Question
Hash Table java COMPLETE THE METHODS THAT HAVE (YOUR CODE HERE) written inside the method needed to be completed. The constructor and insert method are
Hash Table java
COMPLETE THE METHODS THAT HAVE ("YOUR CODE HERE") written inside the method needed to be completed.
The constructor and insert method are done. The hash functions are also done.
import java.util.Iterator;
public interface IHash {
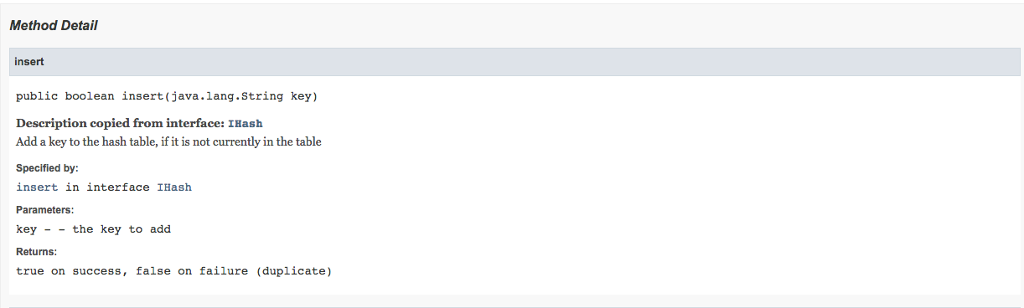
/** Add a key to the hash table, if it is not currently in the table
* @param key - the key to add
* @return true on success, false on failure (duplicate)
*/
public abstract boolean insert(String key);
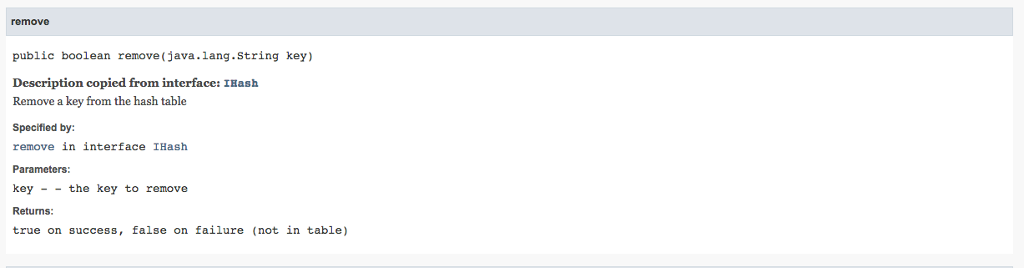
/** Remove a key from the hash table
* @param key - the key to remove
* @return true on success, false on failure (not in table)
*/
public abstract boolean remove(String key);
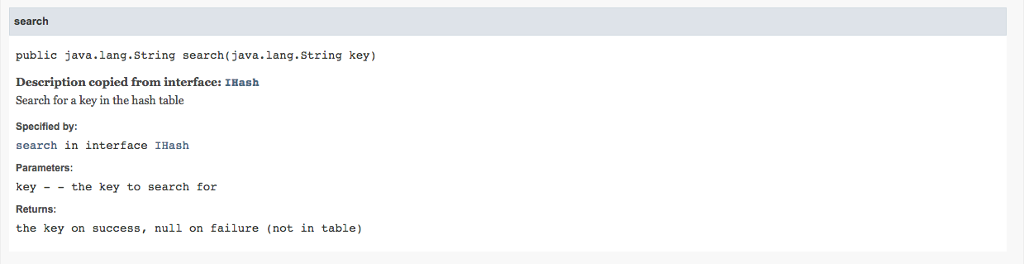
/** Search for a key in the hash table
* @param key - the key to search for
