Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Hello , how am I supposed to do questions 1 a & b ? How to approach 2 ? Reading assignment Contact resistance and resistances-in-parallel
Hello ,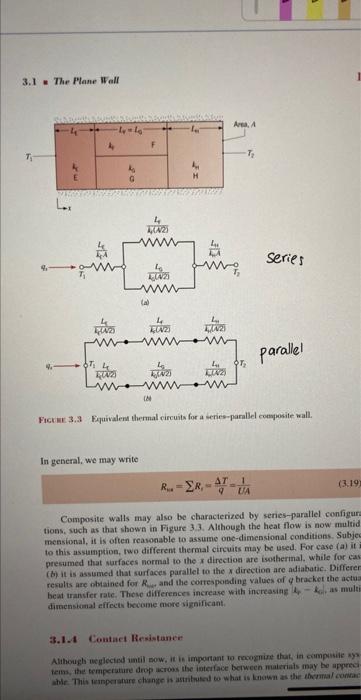
Reading assignment Contact resistance and resistances-in-parallel Background and goal Within the framework of the course "Principles of Chemical Engineering 2M " one-dimensional conduction through composite walls is studied. Systems discussed in class can be analyzed using the concept of thermal resistances-in-series. In addition, all interfaces between different materials are assumed to be perfectly smooth with full contact between both sides of the interface at all points The goal of this assignment is to extend the analysis (and understanding) to topics not covered in class. One of these is concerned with systems which, strictly speaking, exhibit multi-dimensional behavior but can still be approximated as one-dimensional using the idea of thermal resistances-in-parallel. The other topic addressed in this assignment is the concept of contact resistance, which becomes important in imperfect interfaces between materials. Description of assignment Carefully read the short paragraph at the end of Chapter 3.1 .3 on page 101 in the sixth edition of the text book by Incropera and Dewitt. Next, read Chapter 3.1.4 from page 101 until (and including) page 103. Finally, carefully read example 3.3 from page 109 until (and including) page 112. Answers to the following questions must be submitted: 1) Consider figure 3.3 on page 101. Derive (for this case) the total resistance of the system as defined by case (a) in this figure, and once again as defined by case (b) in this figure. Note that, in an analogy with electric circuits, the total resistance of a parallel set up is given by R=(R1)t. (a) Compare the two results for the general case and once again for the special situation when in the special case that k4=kEk1,kF=kg=k2,LE=L7 =LGL11=L Could this situation have been analyzed using a more simple approach? (b) Rederive the two results for the case when kH=kE=kFFk1,kG=0,LE= LF=LO=LH=L. Explain in plain words the physical basis/reasoning behind each of the two results. Which seems more reasonable to you? 2) Consider example 3.3. (a) Re-derive the result for the themal conductivity of the carbon nanotube in symbolic form (do not yet insert numerical values for the different parameters). Insert numerical values for all known parameters into this symbolic result and check to see if you obtain the same result as in the book (b) Repeat the first part of (a) though this time take into account thermal contact resistance between the carbon nanotube and the two islands. Assume it's value (Rlem) is equal on both islands. In addition, assume the portion of the nanotube in contact with each island is isothermal (at a temperature which is obviously different from that of the island). Insert all known numerical values and plot the resultant thermal conductivity of the carbon nanotube as a function of Rem for values of contact resistance varying between 0 and 6106m2K/W, It is known that the contact area between each side of the nanotube and the relevant island is 71015m2 (i.e. the total area of contact between the nanotube and both islands is 1.4 1014m2) General instructions: Reading the assigned material must be completed by all students in an independent manner. At the same time, the answers to the questions can be submitted in groups of up to three students. Answers must be submitted by 9:30 in the moming on Monday the 13- of March. 3.1 - The Plane Hall series Frotiel 3,2 Fiquivalen thermal circuits for a erreseparallel composite wall. In general, we may write Rn=Ri=qT=UM1 Composite walls may also be characterized by series-parallel configur tions, such as that shown in Figare 3.3. Although the heat flow is now multid mensional, it is often reasonable to assume one-dimensional conditions. Subje to this assumption, rwo different thermal eircuits may be used. For case (a) it presumed that surfaces normal to the x dinection are iseshermal. while for cas (b) it is assumed that surfaces parallel to the x direction are adtabatic. Differen results are obrained for R. and the cotrespoeding values of q bracker the acta beat trancfer rate. These differences increase with increasias hfk0, as mult disnenstanal effects tiecome tore ingnificant. 3.1.A Contact Resistance Alihough ocgleciod until sow, it is impontant to rocognise that, in cimpusae sy? tems, the temperature deop across lise interlace between maleriats may be appecel able. This eanperstare change is astatused to what is lenown as the thermal conas how am I supposed to do questions 1 a & b ?
How to approach 2 ? 




Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


