Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
help quick please second time posting cause i need this awnsered do not skip over Analytical Thinking (Algo) [LO11-1, LO11-3, LO11-5] TurStutf, Incorporated, selts a
help quick please second time posting cause i need this awnsered "do not skip over" 
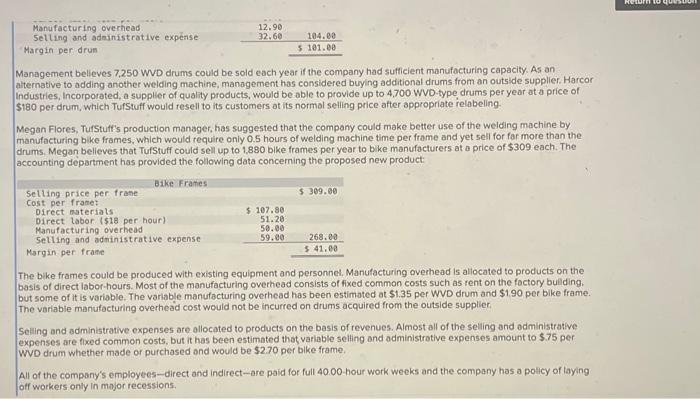
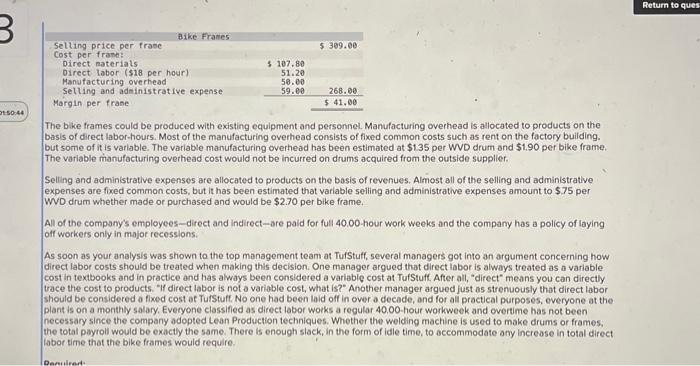

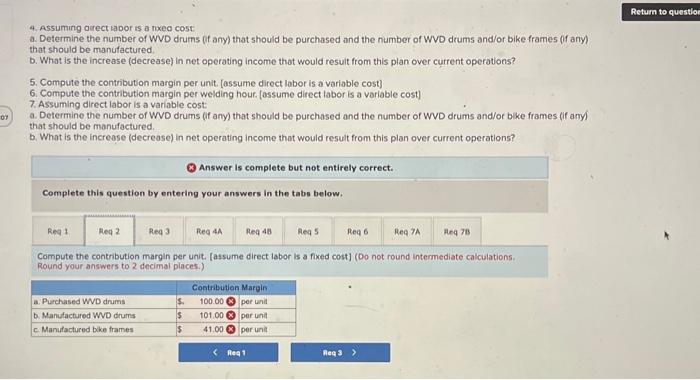
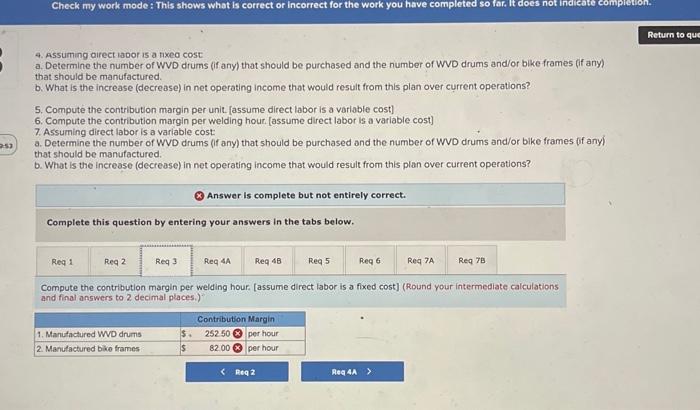
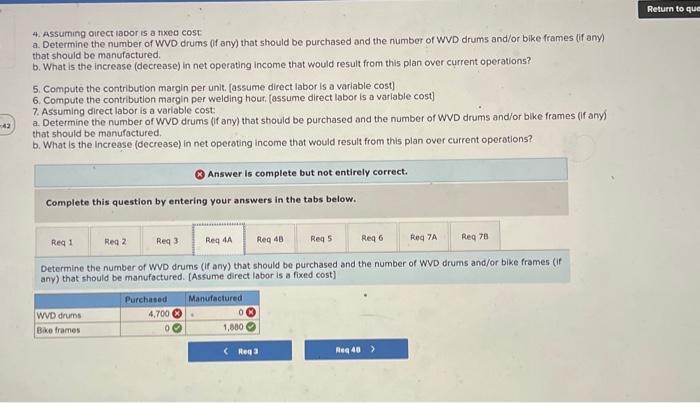
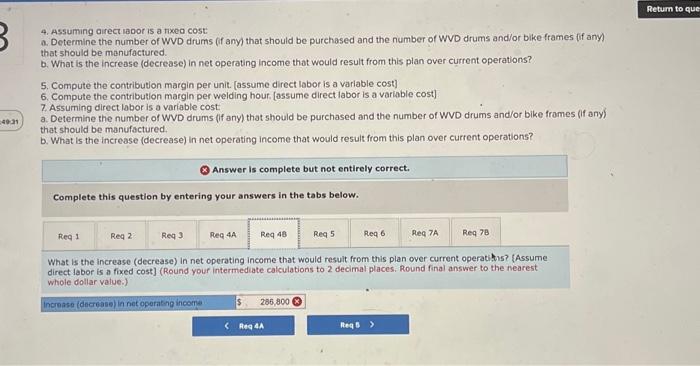
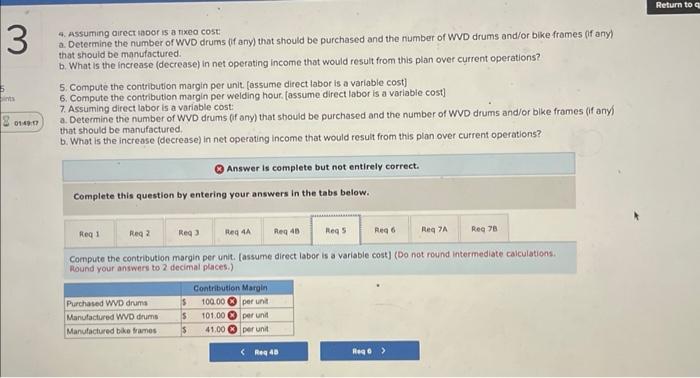
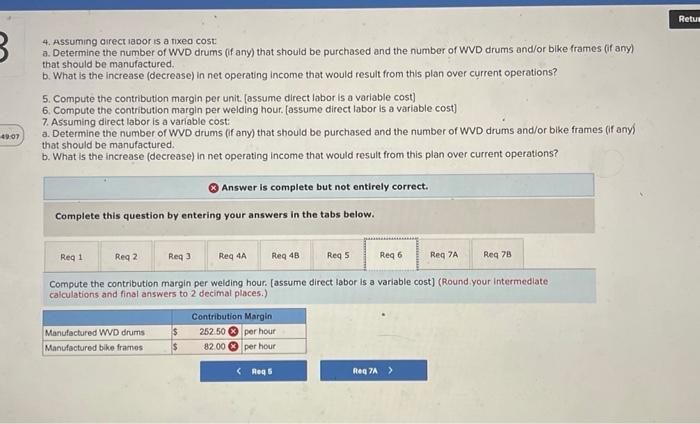
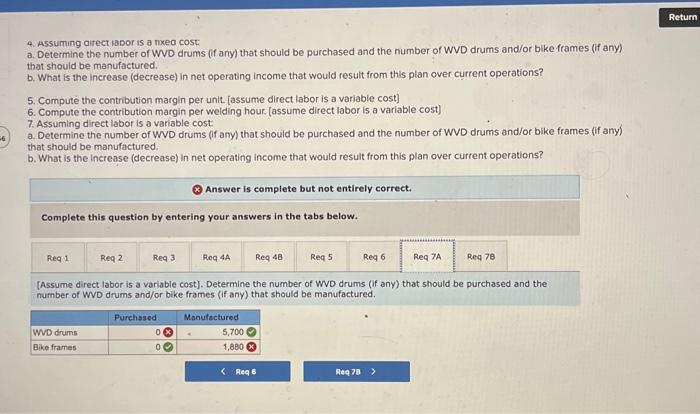
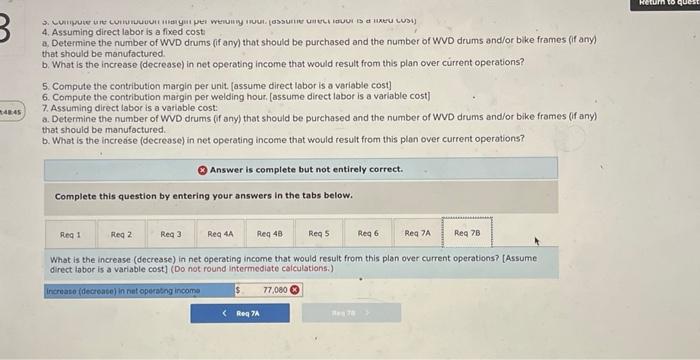
Analytical Thinking (Algo) [LO11-1, LO11-3, LO11-5] TurStutf, Incorporated, selts a wide range of drums, bins, boxes, and other contalners that are used in the chemical industry. One of thed company's products is a heavy-duty corrosion-tesistant metal drum, called the WvD drum, used to store toxic wastes Production is constrained by the capocity of an nutomated welding machine that is used to make precision welds. A total of 2,280 hours of welding time is available annually on the machine. Because each drum requires 0.4 hours of welding machine time, annual production is fimited to 5,700 drums. At present, the welding machine is used exclusively to make the WvD drums. The accounting department has provided the following financial data concerning the Wvo drums: Management believes 7,250 Wvo drums could be sold each year if the company had sufficient manufocturing copocity. As an alternative to adding another welding machine, management has considered buying additional drums from an outside supplier, Harcor Industries, Incorporated, a supplier of cuality products, would bo able to provide up to 4700 WvD-type drums per year at a price of $180 per drum, which Tutstuff would resell to its customers at its normal selling price after appropeiate relabeling Megan Flores, Tuststuff's production manager, has suggested that the company could make better use of the welding machine by manulocturing bike frames, which would require only o.5 hours of welding machine time per frame and yet sell for far more than the drums. Megan believes that Turstuff could sell up to 1,880 bke frames per year to bike manufacturers at o price of 5309 ench. The occounting department has provided the following data concerning the proposed new product Management believes 7,250 WVD drums could be sold each year if the company had sufficient manufacturing capacity. As an alternative to adding another welding mochine, management has considered buying additional drums from an outside supplier. Harcor Industries, Incorporated, a supplier of quality products, would be able to provide up to 4,700 WVD-type drums per year at a price of $180 per drum, which TufStuff would resell to its customers at its normbl selling price after appropriate relabeling. Megan Flores, TurStuff's production manager, has suggested that the company could make better use of the welding machine by manufacturing bike frames, which would require only 0.5 hours of welding machine time per frame and yet seli for far more than the drums. Megan believes that TufStuff could sell up to 1,880 bike frames per year to bike manufacturers at a price of $309 each. The accounting department has provided the following data concerning the proposed new product: The bike frames could be produced with existing equipment and personnel, Manufacturing overhead is allocated to products on the