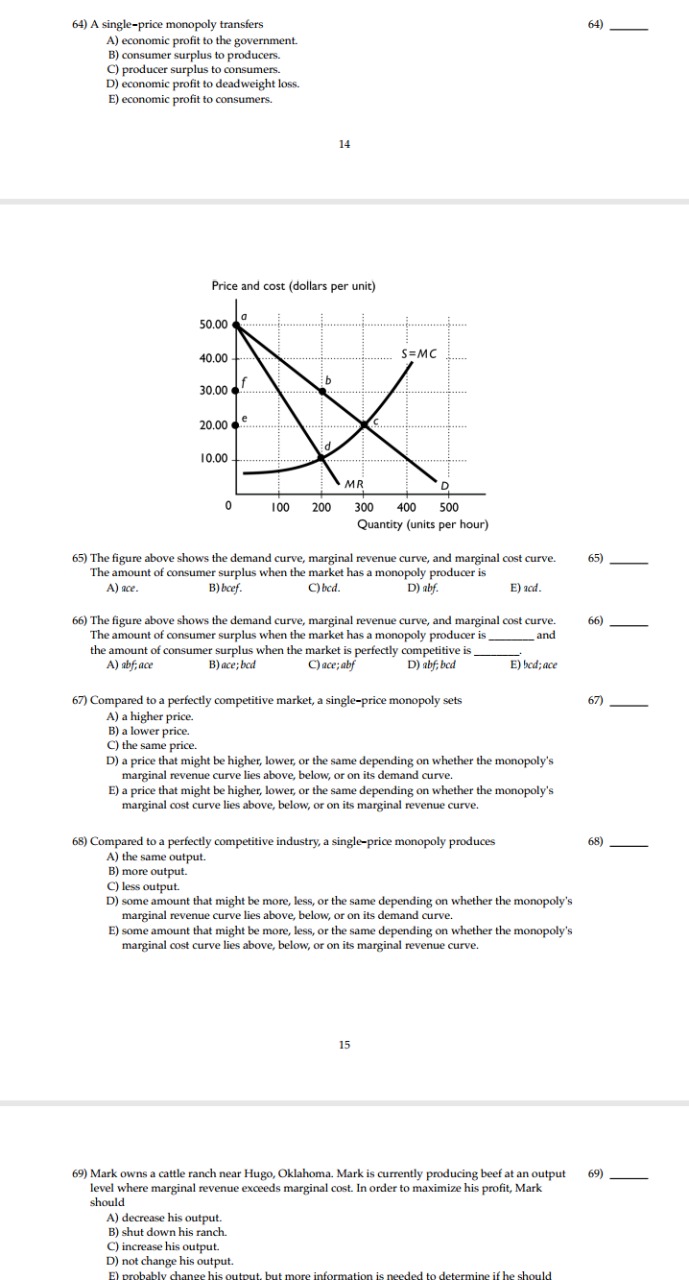
Helpmeanswerthefollowingattachments:
Answer all, thanks.,
Consider the following aggregate expenditure model of an economy:
C = 50 + (8/9)Yd T = (1/4)Y I = 100 G = 150 X = 100 IM = (1/3)Y
where C is consumption, Yd is disposable income, T is taxes, Y is national income, I is investment, G is government spending, X is exports, and IM is imports, all in billions of dollars.
(a) Solve for aggregate expenditure (AE) as a function of Y, and calculate the equilibrium level of national income. Illustrate your equilibrium in a diagram with AE on the vertical and Y on the horizontal axis. [Hint: Leave the fractions as fractions rather than decimals, your answer will work out nicely.] [8]
(b) Using your answer from (a), calculate the level of consumption spending and the level of private saving. Illustrate the private saving function (remember, S is a function of disposable income). Show the current level of saving. [6]
(c) Calculate the government's budget surplus or deficit at the equilibrium level of income. Calculate the trade balance (net exports). Illustrate the trade balance in a diagram of net exports as a function of national income. [6]
(d) Suppose that the government estimates that potential GDP for the economy is 750. By how much would the government have to increase its spending to achieve this level of GDP? Illustrate the effect of the increase in your diagram for part (a). What is effect on the government's budget? Does this result surprise you given the government's original budget situation?
(e) If we assume that the aggregate expenditure model is fully describing the reactions of the economy to the increase in government spending, what implicit assumption are we making about the aggregate supply curve? Illustrate in a diagram.
Price stability is such a vital macroeconomic goal. Discuss> What are the consequences of inflation? Applying economic concepts, explain why people buy the things they buy. What influences a consumer to purchase a product? Discuss the the three categories that form the different kinds of evaluation> Discuss the timing of an evaluation time-wise. Discuss all the five types of timing. Discuss the factors considered in timing of an evaluation. Evaluation may be different according to? Develop at least 10 evaluation design questions. Discuss the experimental approach as an evaluation design approach.64) A single-price monopoly transfers 64) A) economic profit to the government. B) consumer surplus to producers. C) producer surplus to consumers. D) economic profit to dead weight loss. E) economic profit to consumers. 14 Price and cost (dollars per unit) 50.00 40.00 10.00 100 200 300 400 500 Quantity (units per hour) 65) The figure above shows the demand curve, marginal revenue curve, and marginal cost curve. 65) The amount of consumer surplus when the market has a monopoly producer is A) ace. B) beef. C) bed. D) abf. E) and. 66) The figure above shows the demand curve, marginal revenue curve, and marginal cost curve. 66) The amount of consumer surplus when the market has a monopoly producer is . and the amount of consumer surplus when the market is perfectly competitive is A) abface B) ace; bed C)ace; abf D) abf. bed E) bed; ace 67) Compared to a perfectly competitive market, a single-price monopoly sets 67) A) a higher price. B) a lower price. C) the same price. D) a price that might be higher, lower, or the same depending on whether the monopoly's marginal revenue curve lies above, below, or on its demand curve. E) a price that might be higher, lower, or the same depending on whether the monopoly's marginal cost curve lies above, below, or on its marginal revenue curve. 68) Compared to a perfectly competitive industry, a single-price monopoly produces 68) A) the same output. B) more output. C) less output. D) some amount that might be more, less, or the same depending on whether the monopoly's marginal revenue curve lies above, below, or on its demand curve. E) some amount that might be more, less, or the same depending on whether the monopoly's marginal cost curve lies above, below, or on its marginal revenue curve. 15 69) Mark owns a cattle ranch near Hugo, Oklahoma. Mark is currently producing beef at an output 69) level where marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost. In order to maximize his profit, Mark should A) decrease his output. B) shut down his ranch. C) increase his output. D) not change his output. E)1. Suppose the following events occur in the market for cars. For each event, show how the supply and demand graph is affected and explain any shifts/movements along the curves. i. Consumer incomes decrease. ii. New technology decreases production costs. iii. The price of public transportation increases. iv. The cost of steel increases. 2. Which of the following will shift the demand curve? a. Changes in production costs b. Changes in consumer tastes c. Changes in the price of the good 3. Which of the following will shift the supply curve? a. Changes in production costs b. Changes in consumer tastes c. Changes in the price of the good