Question
Giant acquired all of Smalls common stock on January 1, 2014, in exchange for cash of $770,000. On that day, Small reported common stock of
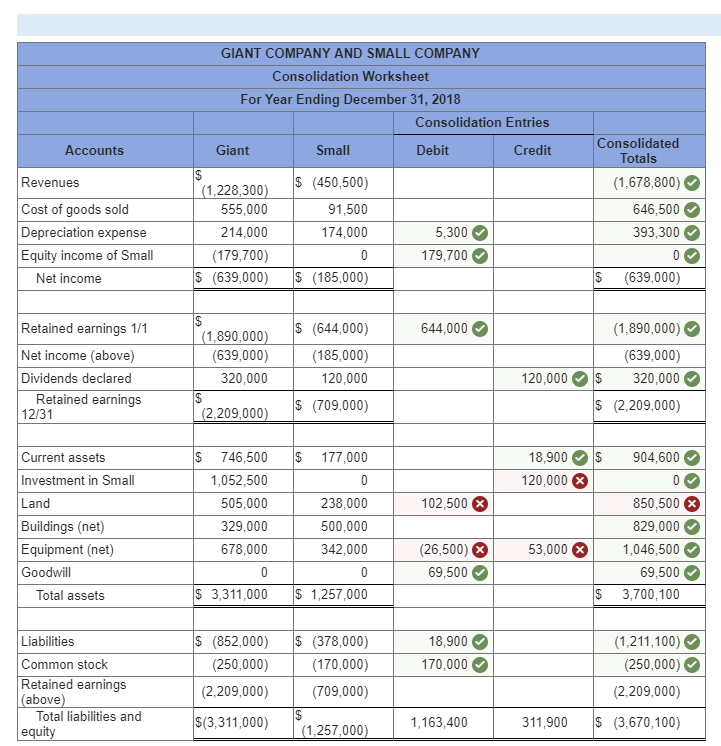
Giant acquired all of Smalls common stock on January 1, 2014, in exchange for cash of $770,000. On that day, Small reported common stock of $170,000 and retained earnings of $400,000. At the acquisition date, $77,500 of the fair-value price was attributed to undervalued land while $53,000 was assigned to undervalued equipment having a 10-year remaining life. The $69,500 unallocated portion of the acquisition-date excess fair value over book value was viewed as goodwill. Over the next few years, Giant applied the equity method to the recording of this investment.
Following are individual financial statements for the year ending December 31, 2018. On that date, Small owes Giant $18,900. Small declared and paid dividends in the same period. Credits are indicated by parentheses.
| Giant | Small | |||||||||
| Revenues | $ | (1,228,300 | ) | $ | (450,500 | ) | ||||
| Cost of goods sold | 555,000 | 91,500 | ||||||||
| Depreciation expense | 214,000 | 174,000 | ||||||||
| Equity in income of Small | (179,700 | ) | 0 | |||||||
| Net income | $ | (639,000 | ) | $ | (185,000 | ) | ||||
| Retained earnings, 1/1/18 | $ | (1,890,000 | ) | $ | (644,000 | ) | ||||
| Net income (above) | (639,000 | ) | (185,000 | ) | ||||||
| Dividends declared | 320,000 | 120,000 | ||||||||
| Retained earnings, 12/31/18 | $ | (2,209,000 | ) | $ | (709,000 | ) | ||||
| Current assets | $ | 746,500 | $ | 177,000 | ||||||
| Investment in Small | 1,052,500 | 0 | ||||||||
| Land | 505,000 | 238,000 | ||||||||
| Buildings (net) | 329,000 | 500,000 | ||||||||
| Equipment (net) | 678,000 | 342,000 | ||||||||
| Goodwill | 0 | 0 | ||||||||
| Total assets | $ | 3,311,000 | $ | 1,257,000 | ||||||
| Liabilities | $ | (852,000 | ) | $ | (378,000 | ) | ||||
| Common stock | (250,000 | ) | (170,000 | ) | ||||||
| Retained earnings(above) | (2,209,000 | ) | (709,000 | ) | ||||||
| Total liabilities and equities | $ | (3,311,000 | ) | $ | (1,257,000 | ) | ||||
- Prepare a consolidation worksheet for Giant and Small for the year ending December 31, 2018
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