* @return the key on success, null on failure (not in table)
*/
public abstract String search(String key);
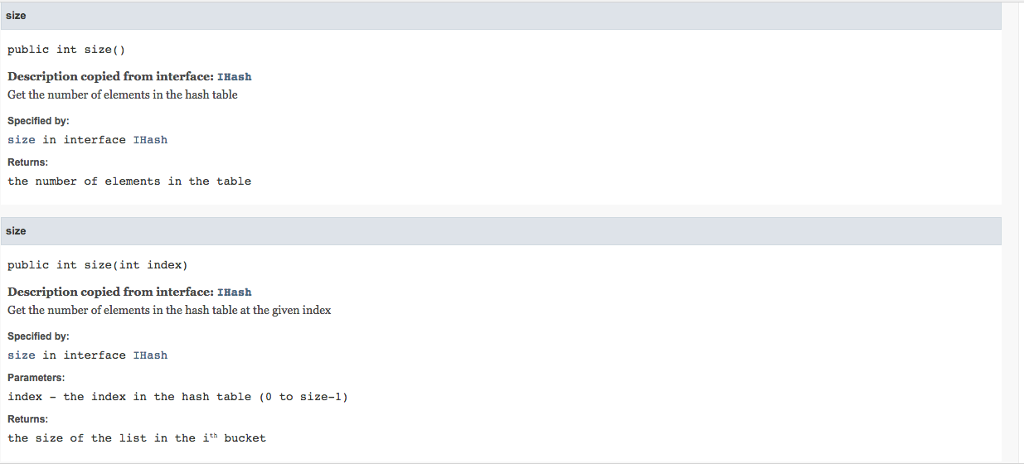
/** Get the number of elements in the hash table
* @return the number of elements in the table
*/
public abstract int size();
/** Get the number of elements in the hash table at the given index
* @param i the index in the hash table (0 to size-1)
* @return the size of the list in the ith bucket
*/
public abstract int size(int i);
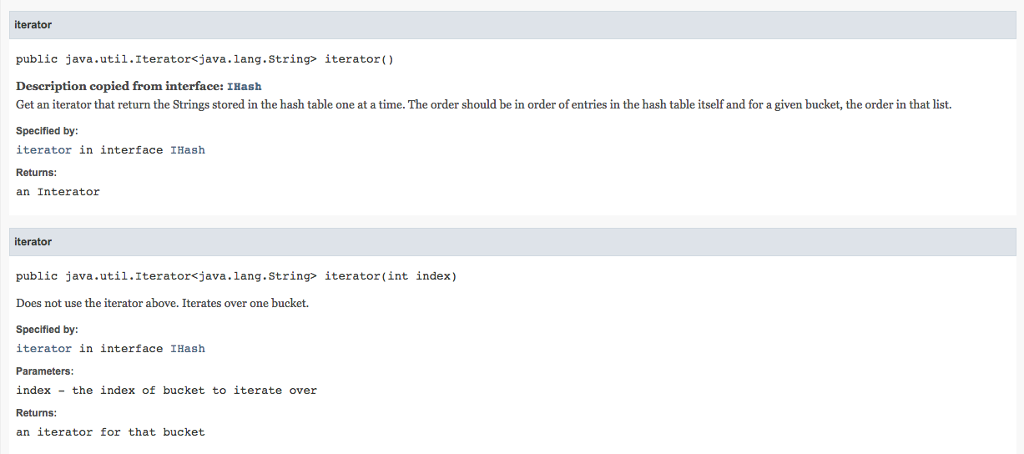
/** Get an iterator that return the Strings stored in
* the hash table one at a time. The order should be in order of entries in
* the hash table itself and for a given bucket, the order in that list.
* @return an Interator
*/
public abstract Iterator
/** Get an iterator for the ith bucket
* @param i the index in the hash table (0 to size-1)
* @return null if the bucket is empty, otherwise an iterator for the bucket
*/
public abstract Iterator
/** Print the entire hash table.
