Question: Goal of this assignment -Practice using Binary Search Trees -Learn to organize a projects code structure on your own (not just filling in a template)
Goal of this assignment
-Practice using Binary Search Trees
-Learn to organize a projects code structure on your own (not just filling in a template)
-Learn to design classes using good OOP design principles discussed in class
-Learn to refactor an existing solution to improve its design
-Learn to practice defensive coding strategies
Instructions
The game you will be implementing is exactly the same as the one you did for pa02, the key differences are:
-you will implement and use a binary search tree instead of a linked list
-as a result, the ordering in which cards are picked will be different
Required files
-cards.cpp, cards.h // These files should contain your implementation of the binary search tree to store a list of cards
-ultility.cpp, ultility.h // These files should contain any other classes that you need to implement your game,
-tests.cpp // These files should contain test code for all the classes and methods you used in your game
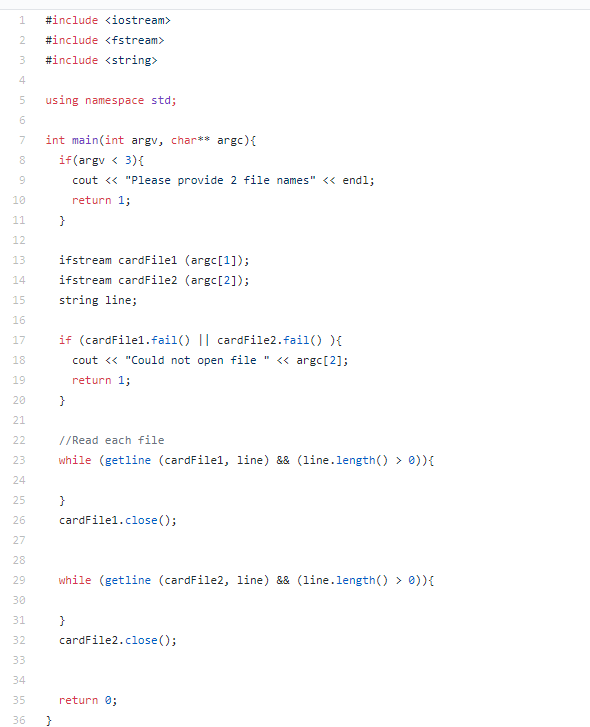
-main.cpp // This file should read in the cards of the two players from input files and put everything together to play the game.
-Makefile // generate two executables- the first should be called game and behaves similarly to the one in pa02, the second should be called tests and must RUN (not just compile) all the test code to unit test your classes and methods
The game
Alice and Bob have realized the simplicity of their revealed-hand version of Go Fish and figured out that they probably should play with their hands concealed. However, theyve already delt two hands of cards and decide to play one last game with revealed hands and make it as fast as possible. To aid this, they decide to play the game exactly the same way as described in pa02 except they will go through their cards in sorted order.
The game proceeds much as in the previous assignment, with Alice taking her turn and then Bob taking his turn. However, now when asking for cards, Alice proceeds FORWARD starting with lowest card and proceeding to the highest card, while Bob proceeds BACKWARDS through his cards in sorted order.
The ordering of cards is described in the next section.
Card ordering
The ordering of cards is determined first by its suit and then by the value:
The ordering least to greatest is: clubs, diamonds, spades, hearts. Thus a club of any value is less than a diamond of any value.
The ordering within each suit is determined by the value from least to greatest as follows: ace, 2, 3, . . . 10, jack, queen, king.
Based on the above two rules, the correct ordering of
h 9, c k, s 3, c a, h j, d 3
would be
c a, c k, d 3, s 3, h 9, h j
Your approach
At the start of the program, you will read in Alice and Bobs starting hands from two files. The names of these files are provided as command line arguments with Alices file in argv[1] and Bobs in argv[2]. The starter code opens the files for you as ifstream objects, which you can treat much like cin. You should read Alice and Bobs cards into two binary search trees. Dont worry about balancing the binary search trees (though you can try and optimize this if you like). Your binary search tree class should obey the card ordering rules given above. While implementing this, you may find it helpful to overload the operators ==, on your card class so that you can easily choose which branches to go down on your binary tree. Note that you need to correctly handle the case of cards with the value 10 (which has two characters) and separately compare the value and suit, so storing the cards as strings is probably not the best approach.
Once you have the sets of cards, the game begins. Alice iterates forward through her binary tree (in increasing order of the cards), checking whether Bob has that card. You should check if Bob has each card using the search function of the BST. Once a matching card is found, you should print the line Alice picked matching card ". The card should then be removed from both players hands by calling delete on the binary search tree. Make sure to delete any dynamically allocated memory when removing the cards from your trees!
The process then repeats, except this time, Bob looks through his cards starting with the largest card and working towards the smallest card. This means that while the first card Alice finds should be the first shared card (in order), the first card Bob finds should be the last shared card (in order). Once there are no matching cards, you should print out the final hands of both players with the matching cards removed.
As before, you should write your own Makefile for this lab so that running make builds an executable called game.
Before you begin
Based on pa02, we are adding an additional requirement that you write a set of unit tests for your binary search tree. These should be in a file called tests.cpp, which you will submit, and you should write your Makefile so that running make test compiles and runs these tests. Note that there will be no Gradescope tests for these unit tests, so you can have the output in whatever format you find most helpful. You should test each of the functions on your binary search tree, which will include, at the very least, find(), delete(), insert(), successor(), and predecessor(). You should write these tests BEFORE implementing the full game to ensure that your binary search tree works correctly. Debugging one set of code is much easier than debugging two at the same time. This will also ensure that your are correctly separating your binary tree class from the rest of your program logic.
Example
Contents of alice_cards.txt:
h 3 s 10 c a c 3 s 5 h 10 d a
Contents of bob_cards.txt:
c 2 d a h 10 c 3 d j s 10 h a
Correct output after running make && ./game alice_cards.txt bob_cards.txt:
Alice picked matching card c 3 Bob picked matching card h 10 Alice picked matching card d a Bob picked matching card s 10 Alice's cards: c a s 5 h 3 Bob's cards: c 2 d j h a
Note: a=ace, k=king, q=queen, j=jack
Requirements
For this lab, you will have a lot of flexibility on your implementation (which just means we wont be providing a code framework for you to fill in). However, there are a few requirements. Keep these in mind as you think about your solution:
-You must use a binary search tree you implemented yourself to solve the problem, not another data structure or a class in the standard library.
-Your binary search tree must implement a constructor, a destructor and other other methods as needed
-You code should be readable
-Your classes should define clear interfaces and hide implementation details as much as possible.
-Your program must properly free all memory it allocates, including your binary tree nodes and any dynamically allocated data stored inside them.
-You do not need to worry about having multiple instances of the same card. Each card will appear only once per hand.
FILES
TEXT FILES TO USE
acards.txt
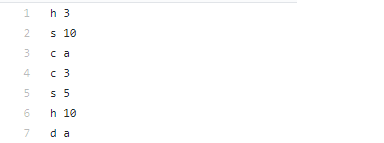
bcards.txt

WHAT THE OUTPUT SHOULD BE

1 //cards.h 2 //Authors: Your name and your partner's name 3 /A11 class declarations go here 4 5 #ifndef CARDSH 6 #define CARDS-H - 8 #endif 1 //cards.h 2 //Authors: Your name and your partner's name 3 /A11 class declarations go here 4 5 #ifndef CARDSH 6 #define CARDS-H - 8 #endif
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


