Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Given: Probability Density Function (PDF): J0(1-x)- if 0 < x < 1 0 otherwise Sample observations: 0.45, 0.75, 0.55, 0.95, 0.25 a) Maximum Likelihood


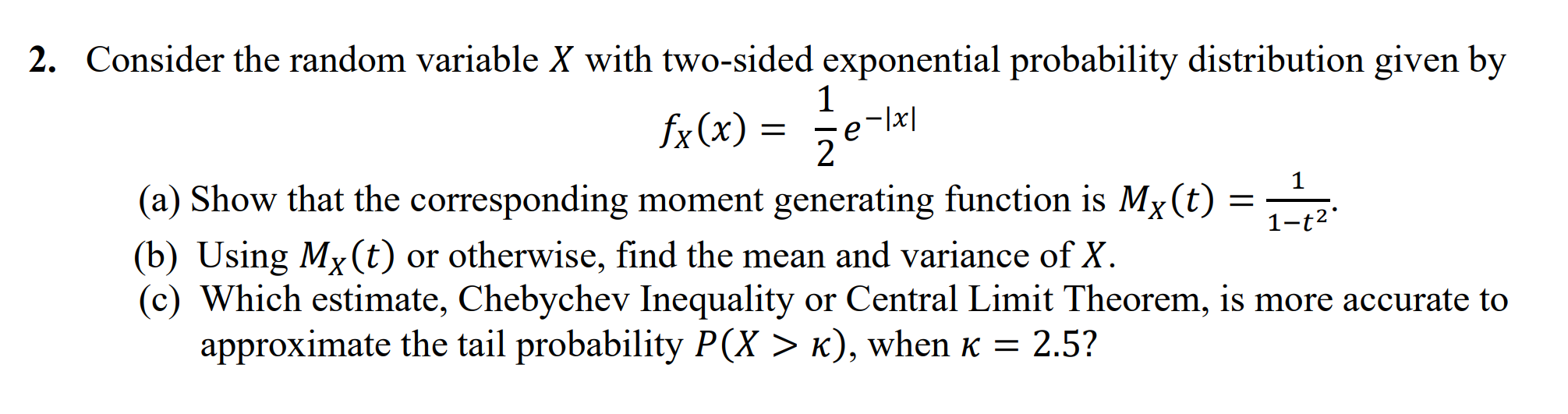
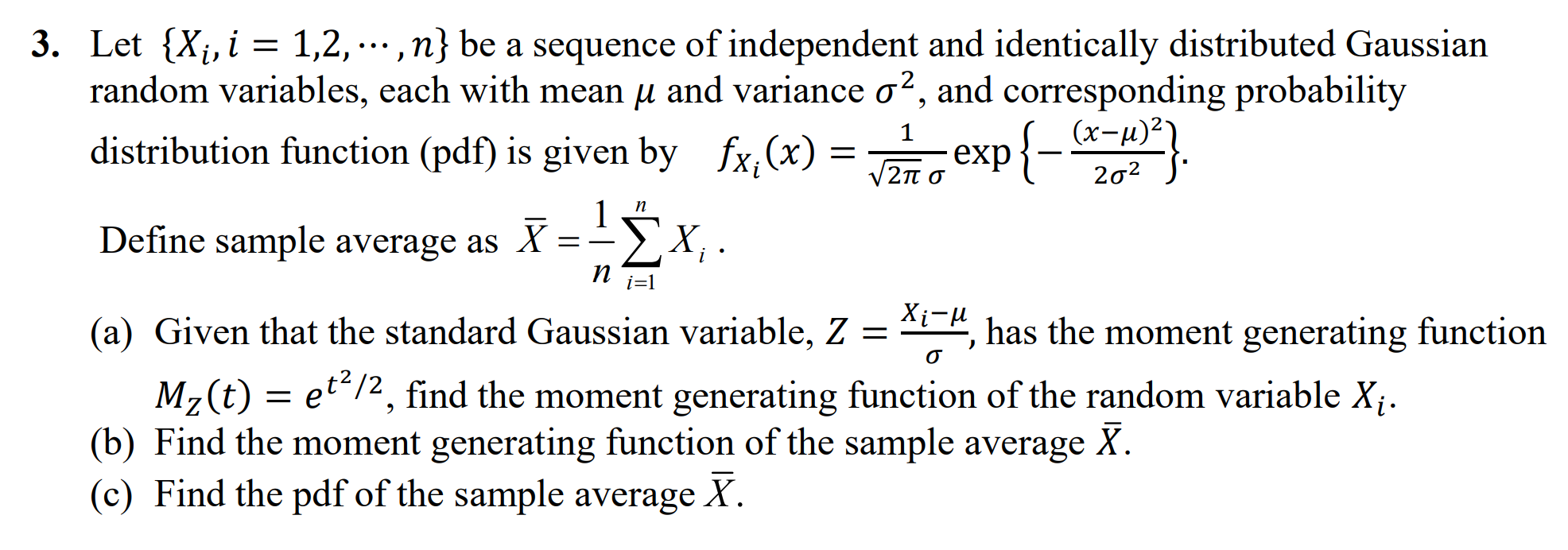



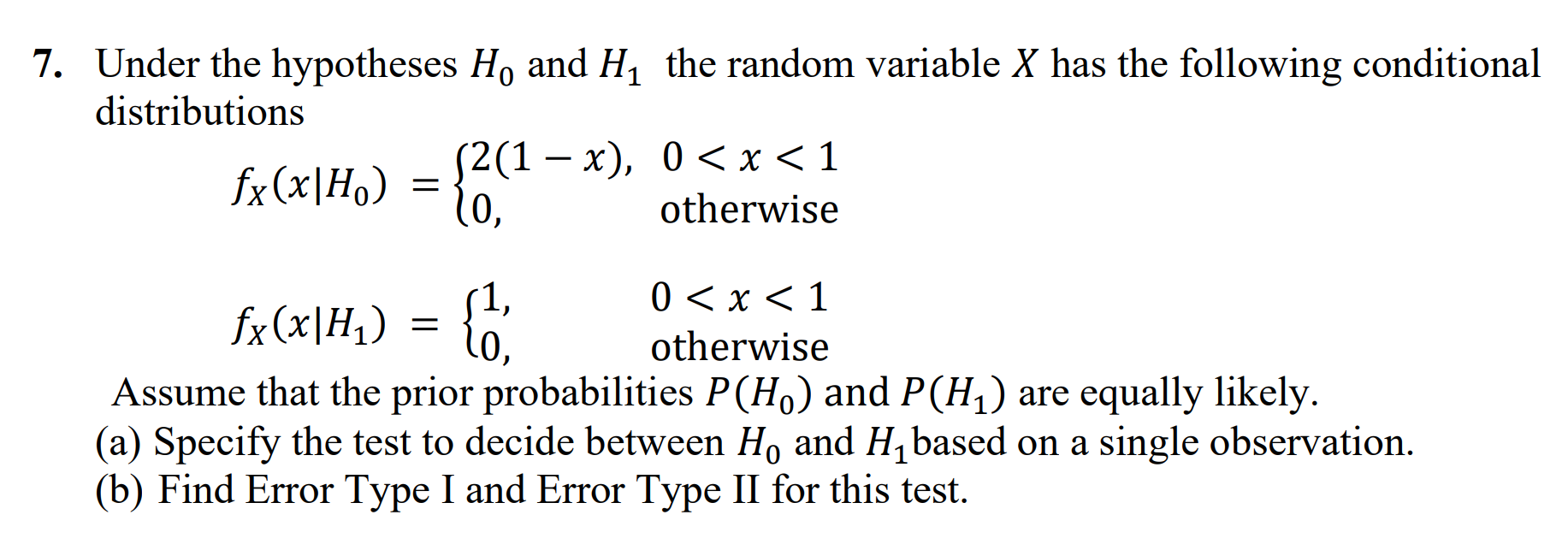
Given: Probability Density Function (PDF): J0(1-x)- if 0 < x < 1 0 otherwise Sample observations: 0.45, 0.75, 0.55, 0.95, 0.25 a) Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE) for 1. Likelihood Function: L(0) = [I10(1 - x;) 0-1 i=1 2. Log-Likelihood Function: l(0) = log L(0) = log (I l(0) = log(0) + _ (1 - x)-1) 1 (0 - 1) log(1 x) l(0) = n log(0) + (0 1) ? log(1 xi) i=1 3. Differentiate and Equate to Zero: dl de = n +) log(1 2x)=0 n log(1-xi 1. A sample of 5 observations (0.45, 0.75, 0.55, 0.95, 0.25) is collected from a continuous distribution with probability density function - fx(x) = {0 (1 (0(1 x) 0-1, - 0 < x < 1 otherwise where > 0 is an unknown parameter. Based on these observations, determine an estimate of using (a) maximum likelihood (b) method of moments 2. Consider the random variable X with two-sided exponential probability distribution given by fx(x) = 1 Ze -|x| (a) Show that the corresponding moment generating function is Mx(t) (b) Using Mx(t) or otherwise, find the mean and variance of X. = 1-t2 (c) Which estimate, Chebychev Inequality or Central Limit Theorem, is more accurate to approximate the tail probability P(X > K), when = 2.5? 3. Let {X, i = 1,2,...,n} be a sequence of independent and identically distributed Gaussian random variables, each with mean and variance , and corresponding probability distribution function (pdf) is given by fx,(x) Define sample average as X = n x; n i=1 1 = 2 -exp { _ (x-1))} 20 S (a) Given