Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
For Problem #1, you willbe asked to enter an amount or an account number. You will enter your answers for this problem in questions 1-43.
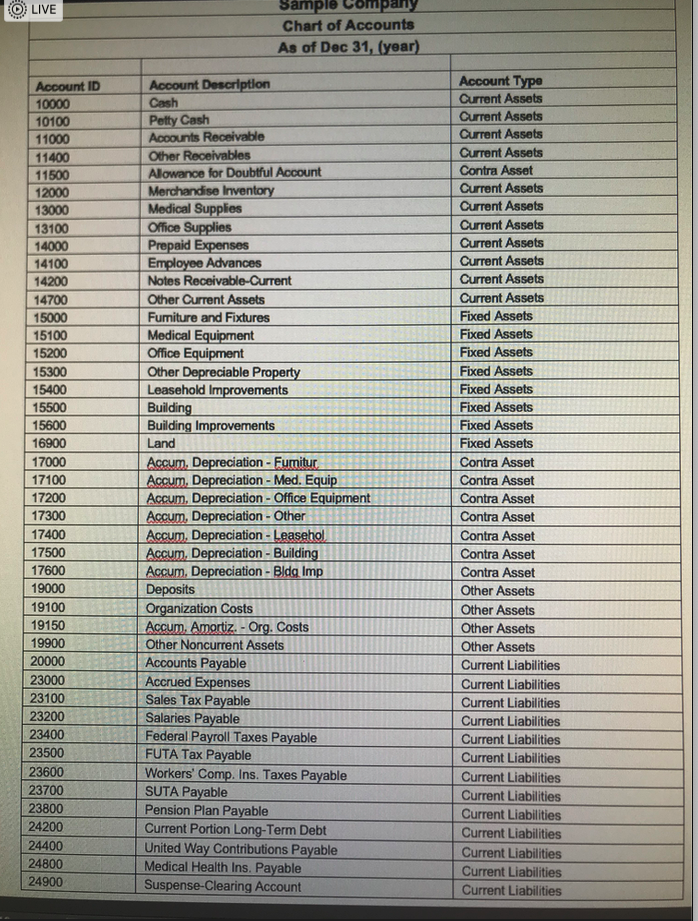
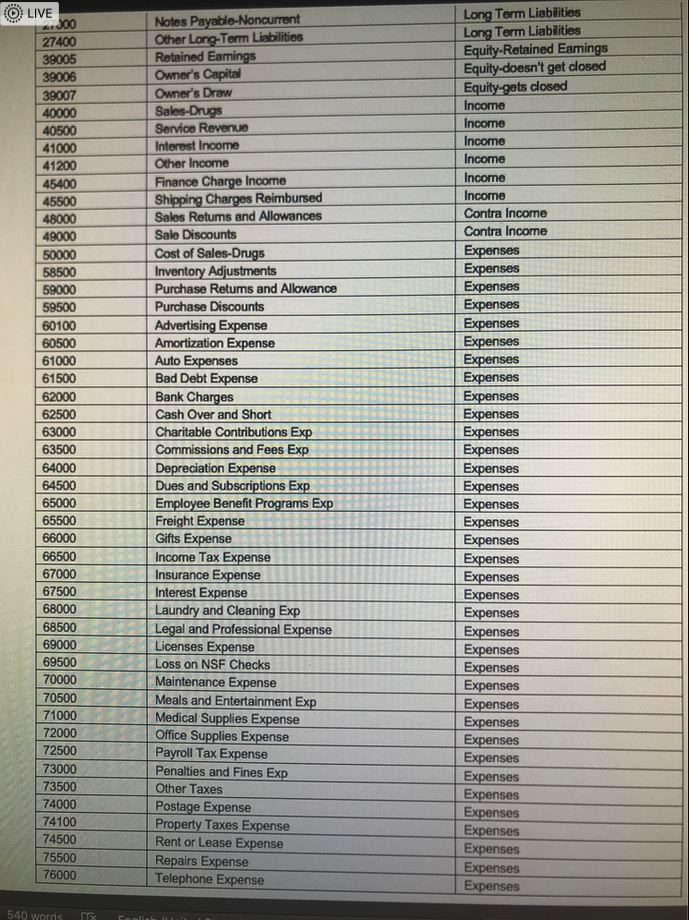
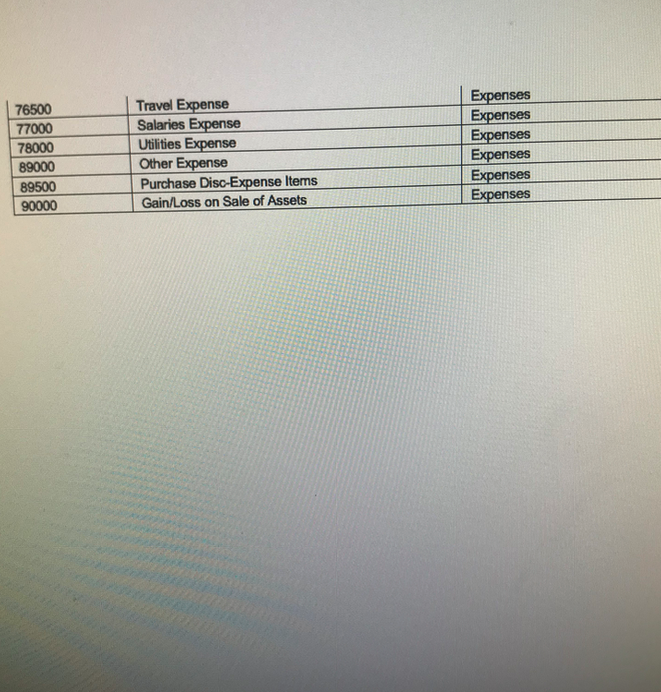


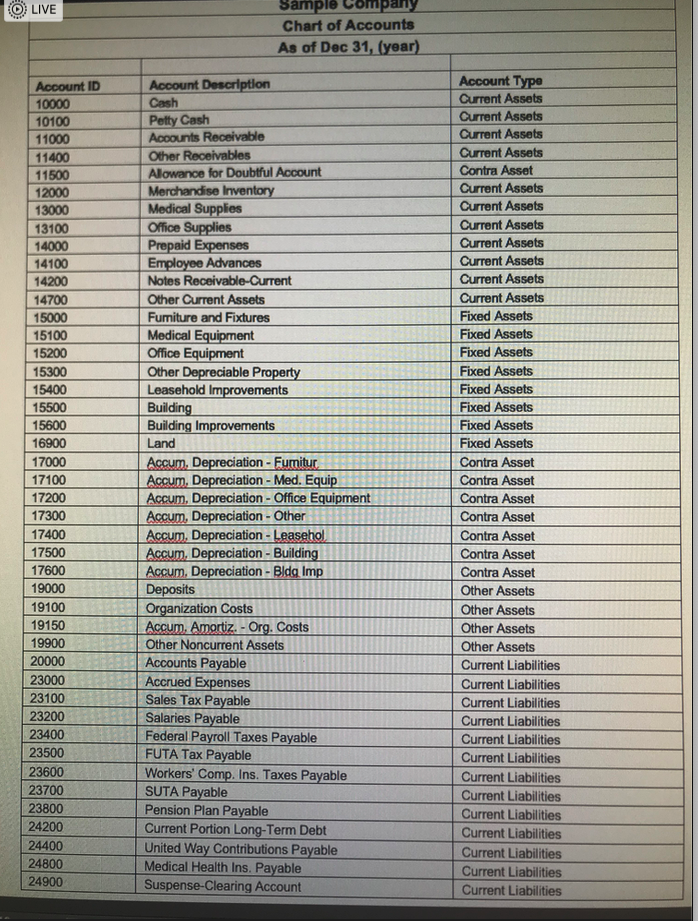
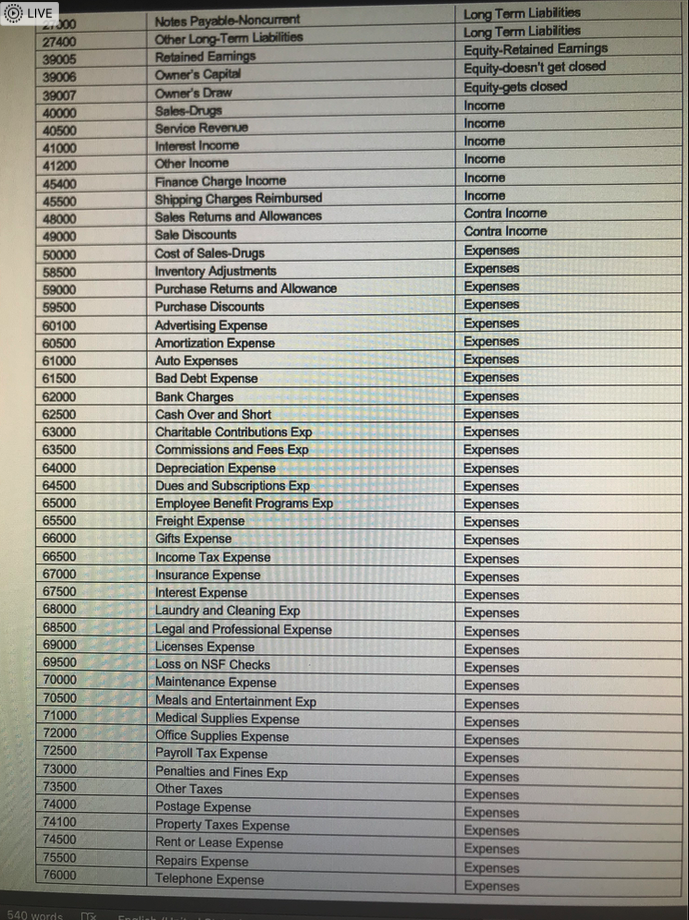
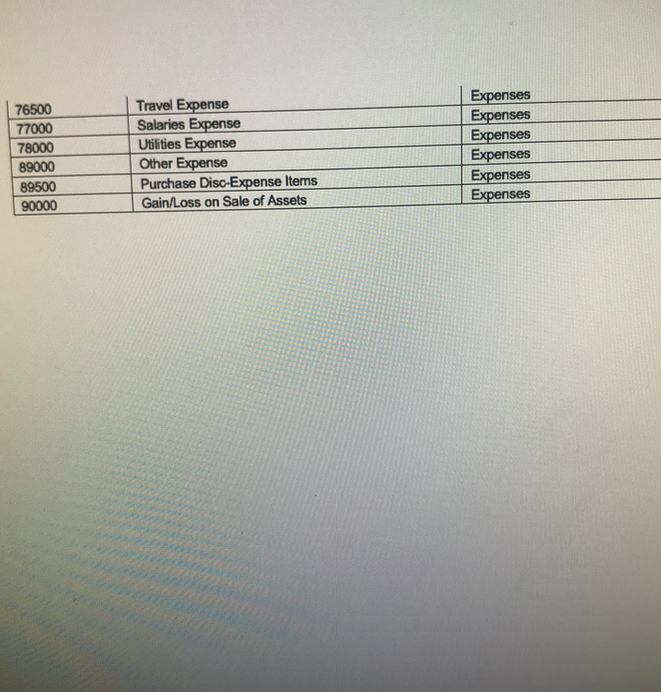
- For Problem #1, you willbe asked to enter an amount or an account number. You will enter your answers for this problem in questions 1-43.Using the Chart of Accounts attached for a Sample Company, identify the (5-digits) GL Account Number for the corresponding debits and credits for your response to this question. Please be sure to use the correct GL Account No. The computer will recognize just the account number. For questions when an amount is involved, just enter the number. Do not put a dollar sign, do not put a comma, do not put cents, and do not put a decimal point. Please observe these guidelines to obtain full credit. No exceptions.Please use Perpetual Inventory method. July 1 Your Name Drug Store purchased medical supplies intended for sale for $1,000.00 from Vendor X. Terms of sale: 2/10, n/30, FOB Destination. The freight charges = $50.00. The journal entry is a debit to ___________ (GL Account No.).
