
Good explanations please!
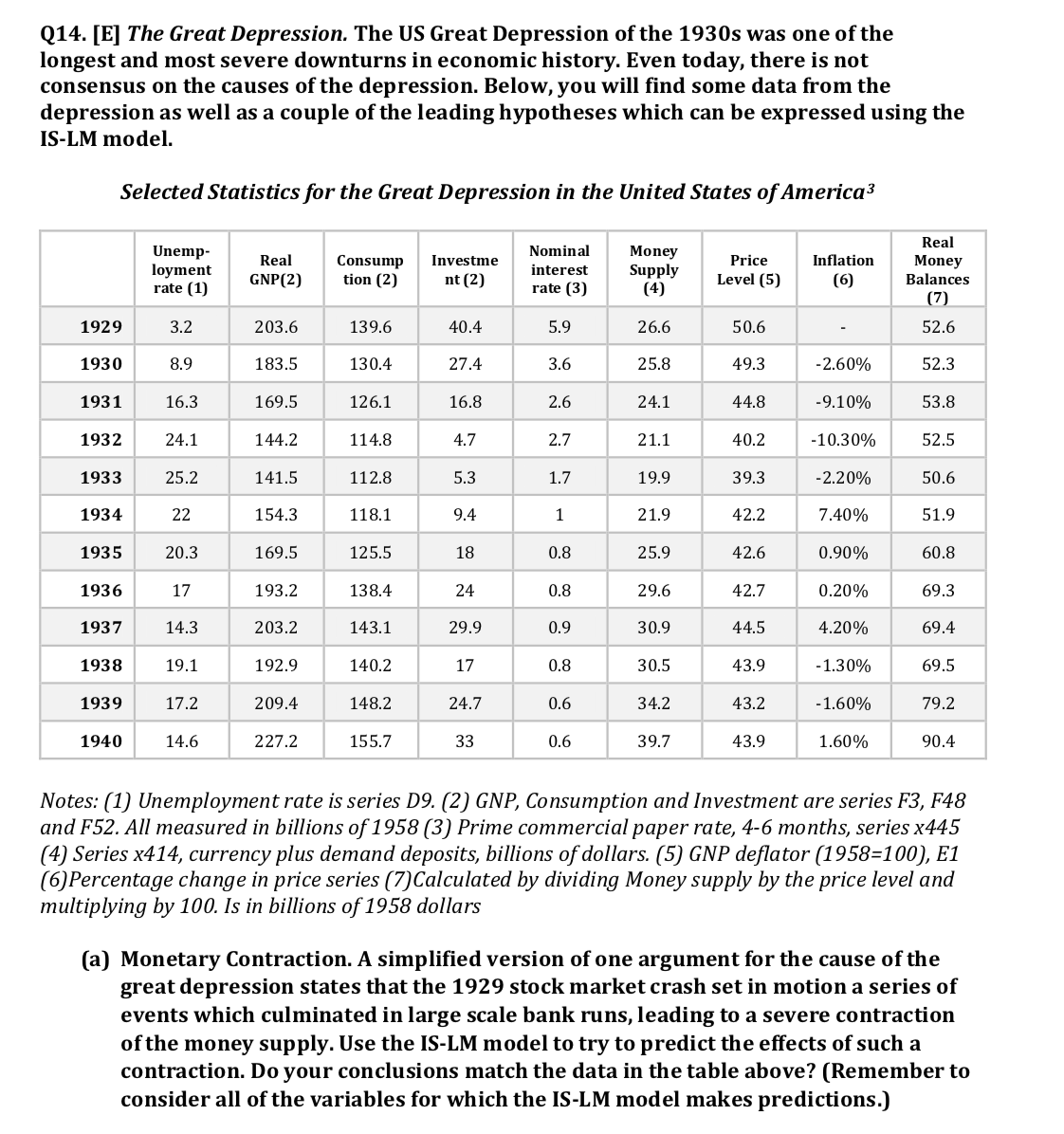
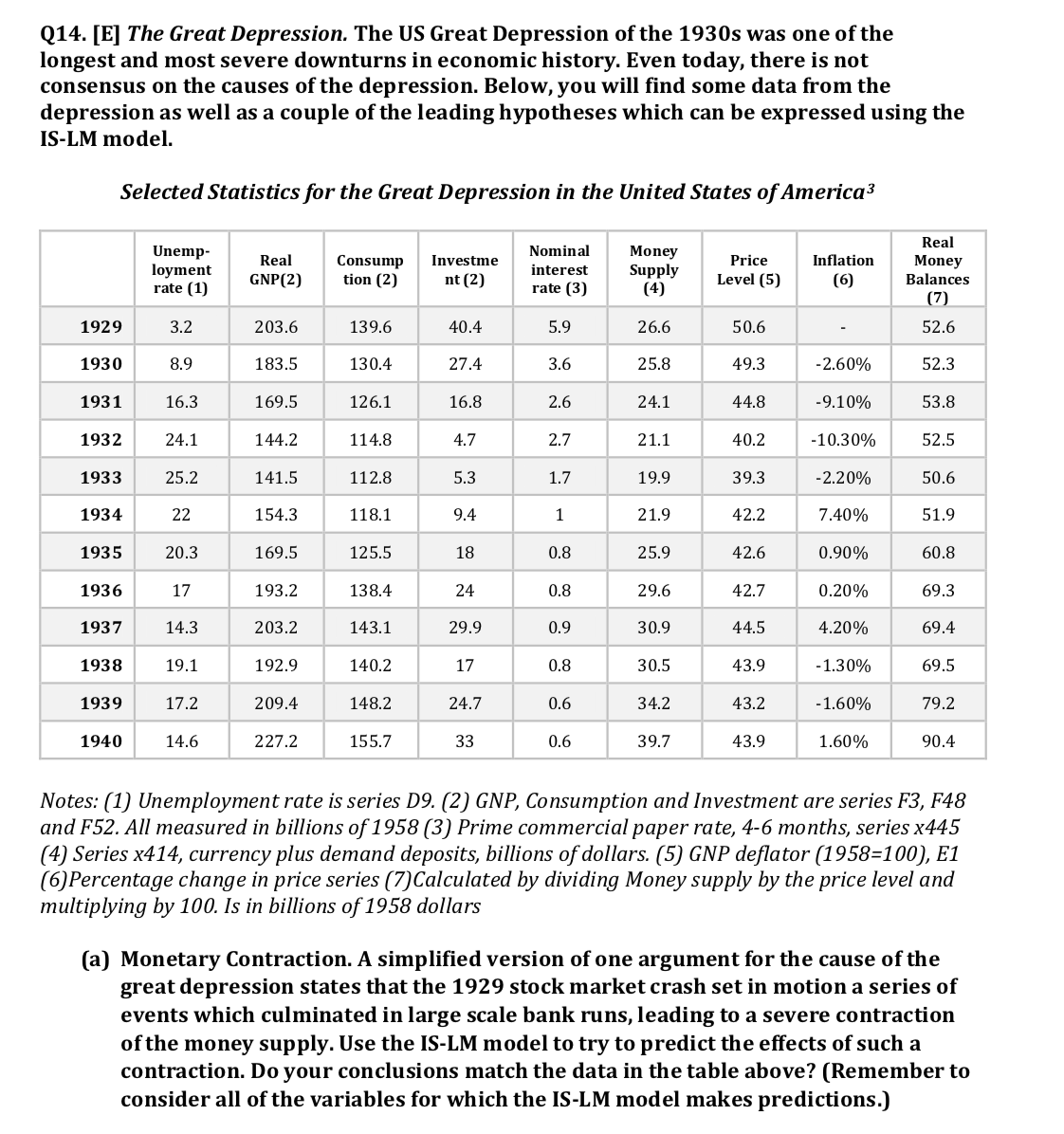
Q14. [E] The Great Depression. The US Great Depression of the 1930s was one of the longest and most severe downturns in economic history. Even today, there is not consensus on the causes of the depression. Below, you will find some data from the depression as well as a couple of the leading hypotheses which can be expressed using the IS-LM model. Selected Statistics for the Great Depression in the United States of America3 Real Unemp- Investme Nominal Money Real Consump Price Inflation Money loyment interest Supply GNP(2) tion (2) nt (2) Level (5) (6) Balances rate (1) rate (3) (4) (7) 52.6 1929 3.2 203.6 139.6 40.4 5.9 26.6 50.6 1930 183.5 130.4 27.4 3.6 25.8 49.3 2.60% 52.3 53.8 1931 16.3 169.5 126.1 16.8 2.6 24.1 44.8 -9.10% 1932 24.1 144.2 114.8 4.7 2.7 21.1 40.2 -10.30% 52.5 25.2 141.5 112.8 5,3 1.7 19.9 39.3 50.6 1933 2.20% 51.9 1934 22 154.3 118.1 94 1 1.9 42.2 7.40% 1935 20.3 169.5 125.5 18 0.8 25.9 42.6 0.90% 60.8 17 193.2 138.4 24 0.8 9.6 42.7 0.20% 69.3 1936 1937 14.3 203.2 143.1 29.9 0.9 30.9 44.5 4.20% 69.4 1938 19.1 192.9 140.2 17 0.8 30.5 43.9 -1.30% 69.5 209.4 148.2 24.7 0.6 34.2 43.2 -1.60% 79.2 1939 17.2 1940 14.6 227.2 155.7 33 0.6 39.7 43.9 1.60% 90.4 Notes: (1) Unemployment rate is series D9. (2) GNP, Consumption and Investment are series F3, F48 and F52. All measured in billions of 1958 (3) Prime commercial paper rate, 4-6 months, series x445 (4) Series x414, currency plus demand deposits, billions of dollars. (5) GNP deflator (1958=100), E1 (6) Percentage change in price series (7) Calculated by dividing Money supply by the price level and multiplying by 100. Is in billions of 1958 dollars (a) Monetary Contraction. A simplified version of one argument for the cause of the great depression states that the 1929 stock market crash set in motion a series of events which culminated in large scale bank runs, leading to a severe contraction of the money supply. Use the IS-LM model to try to predict the effects of such a contraction. Do your conclusions match the data in the table above? (Remember to consider all of the variables for which the IS-LM model makes predictions.)(b) The Money Hypothesis. A second argument focuses on changes in the expected inflation rate. Prices for primary commodities had been falling throughout the 1920s, and the onset of the 1929 financial crisis and subsequent recession increased deflationary pressures. Use the IS-LM model to predict the effect of consumers changing their expectations from inflation to deflation. How well does this fit with the data