Help me with the questions below
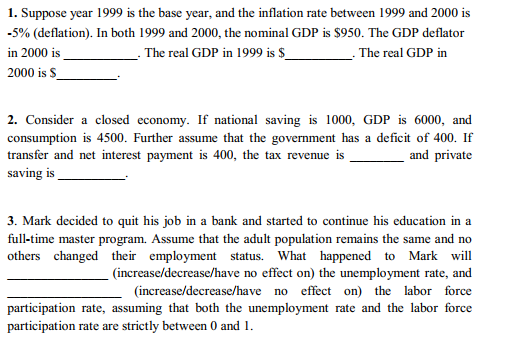
1. Suppose year 1999 is the base year, and the inflation rate between 1999 and 2000 is -5% (deflation). In both 1999 and 2000, the nominal GDP is $950. The GDP deflator in 2000 is The real GDP in 1999 is $ The real GDP in 2000 is $ 2. Consider a closed economy. If national saving is 1000, GDP is 6000, and consumption is 4500. Further assume that the government has a deficit of 400. If transfer and net interest payment is 400, the tax revenue is and private saving is 3. Mark decided to quit his job in a bank and started to continue his education in a full-time master program. Assume that the adult population remains the same and no others changed their employment status. What happened to Mark will (increase/decrease/have no effect on) the unemployment rate, and (increase/decrease/have no effect on) the labor force participation rate, assuming that both the unemployment rate and the labor force participation rate are strictly between 0 and 1.4. Imagine the government in a closed economy decides to decrease government purchases by $100 billion. Such an action leads to a total of $400 billion decrease in goods market equilibrium output. The marginal propensity to consume is 5. Suppose that the economy is characterized by the following behavioral equations: C =160 +0.6Y, / =150 G =150 T = 100 From these information, we know that the equilibrium output ()) is_ . disposable income (Y) is. _ consumption spending is total demand is private saving is _ , public saving is Suppose the government spending decreases by 40, output will fall by_ 6. Suppose that investment is fixed, as in Chapter 3. The paradox of saving suggests that an increase in the desire to save will cause GDP to (increase? decrease?) 7. Assume that the reserve ratio is 0.2. The Reserve Bank carries out open-market operations, purchasing $1 million worth of bonds from banks. This action increased the money supply by $2 million. Suppose this economy has $6 million of total currency after the open market operations. (1) The currency-deposit ratio is (2) The amount of reserve after the open market operation is $ million. (3) The amount of money supply after the open market operation is $ million.9. During the Great Depression, the U.S. economy experienced many bank runs, to the point where people became unwilling to keep their money in banks, preferring to hold on to their cash. We would expect that such a shift away from checkable deposits toward currency to (increase/decrease) the money multiplier