Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
function hOut = evolveWave(hIn,g,H,L,t) % hIn vector of measurements at t=0 % g gravitational acceleration % H water depth % t time at which the
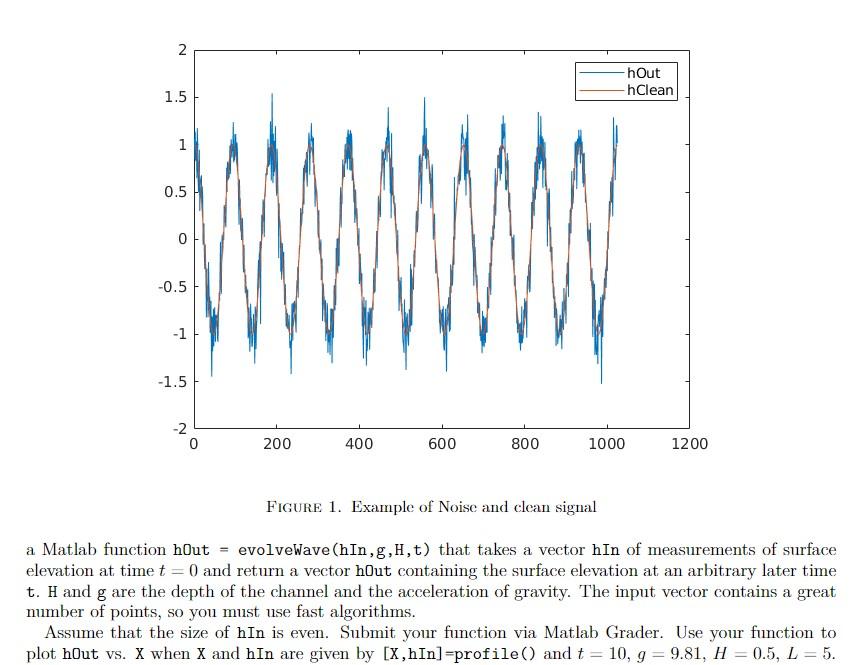
function hOut = evolveWave(hIn,g,H,L,t)
% hIn vector of measurements at t=0
% g gravitational acceleration
% H water depth
% t time at which the surface is evaluated.
end
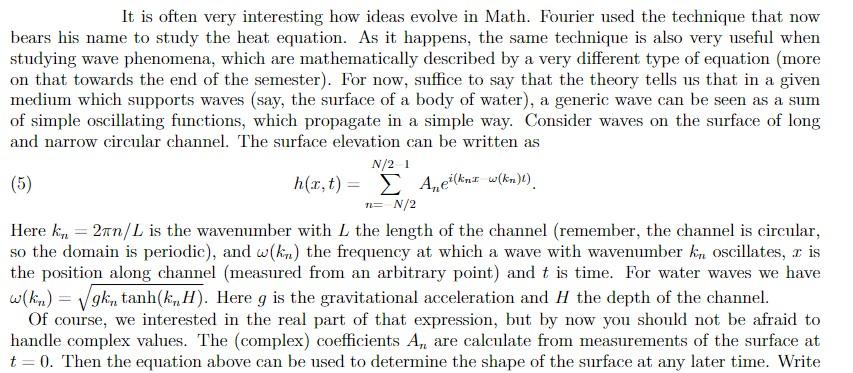
It is often very interesting how ideas evolve in Math. Fourier used the technique that now bears his name to study the heat equation. As it happens, the same technique is also very useful when studying wave phenomena, which are mathematically described by a very different type of equation (more on that towards the end of the semester). For now, suffice to say that the theory tells us that in a given medium which supports waves (say, the surface of a body of water), a generic wave can be seen as a sum of simple oscillating functions, which propagate in a simple way. Consider waves on the surface of long and narrow circular channel. The surface elevation can be written as h(x,t)=n=N/2N/21Anei(knx(kn)t). Here kn=2n/L is the wavenumber with L the length of the channel (remember, the channel is circular, so the domain is periodic), and (kn) the frequency at which a wave with wavenumber kn oscillates, x is the position along channel (measured from an arbitrary point) and t is time. For water waves we have (kn)=gkntanh(knH). Here g is the gravitational acceleration and H the depth of the channel. Of course, we interested in the real part of that expression, but by now you should not be afraid to handle complex values. The (complex) coefficients An are calculate from measurements of the surface at t=0. Then the equation above can be used to determine the shape of the surface at any later time. Write Figure 1. Example of Noise and clean signal a Matlab function hOut = evolveWave (hIn,g,H,t) that takes a vector hIn of measurements of surface elevation at time t=0 and return a vector h0ut containing the surface elevation at an arbitrary later time t. H and g are the depth of the channel and the acceleration of gravity. The input vector contains a great number of points, so you must use fast algorithms. Assume that the size of hIn is even. Submit your function via Matlab Grader. Use your function to plot hOut vs. X when X and h In are given by [X,hIn]= profile () and t=10,g=9.81,H=0.5,L=5Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


