Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
DETERMINE THE CURRENTS FOR THE CIRCUIT BELOW using Mesh Analysis. Hilt VS1 10V R1 ww 4700 R2 2200 R3 8200 VS2 5V Solve the
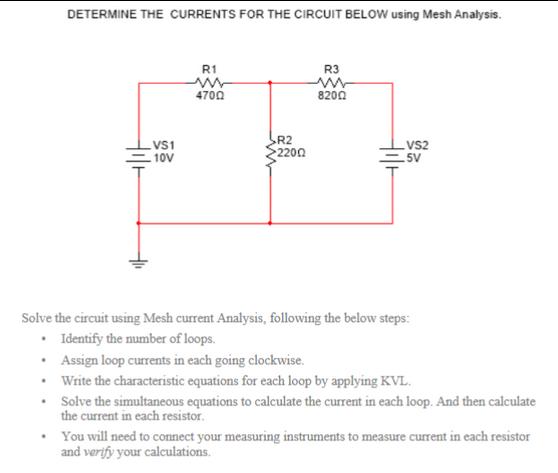
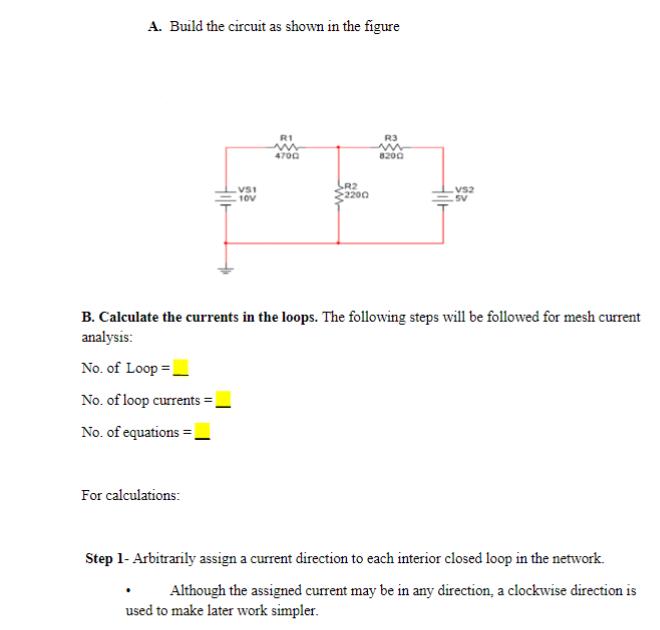

DETERMINE THE CURRENTS FOR THE CIRCUIT BELOW using Mesh Analysis. Hilt VS1 10V R1 ww 4700 R2 2200 R3 8200 VS2 5V Solve the circuit using Mesh current Analysis, following the below steps: Identify the number of loops. Assign loop currents in each going clockwise. Write the characteristic equations for each loop by applying KVL. Solve the simultaneous equations to calculate the current in each loop. And then calculate the current in each resistor. You will need to connect your measuring instruments to measure current in each resistor and verify your calculations. Introduction: Mesh current analysis provides another general procedure for analyzing circuits. using mesh currents as the circuit variables. It is convenient and reduces the number of equations that must be solved simultaneously. Recall that a loop is a closed path with no node passed more than once. A mesh is a loop that does not contain any other loop within it. Loop currents are not actual physical currents. If you're getting a negative value that just means the current is going in the opposite direction. Kirchhoff's voltage law, Ohms law is used in the loop current method. Procedure: A. Build the circuit as shown in the figure 1/3 A. Build the circuit as shown in the figure VS1 -10V For calculations: R1 m 4700 SR2 2200 R3 m VS2 SV B. Calculate the currents in the loops. The following steps will be followed for mesh current analysis: No. of Loop= No. of loop currents = No. of equations = Step 1- Arbitrarily assign a current direction to each interior closed loop in the network. Although the assigned current may be in any direction, a clockwise direction is used to make later work simpler. Step 2 - Using the assigned loop currents, indicate the voltage polarities across all resistors in the circuit. For a resistor which is common to two loops, the polarities of the voltage drop due to each loop current should be indicated on the appropriate side of the component. 2/3 Step 3 - Applying Kirchhoff's voltage law, write the loop equations for each loop in the network (the resistors which are common to two loops will have two voltage drops, one due to each loop). Loop equations Step 3 - Applying Kirchhoff's voltage law, write the loop equations for each loop in the network (the resistors which are common to two loops will have two voltage drops, one due to each loop). Loop equations Step 4 - Solve the resultant simultaneous linear equations. Step 5 - Branch currents are determined by algebraically combining the loop currents which are common to the branch. C. Measure the current: Current through R1 = Current through R3 = Current through R2 = Result and Conclusion:
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Here are the stepbystep calculations using mesh current analysis to solve this circ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


