meag, a Portuguese firm. Meag was a wholesaler of office the stadium for hours in the scorching heat. When we and computer supplies that had extended its business into finally got in, the first thing we wanted to do is to go to computer system installations. Their experience with large the bar and drink a cold beverage. But of course, we were ystems implementation was, however, limited. not alone. We had to fight our way through the crowd to Meag was in partnership with another IT supplier, reach the bar area. There, we learned that we had to have Wintouch, which provided the software. Meag brought in one of those cards (Cartao 21) to be able to order and all the hardware and did the overall installation and pay. To acquire it, we had to go to a kiosk some 50 meters configuration. Meag acted as the prime contractor and away. But the staff there had no cards. They told us to had overall responsibility for the project. Table 1 provides wait because the cards "were on their way'. After a few the breakdown of the system elements and the costs minutes, we could finally buy one of these cards. We then according to Meag's offer to Casa XXI at the time when the returned to the line for the bar. When we finally reached system was being considered. the bar, the bartender told us that n card was notworking. He couldn't tell whether the problem was with We were registering the sales manually: scribbling on a my card or their system. We then wanted to pay with piece of paper. We didn't look too professional, to put it cash, but he told us that this was not possible. I said we mildly! just wanted a bottle of water! We had no time to go and get a new card. I begged him. Faced with the same And as Miguel Seijio pointed out, shoe-boxes are far less problem, some people next to us were getting really angry and started shouting. The bar staff didn't know how to secure than cash registers: react. Some looked in another direction pretending not to hear anything, as if nothing happened! Then the start of Controlling was impossible. We caught people taking the ceremony was announced through the loudspeakers. money out of the shoe box and giving it to others! We The crowd behind us got really impatient and started really caught them! complaining too. Some of the bartenders then began accepting the cash. Others gave away soft drinks to It turned out that the system was able to accept cash appease the angriest. Seeing this, many people then tried payments if properly configured. In principle, bar managers to grab water bottles and run to their seats not to miss the could have changed the configuration, but they needed a start of the ceremony. It was chaos! special password to do so. The passwords had not been distributed in advance, and the bar managers had not been One of the bartenders explained what he experienced: trained to handle the situation. Miguel Seijo added: When the stadium opened its doors, an avalanche of The POSs were not able to accept cash payments because thirsty people who had been waiting outside the stadium the bar managers had not received the codes nor the rushed to the bars to buy drinks, specially water. This instructions that would have allowed them to use the cash collapsed the bars. The pre-paid cards were supposed to registers. In the midst of the initial chaos, Meag staff, had have been activated at designated POSs, but this proved to run from bar to bar to reconfigure a total of 42 POSs. impossible because we were extremely busy coping with They had only two persons to do the job! They had no the avalanche of thirsty people trying to get water. When idea how big the stadium was, and how long it takes to they tried to pay, their cards did not work because they walk from one end of the stadium to the other end! When had not been activated. Then they wanted to pay with they arrived, it was too late. The damage was already done cash, but the POS had not been programmed to accept cash payments. The drawer in the cash register would not But there were other problems. Even in the few cases open. It was frustrating. We didn't know what to do. where the POSs were reconfigured to accept cash payments, There wasn't much we could do away! the system was not able to take orders for one of the most requested products: Water! Seijo explained: Miguel Seijo, responsible for bar operations at Casa XXI, explained It turned out that the price of water bottles had not been entered in the database, and the POS could not sell a The cards were sold at special kiosks in the corridors of product whose price was not in the product database. On the stadium and by walking salespeople. We were afraid top, prices could not be entered manually. It was really a that, if the cards were activated before making them problem. Some salespeople at the bars were smart enough available to the kiosks and to the walking salespeople. to key in the code of another product with the same price hooligans might want to steal them. The monetary value (e.g. a coffee instead of a bottle of water). Others ended of all these (activated) cards is huge. So, for security up giving away the bottles of water without registering reasons, we had decided to activate them as late as the sale or even collecting the cash. possible, i.e. just when the clients are using them for the first time at the bars. But this proved impractical. We Another issue that worried Miguel Seijo was the relatively could not foresee the initial avalanche of people at the long time it took for the system to complete a transaction bars. In those circumstances, the obvious alternative was and its effect on operational efficiency at the bars: to resort to cash payments. But, that did not work because the POS were not ready to accept cash. During the inauguration and in subsequent trials, we discovered that the cycle time to complete a sales and Ready or not, clients and bar staff had no choice but to payment transaction was too long. The sequence - going resort to cash when the pre-paid cards were not working through the menus on the screen, finding the product, The salespeople, therefore, tried to work around the system: