





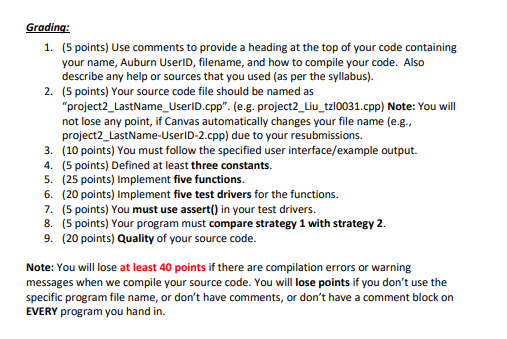
Goals: To learn "while" and "do-while" statements To learn how to define functions To write a test driver To learn how to use assert() To use random numbers Description: In the land of Puzzlevania, Aaron, Bob, and Charlie had an argument over which one of them was the greatest puzzle-solver of all time. To end the argument once and for all, they agreed on a duel to the death (this makes sense?). Aaron was a poor shooter and only hit this target with a probability of 1/3. Bob was a bit better and hit his target with a probability of 1/2. Charlie was an expert marksman and never missed. A hit means a kill and the person hit drops out of the duel. To compensate for the inequities in their marksmanship skills, the three decided that they would fire in turns, starting with Aaron, followed by Bob, and then by Charlie. The cycle would repeat until there was one man standing. That man would be remembered for all time as the Greatest Puzzle-Solver of All Time. Strategy 1: An obvious and reasonable strategy is for each man to shoot at the most accurate shooter still alive, on the grounds that this shooter is the deadliest and has the best chance of hitting back. Write a program to simulate the duel using this strategy. Your program should use random numbers and the probabilities given in the problem to determine whether a shooter hits his target. You will likely want to create multiple functions to complete the problem. My solution had only one function to simulate the duels and it passed in the odds and the three guys as pass-by-reference parameters. Once you can simulate a duel, add a loop to your program that simulates 10,000 duels. Count the number of times that each contestant wins and print the probability of winning for each contestant (e.g., for Aaron your might output "Aaron won 3612/10000 duels or 36.12%). Strategy 2: An alternative strategy for Aaron is to intentionally miss on his first shot, while the rest of duel is as same as that in Strategy 1. Write a function to simulate Strategy 2. Your program will determine which strategy is better for Aaron. Note: You must provide the following user interface. Probabilities might be slightly different for different runs due to the random number, but strategy 2 should be always better than strategy 1. You do not need to display text in red. Please replace "Li" with your name. *** Welcome to Li's Duel Simulator *** Unit Testing 1: Function -at_least_two_alivel) Case 1: Aaron alive, Bob alive, Charlie alive Case passed ... Case 2: Aaron dead, Bob alive, Charlie alive Case passed Case 3: Aaron alive, Bob dead, Charlie alive Case passed .. Case 4: Aaron alive, Bob alive, Charlie dead Case passed ... Case 5: Aaron dead, Bob dead, Charlie alive Case passed ... Case 6: Aaron dead, Bob alive, Charlie dead Case passed ... Case 7: Aaron alive, Bob dead, Charlie dead Case passed ... Case 8: Aaron dead, Bob dead, Charlie dead Case passed ... Press any key to continue... Unit Testing 2: Function Aaron_shoots1(Bob_alive, Charlie_alive) Case 1: Bob alive, Charlie alive Aaron is shooting at Charlie Case 2: Bob dead, Charlie alive Aaron is shooting at Charlie Case 3: Bob alive, Charlie dead Aaron is shooting at Bob Press any key to continue... Unit Testing 3: Function Bob_shoots(Aaron_alive, Charlie_alive) Case 1: Aaron alive, Charlie alive Bob is shooting at Charlie Case 2: Aaron dead, Charlie alive Bob is shooting at Charlie Case 3: Aaron alive, Charlie dead Bob is shooting at Aaron Press any key to continue... Unit Testing 4: Function Charlie_shoots(Aaron_alive, Bob_alive) Case 1: Aaron alive, Bob alive Charlie is shooting at Bob Case 2: Aaron dead, Bob alive Charlie is shooting at Bob Case 3: Aaron alive, Bob dead Charlie is shooting at Aaron Press any key to continue... Unit Testing 