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. July 1 Your Name Drug Store purchased medical supplies intended for sale for $1,000.00 from Vendor X. Terms of sale: 2/10, n/30, FOB Destination. The freight charges = $50.00. The journal entry is a credit to ___________ (GL Account No.).
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. July 1 Your Name Drug Store purchased medical supplies intended for sale for $1,000.00 from Vendor X. Terms of sale: 2/10, n/30, FOB Destination. The freight charges = $50.00. The debit amount is ___________ (amount).
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. July 3 Your Name Drug Store purchased medical equipment for sale for $3,000.00 from Vendor Y. Terms of sale: 1/10, n/30 FOB Shipping Point. The freight charges = $150.00. The entry is a debit to _____________ (GL Account No.)
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. July 3 Your Name Drug Store purchased medical equipment for sale for $3,000.00 from Vendor Y. Terms of sale: 1/10, n/30 FOB Shipping Point. The freight charges = $150.00. The entry is a credit to _____________ (GL Account No.)
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. July 3 Your Name Drug Store purchased medical equipment for sale for $3,000.00 from Vendor Y. Terms of sale: 1/10, n/30 FOB Shipping Point. The freight charges = $150.00. The debit amount is _____________ .
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. July 4 Your Name Drug Store returned $200.00 worth of merchandise purchased from Vendor Y. The debit is to ____________ (GL Account No.)
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. July 4 Your Name Drug Store returned $200.00 worth of merchandise purchased from Vendor Y. The credit is to ____________ (GL Account No.)
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. July 4 Your Name Drug Store returned $200.00 worth of merchandise purchased from Vendor Y. The debit amount is ____________ .
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. July 5 Your Name Drug Store purchased medical supplies for use for $2,000.00 from Vendor Z. Terms of sale, 2/15, n/20, FOB Destination. Freight Charges = $100.00. The debit is to _____________ (GL Account No.)
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. July 5 Your Name Drug Store purchased medical supplies for use for $2,000.00 from Vendor Z. Terms of sale, 2/15, n/20, FOB Destination. Freight Charges = $100.00. The credit is to _____________ (GL Account No.)
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. July 5 Your Name Drug Store purchased medical supplies for use for $2,000.00 from Vendor Z. Terms of sale, 2/15, n/20, FOB Destination. Freight Charges = $100.00. The debit amount is _____________ .
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. On July 7 Your Name Drug Store sold merchandise to Customer A for $8,000.00. Terms: 2/10, n/30. The cost of the inventory is $3,200.00. The $8,000.00 debit is to _______________ (GL Account No.).
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. On July 7 Your Name Drug Store sold merchandise to Customer A for $8,000.00. Terms: 2/10, n/30. The cost of the inventory is $3,200.00.The $8,000.00 credit is to _______________ (GL Account No.).
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. On July 7 Your Name Drug Store sold merchandise to Customer A for $8,000.00. Terms: 2/10, n/30. The cost of the inventory is $3,200.00. The $3,200.00 debit is to _______________ (GL Account No.).
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. On July 7 Your Name Drug Store sold merchandise to Customer A for $8,000.00. Terms: 2/10, n/30. The cost of the inventory is $3,200.00. The $3,200.00 credit is to _______________ (GL Account No.).
