Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Help solving 10) using info below solve 10) below . Koontz Company manufactures a number of products. The standards relating to one of these products
Help solving 10) using info below 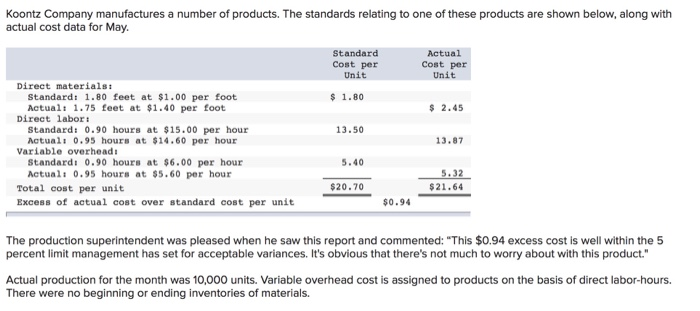





solve 10) below

.
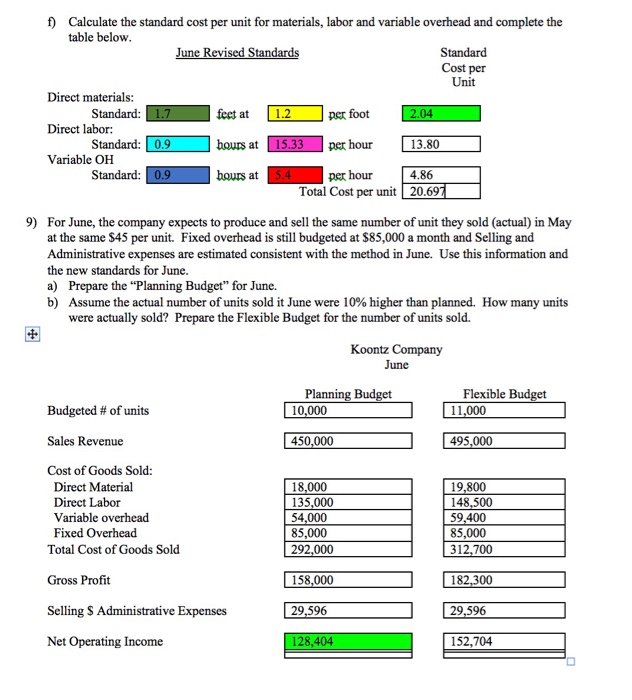
Koontz Company manufactures a number of products. The standards relating to one of these products are shown below, along with actual cost data for May Standard Actual Cost per Cost per Unit Unit Direct materials: Standard: 1.80 feet at $1.00 per foot $ 1.80 Actual: 1.75 feet at $1.40 per foot $ 2.45 Direct labor Standard: 0.90 hours at $15.00 per hour 13.50 Actual: 0.95 hours at $14.60 per hour 13.87 Variable overhead: Standard: 0.90 hours at $6.00 per hour 5.40 Actual: 0.95 hours at $5.60 per hour 5.32 Total cost per unit $20.70 $21.64 Excess of actual cost over standard cost per unit $0.94 The production superintendent was pleased when he saw this report and commented: "This $0.94 excess cost is well within the 5 percent limit management has set for acceptable variances. It's obvious that there's not much to worry about with this product." Actual production for the month was 10,000 units. Variable overhead cost is assigned to products on the basis of direct labor-hours. There were no beginning or ending inventories of materials. a) Material price: Management is working with their materials supplier to negotiate a new price cost of their direct material. Koontz Company is looking for a price that would "half" the price variance they saw in May. What price per foot will management want to negotiate? Hint - Use MPV = (SP-AP)AQ; Set material price variance to 50% of May's variance (either in Ss or per unit) and solve for Actual Price. This will be the new material price standard for June. Show your work here and include your answers in the table below including the highlighted square. Remember to express your answer in terms of "per foot" price. MPV=Half of MPV of May = 7000/2= $3,500 U -3500 = (SP-1.4) * 17500 SR=1.4 -0.2 = $ 1.2 b) The production supervisor is implementing some changes to production that are expected to improve the materials quantity variance. With these changes, the supervisor believes May's favorable quantity variance would have been doubled. Using MQV = (SQ-AQSP; Solve for Actual Quantity that would have doubled May's materials quantity variance. Remember to express your answers in terms of "per unit". This will be the new quantity standard for June. Include this in the table below for the highlighted square. MQV = 2* MQV of May...500*2 = $1,000 F 1000 = 6.18.000 - AQ) * 1 AQ (ie Standard for June) = 17,000 or 1.7 feet per unit c) The company has been providing additional training for their employees and various changes to the production process such that they expect labor efficiency to improve. The company believes June's production can meet the current labor standard (unchanged from May's hour per unit). What will the standard hour per unit be for June? Include in the highlighted square below. 0.9 hour per unit d) The company has increased the wages of its employees by 5% to attempt to provide an incentive and improve moral of the employees. This 5% increase is to the Actual" labor rate paid in May. This will be the new standard labor rate for June. Calculate the new standard per hour and include it in the highlighted square below. Standard Rate = 5% + Actual rate of May = 14.6 + 5% - $ 15.33 per br e) Variable overhead will be applied based on standard hours for June just as it was in May. Include the standard in the highlighted square below. The overhead budget prepared by accounting indicates the rate will be $0.20 per hour lower than last period's actual variable overhead. What is the new standard variable overhead rate? Include the rate in the highlighted square below VOH Rate = Actual rate of max - $ 0.20 per hour = 5.6 -0.2 = $ 5.40 per h f) Calculate the standard cost per unit for materials, labor and variable overhead and complete the table below. June Revised Standards Standard Cost per Unit Direct materials: Standard: 1.7 feet at 1.2 per foot 2.04 Direct labor: Standard: 0.9 hours at 15.33 per hour 13.80 Variable OH Standard: 0.9 hours at 5.4 per hour 4.86 Total Cost per unit 20.697| 9) For June, the company expects to produce and sell the same number of unit they sold (actual) in May at the same $45 per unit. Fixed overhead is still budgeted at $85,000 a month and Selling and Administrative expenses are estimated consistent with the method in June. Use this information and the new standards for June. a) Prepare the "Planning Budget" for June. b) Assume the actual number of units sold it June were 10% higher