-
For this question, consider the impact of variability on the system performance. Assume that the coefficient of variation of the arrival and service processes for each resource pool is 1. You may also assume that the Deal Completion step is immediately initiated by the senior professionals after completing the Negotiation step, i.e., no queueing for Deal Completion.
Hint: Output from a process stage creates the input for the next stage.
1-The aim of the firm is to ensure that the average time that a deal takes to be completed (from end to end) is no more than 27 weeks.
Provide two staffing scenarios that achieve this target.
Qualitatively discuss the pros and cons of your two recommended scenarios.
2-Under each of your two scenarios in part (a), how many deals on average are in process in the system at any given time?
3-The average cost (base salary, bonus, and other perks) of a junior, mid-level, and senior professional is $2500/week, $5000/week, and $15000/week respectively. The average expected value (in NPV terms) from a completed deal is $4M. Due to time value of money and goodwill-related costs, for each week that a deal is in process it is estimated that 1% of its value for the firm is lost. Given these numbers, what is your optimal staffing recommendation to maximize the firms yearly profit?
4-The firm decides to split junior professionals into two groups: each group handles deals generated from different industry sectors (45 per year each). What is the optimal staffing level now?
5-If the policy of splitting junior professionals between sectors leads to a higher yield (due to better initial sourcing of deals because of deeper industry knowledge, or higher customer satisfaction provided by specialist junior professionals) after the preliminary evaluation stage, what is the minimum yield needed to off-set the operational disadvantage of this strategy? Suggest some other advantages of specialization that could attenuate the operational losses due to the lack of pooling economies.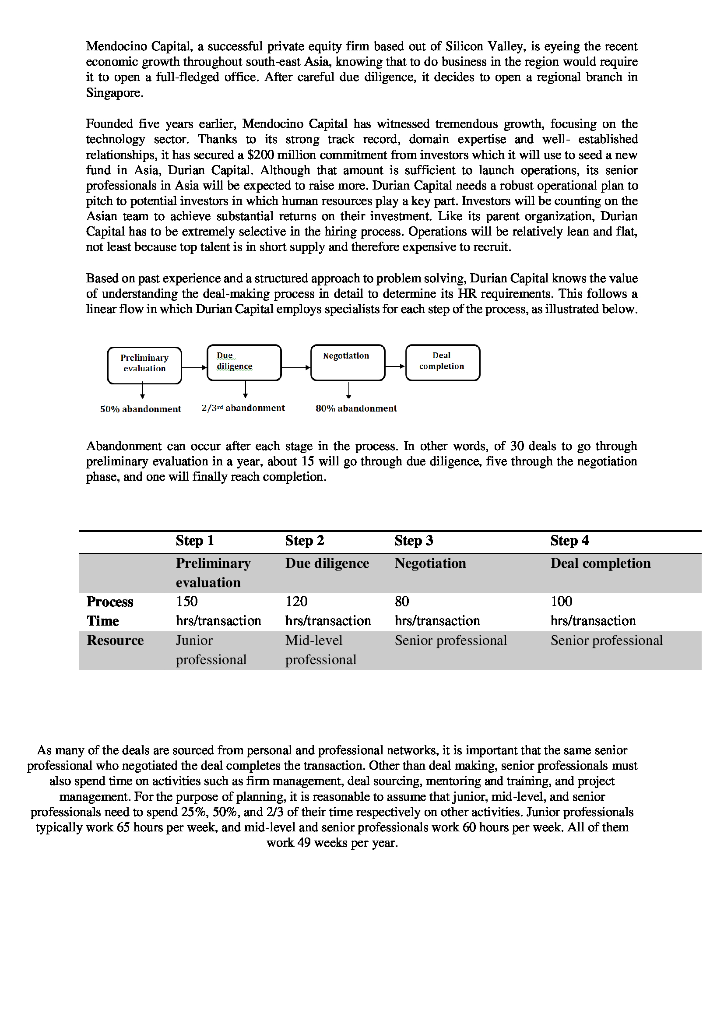
Mendocino Capital, a successful private equity firm based out of Silicon Valley, is eyeing the recent. economic growth throughout south-east Asia, knowing that to do business in the region would require it to open a full-fledged office. After careful due diligence, it decides to open a regional branch in Singapore Founded five ycars carlier, Mendocino Capital has witnessed tremendous growth, focusing on the technology sector. Thanks to its strong track record, domain expertise and well- established relationships, it has secured a $200 million commitment from investors which it will use to seed a new fund in Asia, Durian Capital. Although that amount is sufficient to launch operations, its senior professionals in Asia will be expected to raise more. Durian Capital needs a robust operational plan to pitch to potential investors in which human resources play a kcy part. Investors will be counting on the Asian team to achieve substantial returns on their investment. Like its parent organization, Durian Capital has to be extremely selective in the hiring process. Operations will be relatively lean and flat, not least because top talent is in short supply and therefore expensive to reeruit. Based on past experience and a structured approach to problem solving, Durian Capital knows the value of understanding the deal-making process in detail to determine its HR requirements. This follows a linear flow in which Durian Capital employs specialists for each step of the process, as illustrated below Due Negotlatlon Deal Preliuiuary diligence completion evalualicn 2/3rd abandonment 80% abandonment 50% abandonment Abandonment can occur after each stage in the process. In other words, of 30 deals to go through preliminary evaluation in a year, about 15 will go through due diligence, five through the negotiation phase, and one will finally reach completion. Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 Preliminary Due diligence Negotiation Deal completion evaluation Process 150 80 100 hrs/transaction hrs/transaction hrs/transaction hrs/transaction Resource Junior Mid-level Senior professional Senior professional professional professional As many of the deals are sourced from personal and professional networks, it is important that the same senior professional who negotiated the deal completes the transaction. Other than deal making, senior professionals must also spend time on activities such as firm management, deal sourcing, mentoring and training, and project management. For the purpose of planning, it is reasonable to assume that junior, mid-level, and senior professionals need to spend 25%, 50%, and 2/3 of their time respectively on other activities. Junior professionals typically work 65 hours per week, and mid-level and senior professionals work 60 hours per week. All of them work 49 weeks per year Mendocino Capital, a successful private equity firm based out of Silicon Valley, is eyeing the recent. economic growth throughout south-east Asia, knowing that to do business in the region would require it to open a full-fledged office. After careful due diligence, it decides to open a regional branch in Singapore Founded five ycars carlier, Mendocino Capital has witnessed tremendous growth, focusing on the technology sector. Thanks to its strong track record, domain expertise and well- established relationships, it has secured a $200 million commitment from investors which it will use to seed a new fund in Asia, Durian Capital. Although that amount is sufficient to launch operations, its senior professionals in Asia will be expected to raise more. Durian Capital needs a robust operational plan to pitch to potential investors in which human resources play a kcy part. Investors will be counting on the Asian team to achieve substantial returns on their investment. Like its parent organization, Durian Capital has to be extremely selective in the hiring process. Operations will be relatively lean and flat, not least because top talent is in short supply and therefore expensive to reeruit. Based on past experience and a structured approach to problem solving, Durian Capital knows the value of understanding the deal-making process in detail to determine its HR requirements. This follows a linear flow in which Durian Capital employs specialists for each step of the process, as illustrated below Due Negotlatlon Deal Preliuiuary diligence completion evalualicn 2/3rd abandonment 80% abandonment 50% abandonment Abandonment can occur after each stage in the process. In other words, of 30 deals to go through preliminary evaluation in a year, about 15 will go through due diligence, five through the negotiation phase, and one will finally reach completion. Step 1 Step 2 Step 3 Step 4 Preliminary Due diligence Negotiation Deal completion evaluation Process 150 80 100 hrs/transaction hrs/transaction hrs/transaction hrs/transaction Resource Junior Mid-level Senior professional Senior professional professional professional As many of the deals are sourced from personal and professional networks, it is important that the same senior professional who negotiated the deal completes the transaction. Other than deal making, senior professionals must also spend time on activities such as firm management, deal sourcing, mentoring and training, and project management. For the purpose of planning, it is reasonable to assume that junior, mid-level, and senior professionals need to spend 25%, 50%, and 2/3 of their time respectively on other activities. Junior professionals typically work 65 hours per week, and mid-level and senior professionals work 60 hours per week. All of them work 49 weeks per year