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. On July 9 Your Name Drug Store paid the amount owed to Vendor X on the purchased of July 1. The debit is to ______________ (GL Account No.)
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. July 9 Your Name Drug Store paid the amount owed to Vendor X on the purchased of July 1. The debit amount is ______________ .
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. July 9 Your Name Drug Store paid the amount owed to Vendor X on the purchased of July 1. The amount of Cash paid is _____________ (amount).
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. On July 12 Your Name Drug Store sold merchandise to Customer B for $6,000.00 Terms: 1/10, n/30. The cost of the inventory is $2,400.00. The $6,000.00 debit is to ____________ (GL Account No.).
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. On July 12 Your Name Drug Store sold merchandise to Customer B for $6,000.00 Terms: 1/10, n/30. The cost of the inventory is $2,400.00. The $6,000.00 credit is to ____________ (GL Account No.).
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. On July 12 Your Name Drug Store sold merchandise to Customer B for $6,000.00 Terms: 1/10, n/30. The cost of the inventory is $2,400.00. The $2,400.00 debit is to ____________ (GL Account No.).
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. On July 12 Your Name Drug Store sold merchandise to Customer B for $6,000.00 Terms: 1/10, n/30. The cost of the inventory is $2,400.00. The $2,400.00 credit is to ____________ (GL Account No.).
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. On July 13 Your Name Drug Store paid the amount owed to Vendor Y on the purchased of July 3. The debit is to ____________ (GL Account No.).
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. July 13 Your Name Drug Store paid the amount owed to Vendor Y on the purchased of July 3. The debit amount is to ____________ .
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. July 13 Your Name Drug Store paid the amount owed to Vendor Y on the purchased of July 3. The amount of Cash paid is ______________.
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. July 13 Your Name Drug Store paid the amount owed to Vendor Y on the purchased of July 3. The discount is a credit to ______________ (GL Account No.).
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. On July 15 Your Name Drug Store collected cash from Customer A from the sale of July 7. The amount of Cash collected is ______________.
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. On July 15 Your Name Drug Store collected cash from Customer A from the sale of July 7. The amount of discount is ______________.
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. On July 15 Your Name Drug Store collected cash from Customer A from the sale of July 7. The credit is to ______________ (GL Account No.).
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. On July 15 Your Name Drug Store collected cash from Customer A from the sale of July 7. The credit amount is ______________.
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. On July 17 Customer B returned $300.00 worth of defective merchandise to Your Name Drug Store. The cost is120.00. The $300.00 debit is to __________ (GL Account No.).
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. On July 17 Customer B returned $300.00 worth of defective merchandise to Your Name Drug Store. The cost is120.00.The $300.00 credit is to __________ (GL Account No.).
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. On July 17 Customer B returned $300.00 worth of defective merchandise to Your Name Drug Store. The cost is120.00.The $120.00 debit is to __________ (GL Account No.).
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. On July 17 Customer B returned $300.00 worth of defective merchandise to Your Name Drug Store. The cost is120.00.The $120.00 credit is to __________ (GL Account No.).
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method.On July 21 Your Name Drug Store paid the amount owed to Vendor Z. The debit is to _________________ (GL Account No.).
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. On July 22 Received cash from Customer B on the sale of July 12. The amount of Cash received is ____________ .
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. On July 22 Received cash from Customer B on the sale of July 12. The credit is to ____________ (GL Account No.).
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. On July 22 Received cash from Customer B on the sale of July 12. The discount amount is ____________
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. On July 22 Received cash from Customer B on the sale of July 12. The credit is to ____________ (GL Account No.).
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. On July 30 Purchased medical supplies for use, $1,000.00 paying cash. Terms: FOB Destination, Freight Charges = 50.00. The debit is to ______________ (GL Account).
