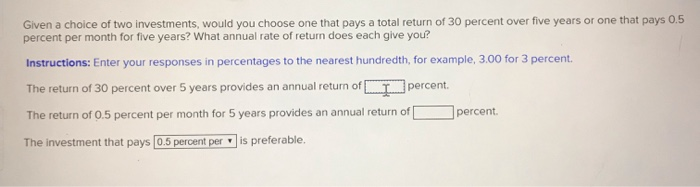
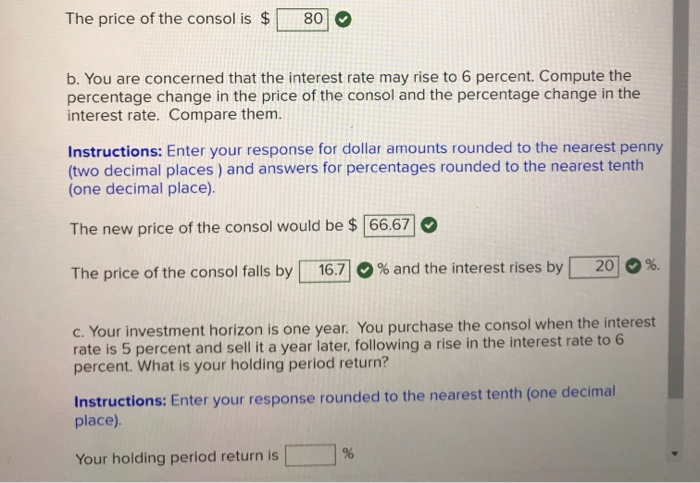
Given a choice of two imvestments, would you choose one that pays a total return of 30 percent over five years or one that pays 0.5 percent per month for five years? What annual rate of return does each give you? Instructions: Enter your responses in percentages to the nearest hundredth, for example, 3.00 for 3 percent. percent The return of 30 percent over 5 years provides an annual return ofT percent eturn of The return of 0.5 percent per month for 5 years provides an annual ret is preferable. The investment that pays 0.5 percent per Assuming that the current interest rate is 3 percent, compute the present value of a five-vear. 5 percent coupon bond with a face value of $1,000. What happens when the interest rate goes to 4 percent? What happens when the interest rate goes to 2 percent? Instructions: Enter your responses rounded to the nearest penny (two decimal places) PV at an interest rate of 3% $ | PV at an interest rate of 4% - $ when the interest rate rises to 4 percent The present value falls PV at an interest rate of 2 % - $ when the interest rate falls to 2 percent The present value rises 80 The price of the consol is $ b. You are concerned that the interest rate may rise to 6 percent. Compute the percentage change in the price of the consol and the percentage change in the interest rate. Compare them. Instructions: Enter your response for dollar amounts rounded to the nearest penny (two decimal places ) and answers for percentages rounded to the nearest tenth (one decimal place). The new price of the consol would be $ 66.67 20 % and the interest rises by 16.7 The price of the consol falls by c. Your investment horizon is one year. You purchase the consol when the interest rate is 5 percent and sell it a year later, following a rise in the interest rate to 6 percent. What is your holding period return? Instructions: Enter your response rounded to the nearest tenth (one decimal place). Your holding period return is What is the yield to maturity on these $100 face value one-year bonds? Instructions: Enter your responses rounded to one decimal place and insert a negative sign () if needed. a. A 6 percent coupon bond selling for $85. Yield to maturity is b. A 7 percent coupon bond selling for $100. Yield to maturity is c. An 8 percent coupon bond selling for $115 Yield to maturity is Of the options above (a-c), which one has the highest yield to maturity and why? has the highest yield to maturity. While Option has the lowest coupon rate, it is selling below Option face value, and so there is a capital gain Suppose you purchase a 3-year, 5-percent coupon bond at par and hold it for two years. During that time, the interest rate falls to 4 percent. Calculate your annual holding period return. Instructions: Enter your response rounded to two decimal places. Holding period return A 10-year zero-coupon bond has a yield of 6 percent. Through a series of unfortunate circumstances, expected inflation rises from 2 percent to 3 percent. The face value of the bond is $100. a. Assuming the nominal yield rises in an amount equal to the rise in expected inflation, compute the change in the price of the bond. Instructions: Enter your responses to the nearest penny (two decimal places). Price (with 2% expected inflation) $ Price (with 3% expected inflation) = $ The price has fallen by $ b. Suppose that expected inflation is still 2 percent, but the probability that it will move to 3 percent has risen. Describe the consequences for the price of the bond. inflation risk. Investors will require compensation for taking There is increased rise fall and the yield will on additional risk, so the price will Approximately how long would it take for an investment of $100 to reach $800 if you earned 5 percent (annual interest)? Instructions: Enter your responses rounded to one decimal place years. What if the interest rate were 10 percent? 