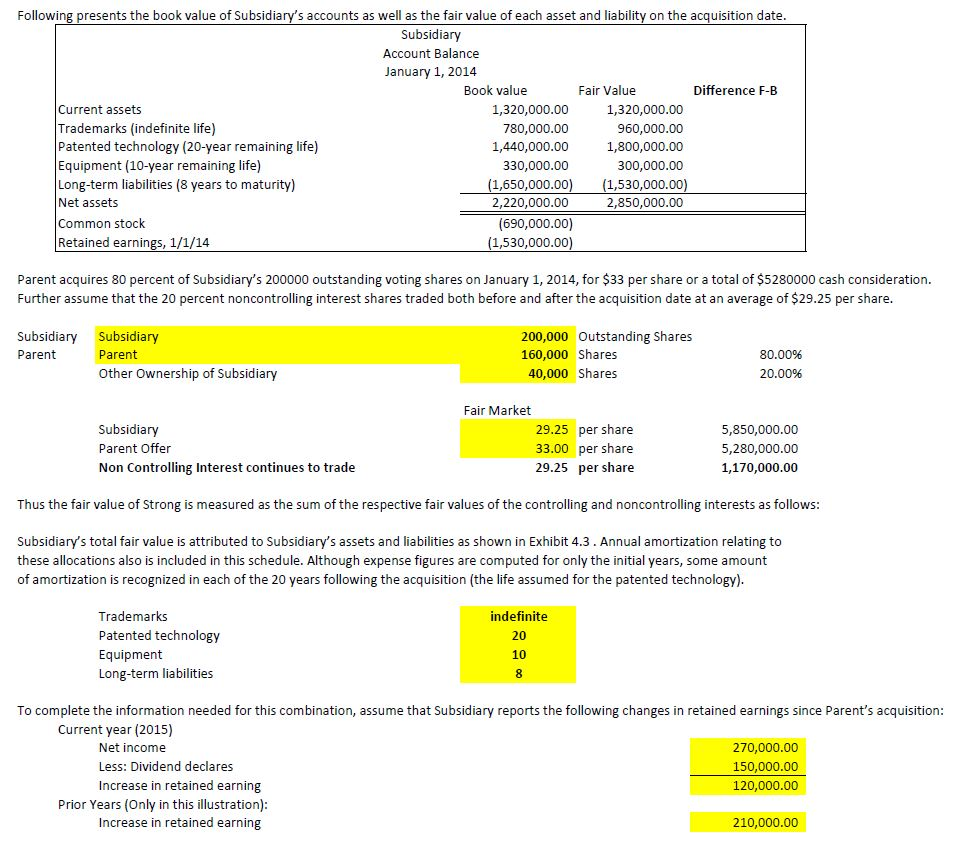
Following presents the book value of Subsidiary's accounts as well as the fair value of each asset and liability on the acquisition date. Subsidiary Account Balance January 1, 2014 Book value Fair Value Difference F-B Current assets 1,320,000.00 1,320,000.00 Trademarks (indefinite life) 780,000.00 960,000.00 Patented technology (20-year remaining life) 1,440,000.00 1,800,000.00 Equipment (10-year remaining life) 330,000.00 300,000.00 Long-term liabilities (8 years to maturity) (1,650,000.00) (1,530,000.00) Net assets 2,220,000.00 2,850,000.00 Common stock (690,000.00) Retained earnings, 1/1/14 (1,530,000.00) Parent acquires 80 percent of Subsidiary's 200000 outstanding voting shares on January 1, 2014, for $33 per share or a total of $5280000 cash consideration. Further assume that the 20 percent noncontrolling interest shares traded both before and after the acquisition date at an average of $29.25 per share. Subsidiary Parent Subsidiary Parent Other Ownership of Subsidiary 200,000 Outstanding Shares 160,000 Shares 40,000 Shares 80.00% 20.00% Subsidiary Parent Offer Non Controlling Interest continues to trade Fair Market 29.25 per share 33.00 per share 29.25 per share 5,850,000.00 5,280,000.00 1,170,000.00 Thus the fair value of Strong is measured as the sum of the respective fair values of the controlling and noncontrolling interests as follows: Subsidiary's total fair value is attributed to Subsidiary's assets and liabilities as shown in Exhibit 4.3. Annual amortization relating to these allocations also is included in this schedule. Although expense figures are computed for only the initial years, some amount of amortization is recognized in each of the 20 years following the acquisition (the life assumed for the patented technology). indefinite Trademarks Patented technology Equipment Long-term liabilities To complete the information needed for this combination, assume that Subsidiary reports the following changes in retained earnings since Parent's acquisition: Current year (2015) Net income 270,000.00 Less: Dividend declares 150,000.00 Increase in retained earning 120,000.00 Prior Years (Only in this illustration): Increase in retained earning 210,000.00 Following presents the book value of Subsidiary's accounts as well as the fair value of each asset and liability on the acquisition date. Subsidiary Account Balance January 1, 2014 Book value Fair Value Difference F-B Current assets 1,320,000.00 1,320,000.00 Trademarks (indefinite life) 780,000.00 960,000.00 Patented technology (20-year remaining life) 1,440,000.00 1,800,000.00 Equipment (10-year remaining life) 330,000.00 300,000.00 Long-term liabilities (8 years to maturity) (1,650,000.00) (1,530,000.00) Net assets 2,220,000.00 2,850,000.00 Common stock (690,000.00) Retained earnings, 1/1/14 (1,530,000.00) Parent acquires 80 percent of Subsidiary's 200000 outstanding voting shares on January 1, 2014, for $33 per share or a total of $5280000 cash consideration. Further assume that the 20 percent noncontrolling interest shares traded both before and after the acquisition date at an average of $29.25 per share. Subsidiary Parent Subsidiary Parent Other Ownership of Subsidiary 200,000 Outstanding Shares 160,000 Shares 40,000 Shares 80.00% 20.00% Subsidiary Parent Offer Non Controlling Interest continues to trade Fair Market 29.25 per share 33.00 per share 29.25 per share 5,850,000.00 5,280,000.00 1,170,000.00 Thus the fair value of Strong is measured as the sum of the respective fair values of the controlling and noncontrolling interests as follows: Subsidiary's total fair value is attributed to Subsidiary's assets and liabilities as shown in Exhibit 4.3. Annual amortization relating to these allocations also is included in this schedule. Although expense figures are computed for only the initial years, some amount of amortization is recognized in each of the 20 years following the acquisition (the life assumed for the patented technology). indefinite Trademarks Patented technology Equipment Long-term liabilities To complete the information needed for this combination, assume that Subsidiary reports the following changes in retained earnings since Parent's acquisition: Current year (2015) Net income 270,000.00 Less: Dividend declares 150,000.00 Increase in retained earning 120,000.00 Prior Years (Only in this illustration): Increase in retained earning 210,000.00







