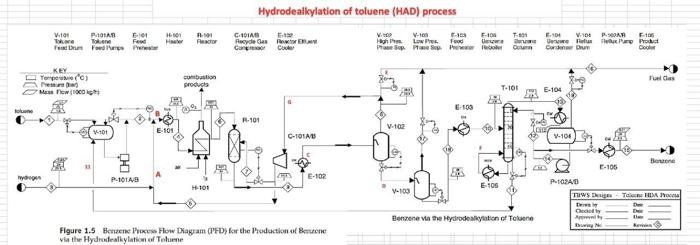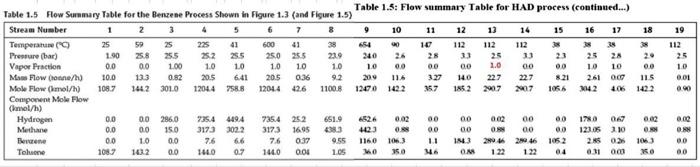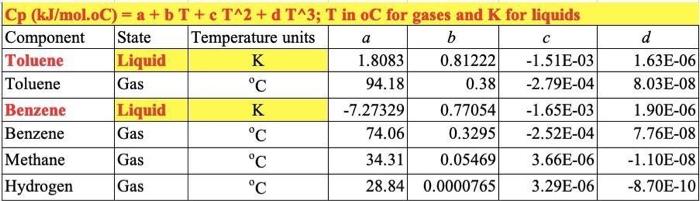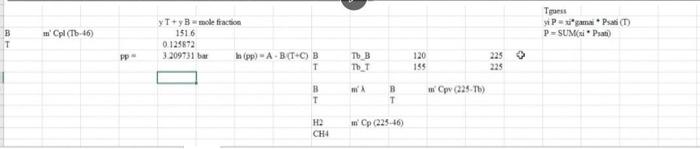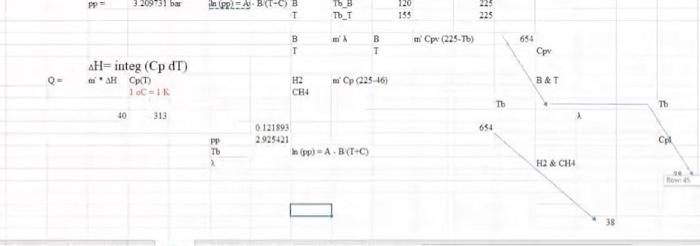
For the HDA Process 1. Calculate the amount of heat required in E-101 to preheat the feed stream mixture (Stream B) from your previously calculated temperature (say, -46C) to 225C. Here you need to determine the boiling point temperatures of the individual vaporizing components (i.e. toluene and benzene), their corrected latent heats of vaporization (AHV) while being heated in E-101. Remember that the heat load consists of 8 individual terms (3 for benzene, 3 for toluene, 1 for H2 and 1 for CH4). You need to list all eight Q's calculated. 2. Find the heat load of the fired heater (H-101) to preheat feed Stream 4 from 225C to 600C (Stream 6). 3. Find the bubble point temperature of the feed entering the distillation column (i.e. Stream 10). 4. Find the bubble point temperature at the bottom of the distillation column (i.e. Stream 11). 5. Find the dew point temperature at the top stream of the distillation column (i.e. Stream 13). Hydrodealkylation of toluene (HAD) process POLAR F-1 W.101 Tore Feed H CDIAS Facydie Ges R Cang Cool V. F-100 High Lowes Sopa Sherler Com E11 W-101 PR F-106 us P This Corden Cooler wed KEY Terperc) Per Me Mewto bution produto Faldas T101 E-104 ESH 103 F-101 V-102 E-101 -TOU V-101 CIE H0 (10 Bone E-106 Ty PINS E-102 H-101 E 105 V-100 E P1020 THIS ET TA accia De Ced A thiye Benzene Via The Hydrodelkylation of Toluen Figure 1.5 Benzene Process Flow Diagram (PFD) for the Production of Bewene via the Hydrodealkylation of Telome 19 112 85 Table 1.5 Flow Summary Table for the Benzene Process Shown in Figure 1.3 (and Figure 1.5) Table 1.5: Flow summary Table for HAD process (continued...) Stream Number 2 3 4 5 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Temperatur 25 59 25 275 4 600 41 654 10 Pressure (bar) 112 112 1.90 25.8 255 252 25.0 255 23.9 240 25 Vapor Praction 0.0 0.0 100 13 23 25 1.0 10 20 20 1.0 10 10 10 0.0 0.0 00 1.0 00 00 10 Mas Flow on/h) 10.0 10 00 133 0.82 2015 6.41 20.5 0.36 92 200 116 327 140 227 227 8.21 115 Mole Flow (mol/h) 108.7 261 OCO 1442 3010 12044 758.8 12014 1100.8 1200 1422 357 Component Mole Flow 1852 2007 2007 1066 3042 4.061422 nel/h) Hydrogen 0.0 0.0 286,0 235.4 4494 735.4 252 651.0 0.02 00 00 002 00 Methane 0.0 1710 067 15.0 0.02 00 3173 3022 3173 16.95 33 4123 0.98 00 00 O. 00 Elevene 0.0 O. 10 0.0 123.05 110 7.6 6.6 76 0:37 1160 1063 11 Telne 1087 1843 28046 29 46 1052 2.85 02106 143.2 00 1440 0.7 1440 001 1.05 MO 350 OM 0.31 000 KO 112 25 10 0.01 00 0.00 08 00 00 955 ::: a Cp (kJ/mol.oC) = a + b T+e T^2 + d T^3; T in oC for gases and K for liquids Component State Temperature units b Toluene Liquid K 1.8083 0.81222 -1.51E-03 Toluene Gas C 94.18 0.38 -2.79E-04 Benzene Liquid K -7.27329 0.77054 -1.65E-03 Benzene Gas C 74.06 0.3295 -2.52E-04 Methane Gas c 34.31 0.05469 3.66E-06 Hydrogen Gas C 28.84 0.0000765 3.29E-06 d 1.63E-06 8.03E-08 1.90E-06 7.76E-08 -1.10E-08 -8.70E-10 Tguess " *Pani (T p-stMKni Pati) " , 46) YT+B mole fraction 1516 0.125872 3209731 bar hipp) A BTC) T 120 155 225 225 WA T T pw (24) . CH4 (22446) 320 bar PP2 -) T T_T 120 195 . B T B T m' py (224) 694 H= integ (Cp dT) 1 H2 CH 24 16) BAT 10 313 654 0.121893 2925421 hipp) A - -) H2 & CH4 No 4 38