that the standard Gaussian variable, Z = Xi-", has the moment generating function Mz(t) = et/2, find the moment generating function of the random variable X. (b) Find the moment generating function of the sample average (c) Find the pdf of the sample average X. X. 4. Let X1, X2, X3,... be a sequence of independent samples of a random variable X with mean and variance . We define a new random sequence Y, Y2, Y3, ' as Y = X = X2 and Yn == - X2n-1 X2n. (a) Find E(Y) and Var(Yn). . . . - (b) If the independent and identically distributed sequence X1, X2, X3, has = 10 and standard deviation = 10, determine how many samples N is needed to guarantee that the sample mean X = 1=1X is between 15 and 20 with probability 0.95. N N n 5. Let X(t) be a zero-mean random process with autocorrelation functions given by Rxx(t1, t2) = 2e5||, where t = |t t|. - - (a) Find the mean and the autocorrelation of the random process Y(t) = ax(t) - bX(t T), where a, b, and T are positive constants. (b) Is Y(t) a wide sense stationary process? (c) Discuss the effect of increasing the constant T on Ryy (0), the power of Y(t). 6. The resistance of a random sample of 10 resistors in the container are measured and found to be 10.2, 9.7, 10.1, 10.3, 10.1, 9.8, 9.9, 10.4, 10.3, and 9.8 km. Assuming that the resistors have a normal distribution with variance = 2. (a) What is the sample mean, median and variance of the resistors? (b) Find the 95% confidence interval for the average resistance of resistors being 10 kN. (c) Does this sample provide significant evidence, at a 5% significance level, that the population mean of the resistors is 10? 7. Under the hypotheses Ho and H the random variable X has the following conditional distributions fx(x\H) = {2(1x), 0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