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. On July 30 Purchased medical supplies for use, $1,000.00 paying cash. Terms: FOB Destination, Freight Charges = 50.00. The debit amount is ______________
- Please use Perpetual Inventory method. On July 30 Purchased medical supplies for use, $1,000.00 paying cash. Terms: FOB Destination, Freight Charges = 50.00. The credit is to ______________ (GL Account No.).
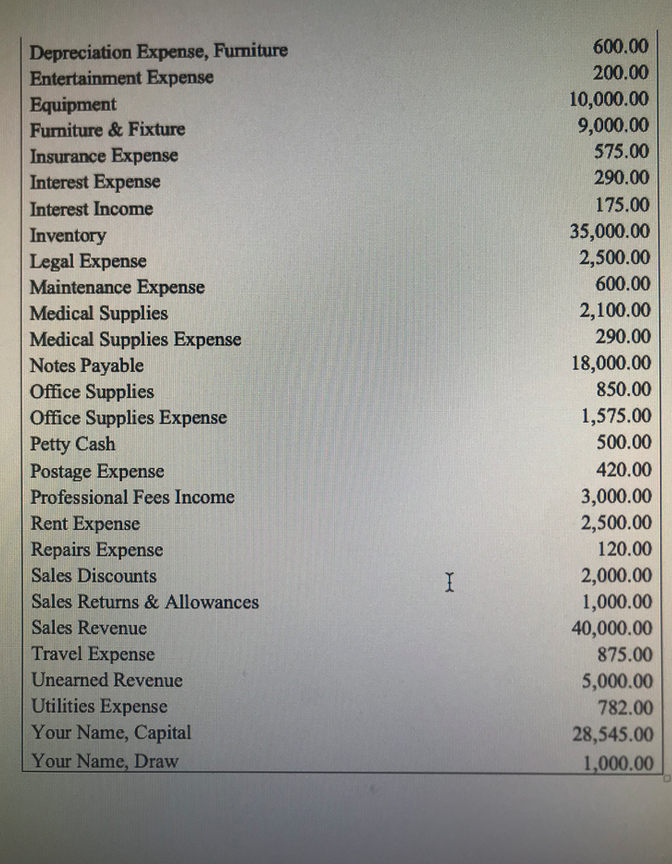
- For Problem #2, you will complete eight requirements concerning the payroll for the manager of Your Name Drugstore. You will then be asked to enter an amount or an account number used to complete these requirements.You will enter your answers for this problem in questions 44-63. For questions where an account number is required, usethe Chart of Accounts attached for a Sample Company to identify the (5-digit) GL account number for the corresponding debits and credits for your response to this question. Please be sure to use the correct GL account number. The computer will recognize just the account number. For questions wherean amount is involved, just enter the number. Do not put a dollar sign, do not put a comma, do not put cents, and do not put a decimal point. Please observe these guidelines to obtain full credit. No exceptions. For example, if your answer is one thousand dollars, you should write it as1000. If your answer is one hundred twenty dollars and fifty cents, you should write it as 120.50. The rules of rounding up and dropping off must be observed to the exact penny to obtain the correct response. Req. #1: The total Gross Pay is ___________________ (amount).
- Req. #2: The total amount of voluntary deductions is ___________________ (amount).
- Req. #2: The total amount of mandatory deductions is ___________________ (amount).
- Req. #2: The total amount of deductions is ___________________ (amount).
- Req. #3: The Net Pay is ___________________ (amount).
- Req. # 4: The total amount of FICA contribution of the employer is ___________________ (amount).
- Req. #4: The total amount of Medicare contribution of the employer is ___________________ (amount).
- Req. #4: The total amount of FUTA contribution is ___________________ (amount). (Use the new FUTA rate.)
- Req. #4: The total amount of SUTA contribution is ___________________ (amount).
- Req. #4: The total amount of workers' compensation contribution is ___________________ (amount).
- Req. #4: The total amount of mandatory contributions of the employer is ___________________ (amount).