clicking to register the order, and scanning the card to they started selling without recording the sale, and pay - took in total some 45 seconds. This was an accepting cash without recording the payment. And, in extremely long time. Even if everything else had worked some cases even selling without accepting any payment as OK, this long transaction time would have created a angry customers claimed they had already paid for the serious bottleneck. It certainly slowed things at the few cards. As one salesperson pointed out: POSs that managed to work that day. We had to use shoe boxes instead of the cash registers to To make things worse, the wireless terminals did not put the money because the cash register would not open! work at all. It turned out that the transmitters malfunctionedbecause of the unusually high temperature. They had been Until now our company had an excellent reputation. We placed on the roof of the stadium where the structure had a good image towards our clients, our employees, our reached temperatures higher than 50"C. As a result, the suppliers, and the Sporting Club. In our business, walking salespeople could not use the system. They had to prestige is very important. But this situation has damaged record things manually and accept payments in cash. Like our reputation. And for me personally it is a huge their colleagues at the bars, they were caught unprepared. embarrassment. Jose Eduardo, the CEO, reflected on the whole episode: After the fiasco of the inaugural day, the trust between Casa We could try to find excuses in the difficult circum- XXI and the technology supplier (Meag) began deteriorate stances we had to operate... We could say that the ing. Whereas the management of Casa XXI pointed out that stadium was not finished until the eleventh hour... But the system had clearly failed, Meag claimed that the system the reality is that on the day of the inauguration, with so had worked fine. much heat, the public needed to consume beverages, to Many questions were being asked. What caused the drink water, ... and we failed them! The fact remains that problem? Who was to blame for the failure? What should be our system did not work. It was chaotic. It was done now? Jose Eduardo wondered whether or not the embarrassing! problem was technical. It seemed that the circumstances during the inauguration were so exceptional that they could The day ended up on a positive note, however, with have rendered a perfectly working system useless anyway. Sporting beating Manchester United 3-1. The public was That was certainly Meag's viewpoint. In the words of Jose jubilant. They seemed to have forgotten the problems they Almeida, Meag's director: encountered when they entered the stadium and went to the bars. Sporting's victory over Manchester United helped There was no failure really. The system worked fine. It all shares of the club jump the next day by 4.03% on the had to do with an organization problem. Portuguese stock exchange. For Casa XXI, however, the picture was much darker. Jose Eduardo had more than one Jose Eduardo remained unconvinced. He became in- reason to be concerned. creasingly critical of Almeida: An 'organizational problem? So what? Does this exon- erate him from responsibility? We delegated the manage- ment of the project to him. Almeida should have alerted Damage assessment and responsibilities us if he considered that there were risks or potential With things literally running out of control, it is not problems, especially if these were 'organizational' be- surprising that at the end of the day Casa XXI lost a lot of cause we, Casa XXI, could have managed the organiza- money. Only through an inventory audit a few days later tional problems. For example, we could have been better could the management figure out how much it had really been sold during the event and how much money prepared: have an alternative plan (a 'plan B'), and train our salespeople for different contingencies. But, the only evaporated' in the process. Miguel Seijo calculated that thing that we kept hearing was: 'do not worry, do not under normal circumstances the revenues should have been worry. There is no problem. Everything will be fine." five times more. The loss for Casa XXI, however, was not only monetary. The articles published in the newspapers in the days According to Jose Eduardo, Meag did not seem to be willing preceding the inauguration had created big expectations. (or capable) to deliver beyond the technical questions Jose Eduardo commented: surrounding the installation and test of the system. The inauguration was an important event for everybody, not just for Casa XXI. Alvalade XXI was the first of Euro What went wrong? 2004 stadiums to be inaugurated. It was something big In the days after the event, Meag was particularly interested that transcended the Sporting and Casa XXI. It was in establishing whether or not there had been technical something grandiose that we wanted to do very well. We problems with the system during the inauguration. Almeida had important guests from all over the world. The was hoping to prove his claim that there were no technical expectation was high. We (Casa XXI) had made publicity. problems. Did the POS not operate properly? Were the POS We said we had a very innovative system. So, everybody terminals not able to communicate and access the pre-paid came here wanting to see and experience our innovation. cards database? Were they not able to accept pre-paid card payment? Meag brought some experts from Wintouch (the software But all the publicity that had helped create an image of vendor) to analyze the files in the back office that contained Casa XXI as a modern and innovative company began the activity logs of the POSs. Almeida examined these backfiring. The press now was being negative. They picked logs on a computer screen, and produced print-outs of up on the troubles and wrote negatively about the failure of the activities of several POSs. Apparently some POSs the much-expected system. The image and reputation of the had managed to record orders and accept payments. Some company were