than planned. How many units were actually sold? Prepare the Flexible Budget for the number of units sold. Koontz Company June Budgeted # of units Planning Budget 10,000 Flexible Budget 11,000 Sales Revenue 450,000 495,000 Cost of Goods Sold: Direct Material Direct Labor Variable overhead Fixed Overhead Total Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit 18,000 135,000 54,000 85,000 292,000 19,800 148,500 59,400 85,000 312,700 158,000 182,300 29,596 29,596 Selling $ Administrative Expenses Net Operating Income 128,404 152,704 Koontz Company had the following situations happen during June. Situation A: One of Koontz Company's full-time employees quit. A replacement employee was hired at $16.50 an hour. This employee worked 160 hours during June. Situation B: Power outages occurred three times during the month that caused all production to shut down for.75 hours twice and 1.5 hours the third time. During these times, 4 workers remained on site, but no work was performed. Situation C: An order of raw material was received damaged during shipping. The end of the stack of material (all material in the order) was damaged such that 12% of the order was not usable. Based on the standard, the order was expected to produce 2,000 of the units for the month of June. Situation D: Purchasing was able to negotiate a $2,000 discount for the damaged order from c) above. 10) Consider the four variances for JUNE; Materials Price Variance, Material Quantity Variance, Labor Rate Variance, and Labor Efficiency Variance. a) For Situation A, which of the four variances will be affected by the situation? will it be favorable or unfavorable? Estimate how much of the variance will be impacted by the situation. Hint: Use the formula for the specific variance impacted. Determine the "change the situation will have on each element of the formula (actual and standards) and determine the dollar value of the impact. b) For Situation B, which of the four variances will be affected by the situation? Will the variance be favorable or unfavorable? Estimate the impact to the variance. c) For Situation C, which of the four variances will be affected by the situation? Will it be favorable or unfavorable? Estimate the impact to the variance. d) For Situation D, which of the four variances will be affected by the situation? Will it be favorable or unfavorable? Estimate the impact to the variance. Using the information for C and D, do you think purchasing did well with its negotiation of the discount? Explain. Koontz Company manufactures a number of products. The standards relating to one of these products are shown below, along with actual cost data for May Standard Actual Cost per Cost per Unit Unit Direct materials: Standard: 1.80 feet at $1.00 per foot $ 1.80 Actual: 1.75 feet at $1.40 per foot $ 2.45 Direct labor Standard: 0.90 hours at $15.00 per hour 13.50 Actual: 0.95 hours at $14.60 per hour 13.87 Variable overhead: Standard: 0.90 hours at $6.00 per hour 5.40 Actual: 0.95 hours at $5.60 per hour 5.32 Total cost per unit $20.70 $21.64 Excess of actual cost over standard cost per unit $0.94 The production superintendent was pleased when he saw this report and commented: "This $0.94 excess cost is well within the 5 percent limit management has set for acceptable variances. It's obvious that there's not much to worry about with this product." Actual production for the month was 10,000 units. Variable overhead cost is assigned to products on the basis of direct labor-hours. There were no beginning or ending inventories of materials. a) Material price: Management is working with their materials supplier to negotiate a new price cost of their direct material. Koontz Company is looking for a price that would "half" the price variance they saw in May. What price per foot will management want to negotiate? Hint - Use MPV = (SP-AP)AQ; Set material price variance to 50% of May's variance (either in Ss or per unit) and solve for Actual Price. This will be the new material price standard for June. Show your work here and include your answers in the table below including the highlighted square. Remember to express your answer in terms of "per foot" price. MPV=Half of MPV of May = 7000/2= $3,500 U -3500 = (SP-1.4) * 17500 SR=1.4 -0.2 = $ 1.2 b) The production supervisor is implementing some changes to production that are expected to improve the materials quantity variance. With these changes, the supervisor believes May's favorable quantity variance would have been doubled. Using MQV = (SQ-AQSP; Solve for Actual Quantity that would have doubled May's materials quantity variance. Remember to express your answers in terms of "per unit". This will be the new quantity standard for June. Include this in the table below for the highlighted square. MQV = 2* MQV of May...500*2 = $1,000 F 1000 = 6.18.000 - AQ) * 1 AQ (ie Standard for June) = 17,000 or 1.7 feet per unit c) The company has been providing additional training for their employees and various changes to the production process such that they expect labor efficiency to improve. The company believes June's production can meet the current labor standard (unchanged from May's hour per unit). What will the standard hour per unit be for June? Include in the highlighted square below. 