20.79 years. How long would it take an investment of $200 to reach $800 at an interest rate of 5 percent? years Why is there a difference between doubling the interest rate and doubling the initial investment? The difference between doubling the interest rate and doubling the initial investment is due to compounding earnings having interest paid on them in subsequent years has a bigger impact than the interest being calculated from a larger initial -the higher interest investment. You are considering buying a new house, and have found that a $100.000, 30-vear fixed-rate mortgage is available with an interest rate of 7 percent. This mortgage requires 360 monthly payments of approximately $651 each. If the interest rate rises to 8 percent. what will happen to your monthly payment? Instructions: Enter your response rounded to the nearest dollar The monthly payment will be $ Instructions: Enter your response rounded to the nearest tenth of a percent (one decimal place). The change in the monthly payment will be percent percent while the change in the interest rate will be Some friends of yours have just had a child. Thinking ahead, and realizing the power of compound interest, they are considering investing for their child's college education, which will begin in 18 years. Assume that the cost of a college education today is $125,000. Also assume there is no inflation and no tax on interest income used to pay college tuition and expenses. Instructions: Enter your responses rounded to the nearest dollar a. If the interest rate is 5 percent, how much money will your friends need to put into their savings account today to have $125,000 in 18 years? They would need to put $ 51940.08 into their savings account today b. If the interest rate were 10 percent? They would need to put $ 22482.35 into their savings account today c. The chance that the price of a college education will be the same 18 years from now as it is today seems remote. Assuming that the price will rise 3 percent per year, and that today's interest rate is 8 percent, what will your friends' investment need to be? The amount of the investment would be $ d. Return to the case with a 5 percent interest rate and no inflation. Assume that your friends don't have enough financial resources to make the entire investment at the beginning. Instead, they think they will be able to split their investment into two equal parts, one invested immediately and the second invested in five years. What is the amount of each part? The required size of the two investments would be $ 29122.59 Most businesses replace their computers every two to three years. Assume that a computer costs $2,000 and that it fully depreciates in 3 years, at which point it has no resale value and is thrown away Instructions: Enter your responses rounded to the nearest dollar a. If the interest rate for financing the equipment is 10 percent, what is the minimum annual cash flow that a computer must generate to be worth the purchase? The minimum annual cash flow must be at least $ b. Suppose the computer did not fully depreciate but still had a $250 value at the time it was replaced. What is the minimum annual cash flow that a computer must generate to be worth the purchase? The minimum annual cash flow must be at least $ Given a choice of two investments, would you choose one that pays a total return of 30 percent over five years or one that pays 0.5 percent per month for five years? What annual rate of return does each give you? Instructions: Enter your responses in percentages to the nearest hundredth, for example, 3.00 for 3 percent The return of 30 percent over 5 years provides an annual return ofT percent. percent. The return of 0.5 percent per month for 5 years provides an annual ret urn of is preferable. The investment that pays 0.5 percent per Assuming that the current interest rate is 3 percent, compute the present value of a five-year, 5 percent coupon bond with a face value of $1,000. What happens when the interest rate goes to 4 percent? What happens when the interest rate goes to 2 percent? Instructions: Enter your responses rounded to the nearest penny (two decimal places) PV at an interest rate of 3 % $ PV at an interest rate of 4% - $ when the interest rate rises to 4 percent The present value falls PV at an interest rate of 2 % - $ when the interest rate falls to 2 percent. The present value rises