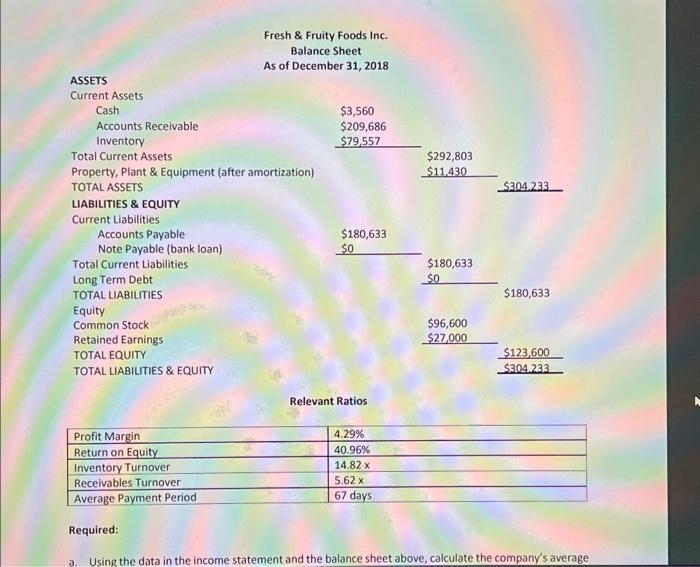
Fresh \& Fruity Foods is a mail-order company operating out of a winery near Summerland, British Columbia. The company specializes in sending British Columbian specialties to catalogue customers nationwide. Sales are seasonal, with most occurring in November and December-when people select Fresh \& Fruity's Famous Fruit Fantasy boxes as Christmas gifts. Although seasonal, the company's sales are predictable, because the bulk of Fresh \& Fruity's customers are regulars who purchase year after year. The company has also managed to smooth out its sales somewhat by offering incentives, such as the Fruit of the Month Club, which encourages customers to buy throughout the year. The nature of the mail-order business is such that most of Fresh \& Fruity's sales are on credit; therefore, the company has historically had a high accounts receivable balance relative to sales. It has also historically been short of cash; forcing it to delay payments to suppliers as long as possible, (its average time to pay accounts in 2018 was 67 days). In January 2019, Tom Appleby and Alice Plummer, the president and treasurer of Fresh \& Fruity, respectively, were discussing the cash flow problem over lunch. "You know, Tom," Alice said as she sliced a piece of avocado, "I was reading the other day about a company called Kringle's Candles & Ornaments, and it occurred to me that we're a lot like them. Most of our assets are current ones, like their accounts receivable and inventory, and over half of ours are financed just like theirs, by current liabilities-that is, accounts payable." She paused for a sip of chardonnay, and continued, "They got around their cash flow problems by issuing long-term debt, which took the pressure off their current obligations. I have been looking at that for our company, too. But then I got to thinking, there's another way that's a good deal easier and would produce results just as quickly." "Oh? And what's that?" Tom replied, his interest captured. "All we have to do," she said, "is to reduce our accounts receivable balance. That will help reduce our accounts payable balance, since, as our customers begin paying us earlier, we can, in turn, pay our suppliers earlier. If we could get enough customers to pay us right away, we could even pay some of the suppliers in time to take advantage of the 2 percent discount they offer for payments within 10 days." (Fresh \& Fruity's suppliers operated on a 2/10, net 60 basis - meaning they offer 60 days to pay the account, however, if Fresh \& Fruity pays in 10 days they will receive a 2% discount.) "That would increase our net income and free up even more cash to take advantage of even more discounts!" She looked excited at the prospect. increase our net income and free up even more cash to take advantage of even more discounts! "She looked excited at the prospect. "Sounds great, but how do we get people to pay us earlier?" Tom inquired, doubtfully. "Easy," Alice continued. "Up to now we've been giving them incentives to pay later. Remember our 'Buy Now, No Payments for Two Months' program? Well, many of our customers use it, and it has caused our accounts receivable balance to run way up. Therefore, what we have to do now is give them incentives to pay earlier. What I propose is to cancel the buy now/pay later plan, and instead offer a 10 percent discount to everyone who pays with their order." "But won't that cause our revenues to drop?" Tom asked, again still doubtful. "Yes, but the drop will be offset by even more new customers who will come in to take advantage of the discount. I figure the net effect on sales will be just about zero, but our accounts receivable balance could be reduced by 50%1 Now here's a kicker I just thought of. After we've reduced our accounts receivable balance as far as practical, I'd like to look into the possibility of reducing our accounts payable still further by replacing them with a bank loan. The effective rate of interest that we pay by not taking our suppliers' discounts is, after all, pretty high. Therefore, what I'd like to do is take out a loan once a year of a sufficient size that would enable us to take all the discounts our suppliers offer. The interest that we'll pay on the loan is bound to be less than what we pay in discounts lost-so we'll see another gain in earnings on our income statement. In fact, these two initiatives together might have a really significant impact" "You've convinced me," Tom said. "Let's go back to the office and run some figures to see what "You've convinced me," Tom said. "Let's go back to the office and run some figures to see what happens!" Assume that Alice Plummer's first initiative to offer a 10 percent discount was to be implemented, and the company's average collection period would drop to 32 days. Because of Alice's first initiative, Fresh \& Fruity would be able to take advantage of the 2 percent discount on one-third of its purchases. Fresh \& Fruity can obtain an 8 percent loan for one year. Fresh & Fruity Foods Inc. Balance Sheet As of December 31, 2018 ASSETS Relevant Ratios Required: a. Using the data in the income statement and the balance sheet above, calculate the company's average a. Using the data in the income statement and the balance sheet above, calculate the company's average collection period in days. Use a 365-day year when calculating sales per day. b. Calculate the cost, as a percent, that the company is paying for not taking the suppliers' discounts. (The suppliers' terms are 2/10, net 60 - have 60 days to pay but will receive a 2% discount if paid within 10 days; but note from the bottom of the balance sheet that Fresh \& Fruity has been taking 67 days to pay its suppliers). c. Assume Alice Plummer's first initiative to offer a 10 percent discount was implemented, and the company's average collection period dropped to 32 days. If net sales per day remained the same, as Alice expects, what would be the new accounts receivable balance? How much cash was freed up by the reduction in accounts receivable? What is the new accounts payable balance if the money is used to pay off suppliers? d. Alice's second initiative calls for Fresh \& Fruity to obtain a bank loan of a sufficient size to enable the company to take all suppliers' discounts. What is the minimum size of this loan? Hint: To take all suppliers' discounts, the average payment period must be 10 days, and net purchases will be Purchases - (Purchases from Figure 1.02 ). Assume all this happens, and solve the following formula for the new accounts payable balance, using: Accounts payable = Average payment period Purchase per day e. Assume Fresh \& Fruity obtains an 8 percent loan for one year in the amount you solved in part e, and it reduces its accounts payable balance accordingly. Now the company is taking 2 percent discounts on all purchases and paying 8 percent a year on the loan balance. What is the net gain from taking the discounts and paying the interest on a before-tax basis