*/
public abstract void print();
}
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
public class Hasher {
// Hashing algorithms, see specification
/**
* Hashing algorithms, see provided documentation in assignment
* @param hashFunction FIRST, SUM, PRIME, OR JAVA
* @return the corresponding HashFunction
*/
public static HashFunction make(String hashFunction) {
switch (hashFunction) {
case "FIRST":
// YOUR CODE HERE
return new HashFunction() {
@Override
public int hash(String key) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return key.charAt(0);
}
};
case "SUM":
// YOUR CODE HERE
return new HashFunction() {
@Override
public int hash(String key) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int sum = 0;
for(int i=0;i
sum+=key.charAt(i);
}
return sum;
}
};
case "PRIME":
// YOUR CODE HERE
return new HashFunction() {
@Override
public int hash(String key) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int hashCode = 7;
for(int i=0;i
hashCode*=31;
hashCode+=key.charAt(i);
}
return hashCode;
}
};
case "JAVA":
// YOUR CODE HERE
return new HashFunction() {
@Override
public int hash(String key) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return key.hashCode();
}
};
default:
usage();
}
return null;
}
// Usage message
private static void usage() {
System.err.println("Usage: java Hasher ");
System.exit(1);
}
// Test code for hasher
public static void main(String[] args) {
args = Debug.init(args);
if (args.length != 2)
usage();
HashFunction sh = make(args[0]);
int hashCode = sh != null ? sh.hash(args[1]) : 0;
System.out.printf("'%s' hashes to %d using %s ", args[1], hashCode, args[0]);
}
}
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
import java.util.*;
public class HashTable implements IHash {
// Method of hashing
HashFunction hasher;
// Hash table : an ArrayList of "buckets", which store the actual strings
ArrayList> hashTable;
/**
* Number of Elements
*/
int numberOfElements;
int size;
/**
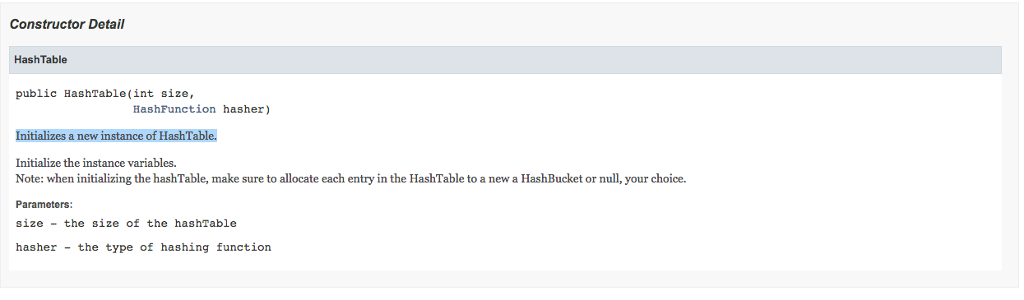
* Initializes a new instance of HashTable.
*
* Initialize the instance variables.
* Note: when initializing the hashTable, make sure to allocate each entry in the HashTable
* to a new a HashBucket or null, your choice.
* @param size the size of the hashTable
* @param hasher the type of hashing function
*/
public HashTable(int size, HashFunction hasher) {
this.hasher = hasher;
this.size = size;
this.numberOfElements = 0;
for(int i = 0; i
hashTable.add(new ArrayList());
numberOfElements++;
}
}
public boolean insert(String key) {
int i = hasher.hash(key) % size;
if(hashTable.get(i).contains(key)) {
return false;
}
else{
hashTable.get(i).add(key);
return true;
}
}
public boolean remove(String key) {
// YOUR CODE HERE
}
public String search(String key) {
// YOUR CODE HERE
}
public int size() {
// YOUR CODE HERE
}
public int size(int index) {
// YOUR CODE HERE
}
// Return iterator for the entire hashTable,
// must iterate all hashBuckets that are not empty
public class HashIterator implements Iterator {
// The current index into the hashTable
private int currentIndex;
// The current iterator for that hashBucket
private Iterator currentIterator = null;
HashIterator() {
// YOUR CODE HERE
}
public String next() {
// YOUR CODE HERE
}
public boolean hasNext() {
// YOUR CODE HERE
}
}
// Return an iterator for the hash table
public Iterator iterator() {
// YOUR CODE HERE
}
/**
* Does not use the iterator above. Iterates over one bucket.
*
* @param index the index of bucket to iterate over
* @return an iterator for that bucket
*/
public Iterator iterator(int index) {
List bucket = hashTable.get(index);
return bucket != null ? bucket.iterator() : null;
}
// Prints entire hash table.
// NOTE: This method is used extensively for testing.
public void print() {
Debug.printf("HashTable size: " + size());
for (int index = 0; index
List list = hashTable.get(index);
if (list != null) {
Debug.printf("HashTable[%d]: %d entries", index, list.size());
for (String word : list) {
Debug.printf("String: %s (hash code %d)", word, hasher.hash(word));
}
}else {
Debug.printf("HashTable[%d]: %d entries", index, 0);
}
}
}
}
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


