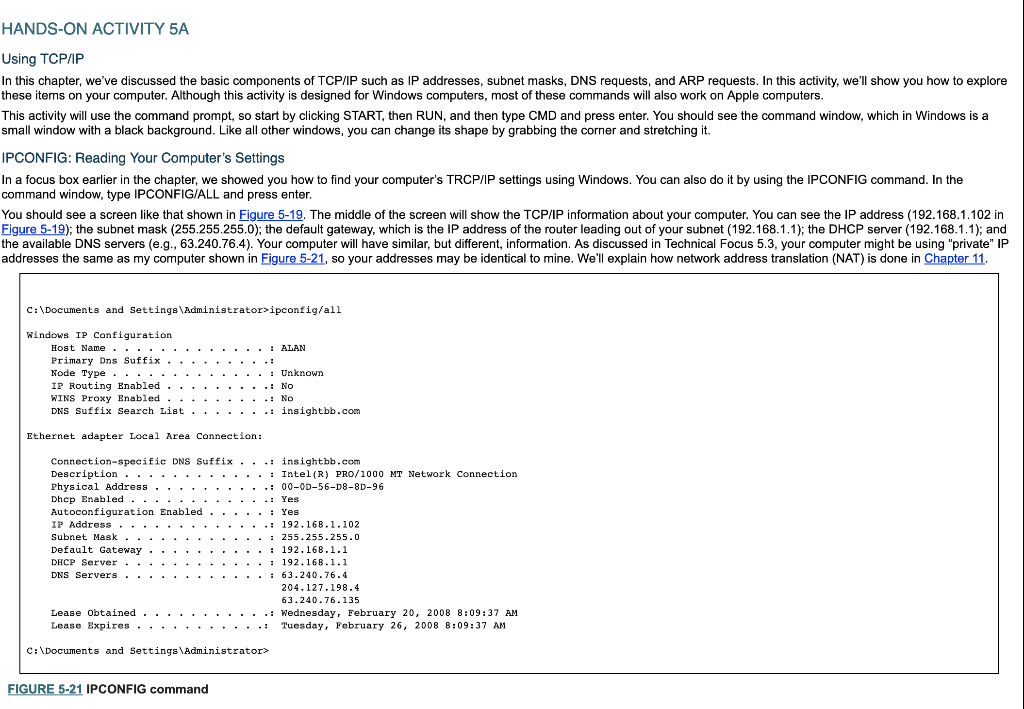

HANDS-ON ACTIVITY 5A Using TCP/IP In this chapter, we've discussed the basic components of TCP/IP such as IP addresses, subnet masks, DNS requests, and ARP requests. In this activity, we'll show you how to explore these items on your computer. Although this activity is designed for Windows computers, most of these commands will also work on Apple computers This activity will use the command prompt, so start by clicking START, then RUN, and then type CMD and press enter. You should see the command window, which in Windows is a small window with a black background. Like all other windows, you can change its shape by grabbing the corner and stretching it. IPCONFIG: Reading Your Computer's Settings In a focus box earlier in the chapter, we showed you how to find your computer's TRCP/IP settings using Windows. You can also do it by using the IPCONFIG command. In the command window, type IPCONFIG/ALL and press enter You should see a screen like that shown in Figure 5-19. The middle of the screen will show the TCP/IP information about your computer. You can see the IP address (192.168.1.102 in Figure 5-19); the subnet mask (255.255.255.0); the default gateway, which is the IP address of the router leading out of your subnet (192.168.1.1); the DHCP server (192.168.1.1); and the available DNS servers (e.g., 63.240.76.4). Your computer will have similar, but different, information. As discussed in Technical Focus 5.3, your computer might be using "private" IP addresses the same as my computer shown in Figure 5-21, so your addresses may be identical to mine. We'll explain how network address translation (NAT) is done in Chapter 11 C: \Documents and Settings\Administrator>ipconfig/all Nindows IP Configuration Node Type IP Routing Enabled . .: Unknown .: No DNS Suffix Search List .: insightbb.com Ethernet adapter Local Area Connection: Connection-specific DNS Suffix ...: insightbb.com Autoconfiguration Enabled . : Yes . Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 DNS Servers 63.240.76-4 204.127.198.4 63.240.76.135 Lease Obtained . .. Lease Expires . . . . . . . . .: Wednesday, February 20, 2008 8:09:37 AM .: Tuesday, February 26, 2008 8:09:37 AM C: LDocuments and Settings Acministrator> FIGURE 5-21 IPCONFIG command FIGURE 5-21 IPCONFIG command Deliverables 1. Use the ipconfig/all command on your computer. What is the IP address, subnet mask, IP address of default gateway, and MAC of your computer? 2. Why does every computer on the Internet need to have these four numbers? HANDS-ON ACTIVITY 5A Using TCP/IP In this chapter, we've discussed the basic components of TCP/IP such as IP addresses, subnet masks, DNS requests, and ARP requests. In this activity, we'll show you how to explore these items on your computer. Although this activity is designed for Windows computers, most of these commands will also work on Apple computers This activity will use the command prompt, so start by clicking START, then RUN, and then type CMD and press enter. You should see the command window, which in Windows is a small window with a black background. Like all other windows, you can change its shape by grabbing the corner and stretching it. IPCONFIG: Reading Your Computer's Settings In a focus box earlier in the chapter, we showed you how to find your computer's TRCP/IP settings using Windows. You can also do it by using the IPCONFIG command. In the command window, type IPCONFIG/ALL and press enter You should see a screen like that shown in Figure 5-19. The middle of the screen will show the TCP/IP information about your computer. You can see the IP address (192.168.1.102 in Figure 5-19); the subnet mask (255.255.255.0); the default gateway, which is the IP address of the router leading out of your subnet (192.168.1.1); the DHCP server (192.168.1.1); and the available DNS servers (e.g., 63.240.76.4). Your computer will have similar, but different, information. As discussed in Technical Focus 5.3, your computer might be using "private" IP addresses the same as my computer shown in Figure 5-21, so your addresses may be identical to mine. We'll explain how network address translation (NAT) is done in Chapter 11 C: \Documents and Settings\Administrator>ipconfig/all Nindows IP Configuration Node Type IP Routing Enabled . .: Unknown .: No DNS Suffix Search List .: insightbb.com Ethernet adapter Local Area Connection: Connection-specific DNS Suffix ...: insightbb.com Autoconfiguration Enabled . : Yes . Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 DNS Servers 63.240.76-4 204.127.198.4 63.240.76.135 Lease Obtained . .. Lease Expires . . . . . . . . .: Wednesday, February 20, 2008 8:09:37 AM .: Tuesday, February 26, 2008 8:09:37 AM C: LDocuments and Settings Acministrator> FIGURE 5-21 IPCONFIG command FIGURE 5-21 IPCONFIG command Deliverables 1. Use the ipconfig/all command on your computer. What is the IP address, subnet mask, IP address of default gateway, and MAC of your computer? 2. Why does every computer on the Internet need to have these four numbers