basis of direct labor-hours. Most of the manufacturing overhead consists of fixed common costs such as rent on the factory buliding. but some of it is variable. The variable manufacturing overhead has been estimated at $1.35 per WVD drum and $1.90 per bike frame. The variabie manufocturing overhead cost would not be incurred on drums acquired from the outside supplier Selling and administrative expenses are allocated to products on the basis of revenues. Almost all of the selling and odministrative expenses are fixed common costs, but it has been estimated that variable seling and administrotive expenses amount to $75 per WVD drum whether made or purchased and would be $2.70 per blke frame. All of the company's employees-direct and indirect-are paid for full 40.00 -hour work weeks and the company has a policy of laying off workers only in major recessions. The bike frames could be produced with existing equipment and personnel. Manufacturing overhead is allocated to products on the basis of direct labor-hours. Most of the manufacturing overhead consists of fixed common costs such as rent on the factory building. but some of it is variable. The variable manufacturing overhead has been estimated at $1.35 per WVD drum ond $1.90 per bike frame. The variable manufacturing overhead cost would not be incurred on drums acquired from the outside supplier. Selling and administrative expenses are allocated to products on the basis of revenues. Almost all of the selling and administrative expenses are fixed common costs, but it has been estimated that variable selling and administrative expenses amount to $75 per Wvo drum whether made or purchased and would be $2.70 per bike frame. All of the company's employees-direct and indirect-are paid for full 40.00 hour work weeks and the company has a policy of laying off workers only in mojor recessions. As soon as your analysis was shown to the top management team at TurStuff, several managers got into an argument concerning how direct labor costs should be treated when making this decision. One manager argued that direct labor is always treated as a variable cost in textbooks and in practice and has always been considered a variable cost at TufStuff. After all, "direct" means you can directly trace the cost to products. "If direct labor is not a variable cost, what is?" Another manager argued just as strenuously that direct labor should be considered a fixed cost of TurStuft, No one had been laid off in over a decade, and for all practical purposes, everyone at the plant is on a monthly salary. Everyone classifled as direct labor works a regular 40.00 -hour workweek and overtime has not been necessary since the company adopted Lean Production techniques. Whether the welding machine is used to make drums or frames, the total payroll would be exactly the same. There is enough slack, in the form of idle time, to accommodate any increase in total direct labor time that the bike frames would require. All of the company's employees-direct and indirect-are poid for ful 40,00 -hour work weeks and the company has a policy of laying off workers only in major recessions. As soon as your analysis was shown to the top management team at TufStuft, several managers got into an argument concerning how direct labor costs should be treated when making this decision. One manager argued that direct lobor is always treated as a variable cost in textbooks and in practice and has always been considered a variable cost at TufStuff After all, "direct" means you can directly trace the cost to products. "if