- Req. #5: The total amount of company's voluntary contribution is ___________________ (amount).
- Req. #6: The debit is to ___________________ (GL account).
- Req. #6: The debit amount is ___________________ (amount).
- Req. #6: The net amount or take-home pay is a credit to ___________________ (GL account).
- Using the Chart of Accounts attached for a Sample Company, identify the (5-digit) GL account number for the corresponding debits and credits for your response to this question. Please be sure to use the correct GL account number. The computer will recognize just the account number. Please observe these guidelines to obtain full credit. No exceptions. Req. #7: The debit is to ___________________ (GL account).
- Req. #7: The debit amount is ___________________ (amount).
- Req. #8: The debit is to ___________________ (GL account).
- Req. #8: The $100.00 credit is to ___________________ (GL account).
- Req. #8: The $400.00 credit is to ___________________ (GL account).
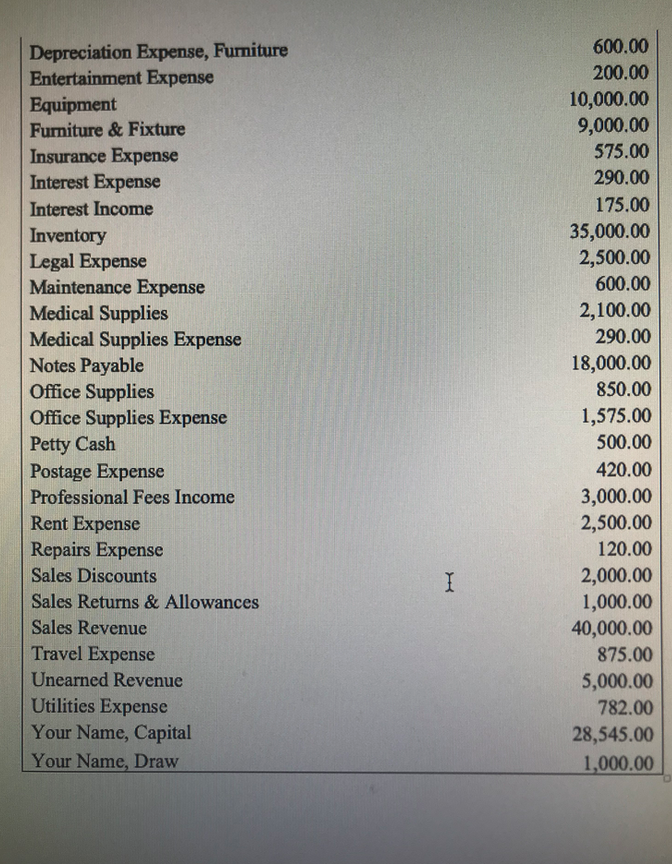
- For Problem #3, you will prepare the behind-the-scenes closing entries for Your Name Drugstore for the year ended December 31. You will then be asked to enter an amountor answer questions concerning your closing entries. You will enter your answers for this problem in questions 64-67. For questions wherean amount is involved, just enter the number. Do not put a dollar sign, do not put a comma, do not put cents, and do not put a decimal point. Please observe these guidelines to obtain full credit. No exceptions. Complete the behind-the-scenesclosing entry to close all the Revenue accounts. This entry includesa credit to Retained Earnings for the amount of ___________________ .
- Complete the behind-the-scenesclosing entry to close all the Expense accounts. This entry includesa debit to Retained Earnings for the amount of ___________________ .
- To close the Owner's Drawing account, the entry is whichof the following?
a. a debit to the Owner's Drawing account
b. a credit to the Owner's Capital account
c. a debit to the Miscellaneous Expense account
d. a credit to the Owner's Drawing account
e. a debit to the Cash account
67.In manual accounting, the Income Summary Account is closed to ________.
- a. Cash
- b. Owner's Capital
- c. Owner's Draw
- d. Revenue
- e. Expenses


Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