at stake. The situation was indeed serious, of these payments were done with cash and some with and Jose Eduardo was very worried. pre-paid cards. This evidence suggested that perhaps theproblem might not have been a technical one after all as another mistake. The next game was on August 23 and, Almeida was quick to point out. given the short time available, the options were really An independent advisor hired by Jose Eduardo reviewed limited. the facts and tried to uncover what Almeida had labeled as Although Casa XXI had serious doubts about the "organizational" issues. The following factors seemed to management capability of Meag, the possibility of looking have played a role: for another supplier at that stage seemed far-fetched. After . The construction of the stadium was completed with a all, there was some hope that the system was going to work significant delay. As a consequence, the system could the next time if, as it seemed, the problems could be solved. only be installed a few days before the inauguration. The management of Casa XXI felt that if the problem had to There was very little time to test the system in the do with non-technical factors (e.g. training of the salesmen, stadium. The IBM network, for example, had been shortening of the transaction time, pre-activation of the completed only the night before the inauguration. cards, ability to switch to cash payments), then they should The day of the inauguration was unusually hot (tem- be able to prepare effectively and handle the situation the perature was almost 40"C). The antenna and the next time. The question remained on the technical side. communication equipment for the wireless terminals, Thus, it was critical to ensure that the system was which was installed on the roof of the stadium, could not technically in good order. An action plan was devised to stand the extremely high temperatures and stopped that effect. working. The wireless terminals became useless. The plan included the installation of a new wireless The POS could not accept payments in cash because the communication system and new antennas (with cooling system would not allow it. Some special access codes system) and, subsequently, two major tests: one with the (passwords) were required for the system to allow walking salesmen ('ambulantes') to test the wireless sales people to accept cash payments. The salespeople at terminals, and another with all the sales staff to test the the bars did not have them and, in any case, they had not whole system with a full load. In parallel, the salespeople at been trained to operate with cash. the bars would be thoroughly trained on the operation of Many pre-paid cards did not work because they had not POS terminals and given instructions on what to do if, at been activated. The cards were bought at the kiosks and the last minute, they had to resort to cash payment. If the were supposed to have been activated at the bar. But this results of the tests were not satisfactory, the management of proved impossible because the bars had to cope with the Casa XXI was ready to switch to cash payment for the next initial avalanche of people. In addition, many cards had game in order to avoid more bad publicity. This would also arrived at the kiosks too late for people to buy them allow more time to solve technical problems. anyway (the people were already at the bar trying to buy Another issue had to do with the logistics of the cards. and pay with cash). Since the network was not available at the kiosks where The personnel at the bars lacked proper training. They cards were sold, the cards could not be activated at the were unprepared for the contingencies experienced moment they were sold. In the original design, they were during the inauguration. They did not know how to supposed to be activated at the bar the first time they were react, and had no instructions to follow. used. But, as the experience with the inaugural match An additional factor was the transaction time. It took far showed, this was not practical. In order to avoid bottle- too long for the terminals to complete the ordering, and necks at the bars, the solution was to have the cards payment cycle. At 45 s, it had the potential of becoming a activated before being distributed to the kiosks and sold to serious bottleneck especially during the 15 min break the clients. This involved some financial risk, in case cards between the first and the second half of the match. were stolen before being sold. Another solution would be to extend the network to the kiosks and do the activation there In essence, there had been organizational problems and at the very moment the cards were being sold. This was a some technical problems. The organizational problems had solution envisaged for the future, but not possible for the been identified and Casa XXI could now take the lead in next match just a few days away. addressing them for subsequent matches. With respect to technology, the situation was less clear. The only certain thing was that the wireless transmitter had to be replaced A decisive test and a better cooling system had to be installed. Further The 'full load" test was crucial to decide whether or not to tests were needed to determine that the system was 100% go ahead with the pre-paid card system for the next match. trouble free both for the mobile sales and the bars. The fact The full load test had been decided the week before, with that some POSs seemed to have worked during the the agreement of all the parties. The main objective was to inauguration, did not guarantee that the overall system ensure that everything would be working properly in order was reliable. In fact, the system had never really worked at to avoid problems with costumers, the Sporting and the full load, that is, with all terminals concurrently accessing press. Jose Eduardo explained: the cards database. The uncertainty remained. Meag had promised us that the system would be fully operational for the second match. But, I did not trust Action plan them. I demanded to see the evidence that it would work, By August 13, Jose Eduardo was