direct labor is not a variable cost, what is?" Another manager argued just as strenuously that direct labor should be considered a fixed cost at TulStuff. No one had been laid off in over a decade, and for all practical purposes, everyone at the plant is on a monthly salary. Everyone classified as direct labor works a regular 40.00 -hour workweek and overtime has not been necessary since the compary adopted Lean Production tectniques. Whether the welding machine is used to make drums or frames. the total payroll would be exactly the same. There is enough slack, in the form of idle time, to accommodate any increase in total direct labor time that the bike frames would require. Required: 1. Would you be comfortable relying on the financlal data provided by the accounting department for making decisions related to the WVD drums and bike frames? 2. Compute the contribution margin per unit. fassume direct labor is a foxed cost) 3. Compute the contribution margin per welding hour. [assume direct labor is a fixed cost] 4. Assurning direct labor is a fixed cost: a. Determine the number of WVD drums (if any) that should be purchased and the number of WVD drums and/or bike frames (if any) that should be manufactured. b. What is the increase (decrease) in net operating income that would result from this plan over current operations? 5. Compute the contribution margin per unit. [assume direct labor is a variablo cost] 6. Compute the contribution margin per welding hour. [assume direct labor is a variable cost] 7. Assuming direct labor is a variable cost a. Determine the number of WVD drums (if any) that should be purchased and the number of WVD drums and/or bike frames (if any) that should be manufactured. b. What is the increase (decrease) in net operating income that would result from this plan over current operations? 4. Assuming arect lador is a noxed cost a. Determine the number of WVD drums (f any) that should be purchased and the number of WVD drums and/or bike frames (ff any) that should be manufactured. b. What is the increase (decrease) in net operating income thot would resuit from this plan over current operations? 5. Compute the contribution margin per unit. [assume direct labor is a variable cost] 6. Compute the contribution margin per welding hour. [assume direct labor is a variable cost] 7. Assuming direct labor is a variable cost: a. Determine the number of WVD drums (if any) that should be purchased and the number of WVD drums and/or bike frames (if any) that should be manufactured. b. What is the increase (decrease) in net operating income that would result from this plan over current operations? Answer is complete but not entirely correct. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Compute the contribution margin per unit. [assume direct labor is a fixed cost) (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to 2 decimal places.) 4. Assuming oirect lador is a nxeo cost a. Determine the number of WVD drums (if any) that should be purchased and the number of WVD drums and/or bike frames (if any) that should be manufactured. b. What is the increase (decrease) in net operating income that would result from this plan over current operations? 5. Compute the contribution margin per unit. [assume direct labor is a variable cost] 6. Compute the contribution margin per welding hour. [assume direct labor is a variable cost] 7. Assuming direct labor is a variable cost a. Determine the number of WVD drums (if any) that should be purchased and the number of WVD drums and/or bike frames (if any) that should be manufactured. b. What is the increase (decrease) in net operating income that would result from this plan over current operations? * Answer is complete but not entirely correct. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Compute the contribution margin per welding hour. [assume direct labor is a fixed cost] (Round your intermediate calculations and final answers to 2 decimal places.) 4. Assurning oirect lador is a nxe0 cost a. Determine the number of WVD drums (f any) that should be purchased and the number of WVD drums and/or bike frames (if any) that should be manufactured. b. What is the increase (decrease) in net operating income that would result from this plan over current operations? 5. Compute the contribution margin per unit. [assume direct labor is a variable cost] 6. Compute the contribution margin per welding hout, [assume direct lobor is a varlable cost] 7. Assuming direct labor is a variable cost a. Determine the number of WVD drums (if any) that should be purchased and the number of WVD drums and/or bike frames (If any) that should be manufactured. b. What is the increase (decrease) in net operating income that would result from this plan over current operations? Answer is complete but not entirely correct. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Determine the number of WVD drums (if any) that should be purchased and the number of WVD drums and/or bike frames (if any) that should be manufactured. [Assume direct labor is a fixed cost] 4. Assuming airect laoor is a nxeo cost: a. Determine the number of WVD drums (f any) that should be purchased and the number or WVD drums and/or bike frames (ff any) that should be manufactured. b. What is the increase (decrease) in net operating income that would result from this plan over current operations? 5. Compute the contribution margin per unit. [assume direct lobor is a variable cost] 6. Compute the contribution margin per welding hour. [assume direct labor is a variabie cost] 7. Assuming direct labor is a variable cost a. Determine the number of WVD drums (if any) that should be purchased and the number of WVD drums and/or bike frames (If any) that should be manufactured b. What is the increase (decrease) in net operating income that would result from this plan over current operations? Answer is complete but not entirely correct. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. What is the increase (decrease) in net operating income that would result from this plan over current operatithis? [Assume direct labor is a fixed cost] (Round your intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places. Round final answer to the nearest whole dollar value.) 4. Assuming airect inoor is a nixeo cost: a. Determine the number of WVD drums (if any) that should be purchased and the number of WD drums and/or bike fromes (f any) that should be manufactured: b. What is the increase (decrease) in net operating income that would result from this plan over current operations? 5. Compute the contribution margin per unit. [assume direct labor is a variable cost] 6. Compute the contribution margin per welding hour. [assume direct labor is a variabie cost] 7. Assuming direct labor is a variable cost: a. Determine the number of WVD drums (if any) that should be purchased and the number of WVD drums and/or blke frames (If any) that should be manufactured. b. What is the increase (decrease) in net operating income that would result from this plan over current operations? Answer is complete but not entirely correct. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Compute the contribution margin per unit. (assume direct labor is a variable cost) (Do not round intermediate caiculations. Aound your answers to 2 decimal places.) 4. Assuming airect iador is a nixed cost: a. Determine the number of WVD drums (ff any) that should be purchased and the number of WVD drums and/or bike frames (if any) that should be manufactured b. What is the increase (decrease) in net operating income that would result from this plan over current operations? 5. Compute the contribution margin per unit. [assume direct labor is a varlable cost] 6. Compute the contribution margin per welding hour. [assume direct labor is a variable cost] 7. Assuming direct labor is a variable cost: a. Determine the number of WVD drums (if any) that should be purchased and the number of WVD drums and/or bike frames (if any) that should be manufactured. b. What is the increase (decrease) in net operating income that would result from this plan over current operations? Answer is complete but not entirely correct. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Compute the contribution margin per welding hour. [assume direct labor is a variable cost] (Round your intermedlate calculations and final answers to 2 decimal places.) 4. Assuming airect rador is a nixea cost: a. Determine the number of WVD drums (if any) that should be purchased and the number of WVD drums and/or bike frames (if any) that should be manufactured. b. What is the increase (decrease) in net operating income that would result from this plan over current operations? 5. Compute the contribution margin per unit. [assume direct labor is a variable cost] 6. Compute the contribution margin per weiding hour. [assume direct labor is a variable cost] 7. Assuming direct iabor is a variable cost a. Determine the number of WVD drums (if any) that should be purchased and the number of WVD drums and/or bike frames (if any) that should be manufactured. b. What is the increase (decrease) in net operating income that would result from this plan over current operations? Answer is complete but not entirely correct. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. [Assume direct labor is a variable cost]. Determine the number of WVD drums (if any) that should be purchased and the number of WVD drums and/or bike frames (if any) that should be manufactured. 4. Assuming direct labor is a fixed cost: a. Determine the number of WVD drums (if any) that should be purchased and the number of WVD drums andlor bike frames (if any) that should be manufactured. b. What is the increase (decrease) in net operating income that would result from this plan over current operations? 5. Compute the contribution margin per unit. [assume direct lobor is a variable cost] 6. Compute the contribution margin per welding hour. [assume direct labor is a variable cost] 7. Assuming direct labor is a varioble cost: 7. Determine the number of WVD drums (f any) that should be purchased and the number of WVD drums and/or bike frames (if any) that should be manufactured. b. What is the increase (decrease) in net operating income that would result from this plan over current operations? (x) Answer is complete but not entirely correct. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. What is the increase (decrease) in net operating income that would result from this plan over current operations? [Assume direct tabor is a variable cost) (Do not round intermediate calculations.) 











Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


