Question
Group PSA, headquartered in Paris, France is the second largest European-based auto-manufacturer in the world. In early 2000s, the group had to eliminate its American
Group PSA, headquartered in Paris, France is the second largest European-based auto-manufacturer in the world. In early 2000s, the group had to eliminate its American operations due to extraordinary price competition resulting from a lack of unique features, the ease of entry into the market by new auto makers, well-financed local (US) auto makers and a series of mergers, acquisitions and joint ventures happening in the automobile industry in the 1990s.
The group has been plotting to come back to the US due to post-COVID demands of its most popular and recognized brands Peugeot and Citroën. Group PSA has recently acquired Opel, and Vauxhall from GM and planning to either acquire or partner with European brands (such as, Fiat and Renault) and Japanese brands (Lexus and Mazda CX60), which have large presences in the US and have a profitable market share in the US auto industry.
PSA has invested heavily in research and development on product innovation (in particular, to come up with unique features) and promotion as well as meeting the US safety and emissions rules. In addition, to tackle the exceptionally competitive US market, the company has opened its US headquarters in Atlanta with a core team to build its US strategy, particularly deciding on acquiring or partnering with either or both European and Japanese brands.
Questions
What factors led to the troubles of the Group PSA in the 1990s?
What can PSA gain by entering the US market?
Which partner(s) would be more strategic and why?
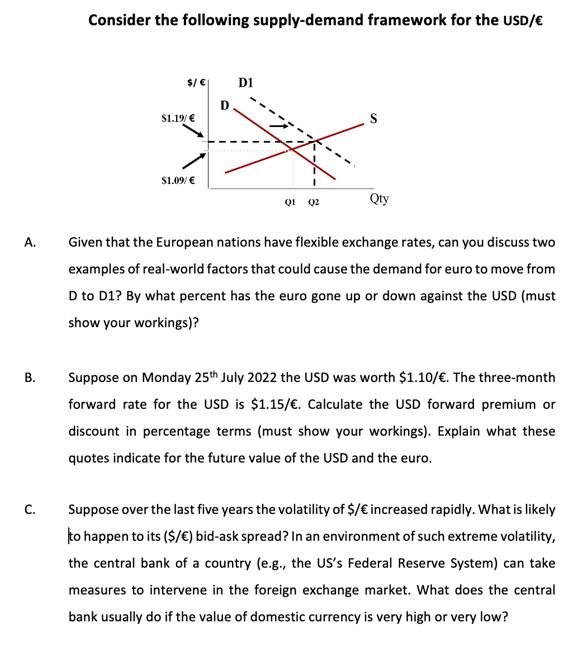
A. B. C. Consider the following supply-demand framework for the USD/ $/ $1.19/ $1.09/ D D1 01 02 S Qty Given that the European nations have flexible exchange rates, can you discuss two examples of real-world factors that could cause the demand for euro to move from D to D1? By what percent has the euro gone up or down against the USD (must show your workings)? Suppose on Monday 25th July 2022 the USD was worth $1.10/. The three-month forward rate for the USD is $1.15/. Calculate the USD forward premium or discount in percentage terms (must show your workings). Explain what these quotes indicate for the future value of the USD and the euro. Suppose over the last five years the volatility of $/ increased rapidly. What is likely to happen to its ($/ ) bid-ask spread? In an environment of such extreme volatility, the central bank of a country (e.g., the US's Federal Reserve System) can take measures to intervene in the foreign exchange market. What does the central bank usually do if the value of domestic currency is very high or very low?
Step by Step Solution
3.51 Rating (164 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
Lets address each part of the question A Realworld factors causing demand for euro to move from D to D1 1 Interest Rate Differentials If the European ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


