Question
Given the implementation of Binary Tree: template class BinNodePtr { private: int it; // The node's value BinNodePtr* lc; // left child pointer BinNodePtr* rc;
Given the implementation of Binary Tree:
template class BinNodePtr {
private:
int it; // The node's value
BinNodePtr* lc; // left child pointer
BinNodePtr* rc; // right child pointer
public:
int& val() { return it; }
BinNodePtr* left() const { return lc;}
BinNodePtr* right() const { return rc;}
};
void traversal(BinNode
if (subroot == NULL) return;
cout val();
traversal(subroot->left());
traversal(subroot->right());
}
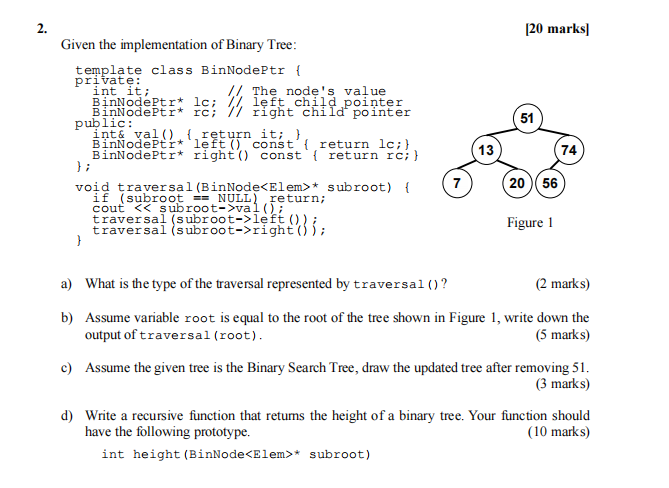
Figure 1
a)
What is the type of the traversal represented by traversal()?
(2 marks)
b)
Assume variable root is equal to the root of the tree shown in Figure 1, write down the
output of traversal(root).
(5 marks)
c)
Assume the given tree is the Binary Search Tree, draw the updated tree after removing 51.
(3 marks)
d)
Write a recursive function that returns the height of a binary tree. Your function should
have the following prototype.
(10 marks)
int height(BinNode
2. 2. [20 marks] 51 Given the implementation of Binary Tree: template class BinNodePtr { private: int it; The node's value BinNode Ptr* lc; left child pointer BinNodePtr* rc; right child pointer public: int& val() { return it; } BinNodeftr* 'left() const { return lc;}. BinNodeftr* right') const { return rc; } }; void traversal (BinNode
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