wondering: 'what do we do that is a comprehensive test with many people using the now? With its reputation at stake and all eyes on the new POSs, accepting orders and making payments with payment system, Casa XXI could not afford to make Cartao 21 concurrently in order to simulate the sametransaction environment as during the match. The test resolve all technical problems to ensure that next time the was supposed to take place ten days before the second Cartdo 21 system will work flawlessly match, but they kept postponing and postponing it. We had only four days left before the next match, and then I In the meantime, and in preparation for the next match, told them: "ready or not, you do the test tomorrow'. Casa XXI addressed the other organizational problems that That's it. Either it works, or it doesn't! were not related to Cartao 21. For example, the salespeople were given extensive training, including how to operate the And it did not work. When the test finally took place, POS to accept cash payments. The transaction time was both the results and conduct of the test itself were reduced from 45 to 8 seconds. This was achieved by limiting disappointing. Meag seemed to have overlooked key the product range (i.e. number of items available for sale at operational details, for example some hardware elements the bar) and also by simplifying the menu structure and the were not switched on, and some terminals were not properly number of screens (ie. all products appear now in one configured. The following problems were reported: single screen). Printers without proper connection or malfunctioning On August 23, the second football match of the season The system printed invoices showing products that had took place. As planned, all the products sold by Casa XXI on that day had to be paid in cash. The bar staff and the not been requested Equipment without proper configuration (ie. different walking salespeople system had to tell clients to hold their points of sale were configured in different ways.) pre-paid cards for the next event. Some displays were not connected or even working In the end, the result was positive. No major incidents were reported. All the bars were able to sell all products to Commenting on the printer problems, Miguel Seijo all clients and accept cash payments. The experience added: demonstrated that the Wintouch software was able to work properly with the configuration in the stadium. It became Meag didn't do an analysis of critical incidents. For clear that the problem was now confined to the part of the example, when you slide the card through the reader after system dealing with the Cartao 21 payment system. But, having keyed in the order, the POS normally prints a what was wrong with the payment system? ticket. But, if the printer runs out of paper, then nothing happens. You think that the scanner cannot read the card (some cards were difficult to read). Then the tendency is Technical audit to try again. You slide the card a second time. Although In an attempt to clarify what was wrong with the payment the printer does not print anything, the system takes system, Wintouch asked help from one of its partner money from the card (the client is charged twice!). But companies, Processos Criativos, which had substantial the printer remains still. Nothing happens. What do you experience with Wintouch installations. do! You slide it again (and the card is charged yet a third The assessment by Processos Criativos revealed some time), but the printer does not react. You get impatient, facts that could have had a negative impact on the overall and repeat it four or five times. Then what happens? performance of the payment system running at full load Well, ... the POS hangs up! This is the result of a during a match. One of the potential problems had to do technical problem. The printer is connected through a with the way Meag had configured the Wintouch software parallel port and cannot send a signal back to the POS and how it communicated with the back office database to saying 'I am out of paper, I cannot print, put more paper'- record the transactions. This was cumbersome and took too We had to address this critical incident because it could long. But, the most significant finding was that the system compromise seriously the operation of the system. was not using the right version of the SQL server. The SQL server was the core of the Cartao 21 payment system, that is, the database for keeping track of the value of all the pre- The crucial test, which was supposed to provide reassur- paid cards. ance, only increased the level of anxiety. Under the Meag had installed a configuration that was running the circumstances, and with only 3 days left before the next "MSDE" version of the SQL server. This was a desktop game, the fear that something would go wrong escalated. version intended to be used by software developers to program and test systems, but not to run full-scale configurations. Apparently Meag had not acquired the A match without cards proper Microsoft software licenses, that is,, the SQL Server The management of Casa XXI decided not to subject itself 7.0 Standard Edition or SQL Server 7.0 Enterprise Edition to further risks for the match on 23 August. Jose Eduardo (for details see Table 2). explained: A key limitation of the MSDE version is that the maximum number of concurrent users is only five. This I decided we would not use the Cartao 21 for the next constraint could explain why the system did not perform match. We could not run the risk of having a second when operating at full load (the potential number of failure. All the eyes were on us: the public, the press, the concurrent users at the stadium was around 70). It could Sporting Club. They were all waiting to see what certainly have been the reason why the system failed on the happened with the Cartao 21 payment system. So, we day of the inauguration. resorted to the 'plan B', i.e. cash payments. I explained to This finding contributed to further discredit Meag. The the press that we at Casa XXI were taking the time to patience of Jose Eduardo was running thin, and