5: Function Aaron_shoots2(Bob_alive, Charlie_alive) Case 1: Bob alive, Charlie alive Aaron intentionally misses his first shot Both Bob and Charlie are alive. Case 2: Bob dead, Charlie alive Aaron is shooting at Charlie Case 3: Bob alive, Charlie dead Aaron is shooting at Bob Press any key to continue... Ready to test strategy 1 (run 10000 times): Press any key to continue... Aaron won 3565/10000 duels or 35.65% Bob won 4226/10000 duels or 42.26% Charlie won 2209/10000 duels or 22.09% Ready to test strategy 2 (run 10000 times): Press any key to continue... Aaron won 4216/10000 duels or 42.16% Bob won 2465/10000 duels or 24.65% Charlie won 3319/10000 duels or 33.19% Strategy 2 is better than strategy 1. Requirements: 1. You must follow the above user interface to implement your program. 2. You must implement the following functions: 1) bool at_least_two_alive (bool A_alive, bool B_alive, c_alive) /* Input: A alive indicates whether Aaron is alive */ B alive indicates whether Bob is alive +/ c_alive indicates whether Charlie is alive +/ /* Return: true if at least two are alive */ otherwise return false */ 2) void Aaron_shoots1 (bool& B_alive, bool& C_alive) /* Strategy 1: Use call by reference + Input: B_alive indicates whether Bob alive or dead calive indicates whether Charlie is alive or dead + Return: Change B_alive into false if Bob is killed. Change C_alive into false if Charlie is killed. 3) void Bob_shoots (bool& A_alive, bool& C_alive) /* Call by reference Input: A_alive indicates if Aaron is alive or dead C alive indicates whether Charlie is alive or dead + Return: Change A alive into false if Aaron is killed. Change C_alive into false if Charlie is killed. 4) void Charlie_shoots (bool& A_alive, boole B_alive) /* Call by reference Input: A_alive indicates if Aaron is alive or dead B alive indicates whether Bob is alive or dead + Return: Change A alive into false if Aaron is killed. Change B alive into false if Bob is killed. 5) void Aaron_shoots 2 (bool& B_alive, bool& C_alive) /* Strategy 2: Use call by reference + Input: B_alive indicates whether Bob alive or dead calive indicates whether Charlie is alive or dead + Return: Change B_alive into false if Bob is killed. change c alive into false if Charlie is killed. + 2. You must implement five unit-test drivers (five functions) to test the above five functions (see the example output on pages 2 and 3). 3. You must use assert in your test driver. 4. You must define at least three constants in your implementation. For example, the total number of runs (i.e., 10,000) can be defined as a constant. Hints: 1. How to implement "Press any Enter to continue..." cout # include
# include Cassert.h> # include 3. Initialize your random number generator as below: srand(time(0)); 4. A sample code of generating a random number is given below: /* Assume that the probabilty of hit a target is 25 percent +/ int shoot_target_result; shoot_target_result - rand() $100; if (shoot_target_result # include # include # include using namespace std; //prototypes bool at least_two_alive (bool A_alive, bool B_alive, bool C_alive); /* Input: A alive indicates whether Aaron is alive +/ B_alive indicates whether Bob is alive */ C alive indicates whether Charlie is alive / /* Return: true if at least two are alive +/ otherwise return false */ + Add other function prototypes below +/ void test_at_least_two_alive (void); /* This is a test driver for at least_two_alive () */ + Add more prototypes for other test drivers below +/ int main() 1 This is the main function } /* Implementation of at_least_two_alive() +/ bool at least_two_alive (bool A alive, bool B_alive, bool C_alive) /* add the implementation below +/ 1 } /* Implementation of the test driver for at_least_two_alive () +/ void test_at_least_two_alive (void) { cout