0.9 hour per unit d) The company has increased the wages of its employees by 5% to attempt to provide an incentive and improve moral of the employees. This 5% increase is to the Actual" labor rate paid in May. This will be the new standard labor rate for June. Calculate the new standard per hour and include it in the highlighted square below. Standard Rate = 5% + Actual rate of May = 14.6 + 5% - $ 15.33 per br e) Variable overhead will be applied based on standard hours for June just as it was in May. Include the standard in the highlighted square below. The overhead budget prepared by accounting indicates the rate will be $0.20 per hour lower than last period's actual variable overhead. What is the new standard variable overhead rate? Include the rate in the highlighted square below VOH Rate = Actual rate of max - $ 0.20 per hour = 5.6 -0.2 = $ 5.40 per h f) Calculate the standard cost per unit for materials, labor and variable overhead and complete the table below. June Revised Standards Standard Cost per Unit Direct materials: Standard: 1.7 feet at 1.2 per foot 2.04 Direct labor: Standard: 0.9 hours at 15.33 per hour 13.80 Variable OH Standard: 0.9 hours at 5.4 per hour 4.86 Total Cost per unit 20.697| 9) For June, the company expects to produce and sell the same number of unit they sold (actual) in May at the same $45 per unit. Fixed overhead is still budgeted at $85,000 a month and Selling and Administrative expenses are estimated consistent with the method in June. Use this information and the new standards for June. a) Prepare the "Planning Budget" for June. b) Assume the actual number of units sold it June were 10% higher than planned. How many units were actually sold? Prepare the Flexible Budget for the number of units sold. Koontz Company June Budgeted # of units Planning Budget 10,000 Flexible Budget 11,000 Sales Revenue 450,000 495,000 Cost of Goods Sold: Direct Material Direct Labor Variable overhead Fixed Overhead Total Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit 18,000 135,000 54,000 85,000 292,000 19,800 148,500 59,400 85,000 312,700 158,000 182,300 29,596 29,596 Selling $ Administrative Expenses Net Operating Income 128,404 152,704 Koontz Company had the following situations happen during June. Situation A: One of Koontz Company's full-time employees quit. A replacement employee was hired at $16.50 an hour. This employee worked 160 hours during June. Situation B: Power outages occurred three times during the month that caused all production to shut down for.75 hours twice and 1.5 hours the third time. During these times, 4 workers remained on site, but no work was performed. Situation C: An order of raw material was received damaged during shipping. The end of the stack of material (all material in the order) was damaged such that 12% of the order was not usable. Based on the standard, the order was expected to produce 2,000 of the units for the month of June. Situation D: Purchasing was able to negotiate a $2,000 discount for the damaged order from c) above. 10) Consider the four variances for JUNE; Materials Price Variance, Material Quantity Variance, Labor Rate Variance, and Labor Efficiency Variance. a) For Situation A, which of the four variances will be affected by the situation? will it be favorable or unfavorable? Estimate how much of the variance will be impacted by the situation. Hint: Use the formula for the specific variance impacted. Determine the "change the situation will have on each element of the formula (actual and standards) and determine the dollar value of the impact. b) For Situation B, which of the four variances will be affected by the situation? Will the variance be favorable or unfavorable? Estimate the impact to the variance. c) For Situation C, which of the four variances will be affected by the situation? Will it be favorable or unfavorable? Estimate the impact to the variance. d) For Situation D, which of the four variances will be affected by the situation? Will it be favorable or unfavorable? Estimate the impact to the variance. Using the information for C and D, do you think purchasing did well with its negotiation of the discount? Explain Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