he wasTable 2 Feature comparison of SQL Server 7.0 and MSDE 1.0 Feature SQL Server 7.0 SQL Server 7.0 SQL Server 7.0 MSDE 1.0 enterprise edition standard edition desktop edition General (depends upon hardware platform and application requirements) Theoretical maximum database size Unlimited Unlimited Unlimited 2 GB per database Theoretical maximum number of 32,767 32,767 concurrent users Theoretical maximum number of 32 2 processors wondering how to proceed. His key concern, however, was existing installation and software, whereas the other two to get the payment system to work, and soon. alternatives implied new hardware and/or software. Since With a substantial investment already made, with all the Processos Criativos had worked in other installations with publicity, and with Casa XXI's credibility at stake, he Wintouch, they had an in-depth knowledge of the front strongly felt that the project could not be aborted. There office software and how to configure it. The company had was too much at stake, including his personal reputation. some reservations about the use of Microsoft Access as the The system had to go ahead in one way or another. database in the back office and proposed to migrate (at a Achieving success with the new pre-paid card payment later stage) to another database system. Processos Criativos, system was crucial. But, should the future plans include however, was willing to audit the existing configuration, Meag and work with the installed hardware and software. SVDI proposed a solution based on the architecture of Considering other alternatives large real-time reservation systems (e.g., those used in the Jose Eduardo wanted to consider other suppliers, but he tourism industry). It would imply changes both in hard- was facing a considerable time pressure. Based on previous ware and software. Although the team looked experienced contacts, three other suppliers were contacted: Processos and competent, it was not clear that the proposed solution Criativos, SVDI, and Restinfor. could be developed in time for the next match. The Each candidate supplier was asked to make a separate proposal did not include any cost data, and this made the presentation on 1 September. Typically, each presentation comparison with the other proposals difficult. SVDI highlighted the company's business background, the claimed that they not had enough time to prepare a formal financial strengths and the expertise that would qualify bid. An advantage of SVDI was their involvement in the them for the job, including examples of projects and clients development of the other payment systems at the stadium in the catering sector. Following this introduction in which (ie. sale of tickets for the football matches and access they established their credentials, the companies presented control at the gates of the stadium) as well as their their particular solutions for the payment system for Casa knowledge of the operating environment at the stadium and XXI. In some cases, the presentation ended with a proposed their experience with the IBM fiber optic network. action plan contemplating the practical issues of a possible Restinfor proposed a solution based on state-of-the-art implementation. technology. The POS would be based on Aquapad terminals The day after the presentations, the candidates and their (see specifications in Figure 7). These were battery- solutions were assessed by members of the management of operated terminals running the Linux operating system Casa XXI with the help of an external advisor. The (an open source standard that is increasingly gaining alternatives were examined from the perspective of four acceptance with large companies) and the WinRest front key criteria: technological solution, project management, office software. A special hardware feature of these company background and expertise, and costs involved. A terminals was the exclusive use of flash memory (instead multi-criteria evaluation sheet was developed (see Table 3). of a hard disk) to store data and programs. Flash memory The criteria included several questions and each question meant much higher reliability than hard disks, which are was given a specific weight. Each alternative was reviewed electro-mechanical devices and have a higher failure rate. against these questions, and each question received a score. Since the Aquapad was battery-operated, the POS would The total score was computed by adding the weighted require no UPS (uninterrupted power supply) to protect scores of the individual questions. Unfortunately, the result against the risk of a power failure. And, in the unlikely of the exercise showed no clear winner. The differences in event of a hardware failure, a terminal could be replaced by the final score were too small and were regarded as a new one easily (Aquapads were very portable) and could insignificant for decision-making purposes. Then, to move be configured in a matter of seconds. In this configuration, beyond the mechanics of the method and the numerical the pre-paid card payment system would be based on an results, a special meeting was convened. The team Oracle database, which would allow very fast transactions contrasted the alternatives and discussed the pros and (order and payment in less than 5 seconds). The company cons of each of them. had experience with similar installations (although in a The three alternatives were very different with respect to smaller scale) and was confident that could get the system technology. Processos Criativos was ready to use the to work within the required time frame. From the viewpointQuestion 1 (a) In the process of writing a business case for Casa XXI, discuss the justification of implementing the innovative payment system (Cartao 21) in the Alvalade XXI stadium project. (10 marks) (b) Jose Eduardo is considering the possibility of selecting another vendor or to continue with Meag even after the latter has failed the Cartao 21 System. List any FIVE (5) criteria and the decision-making reasoning that will help Jose with the selection. (10 marks)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


