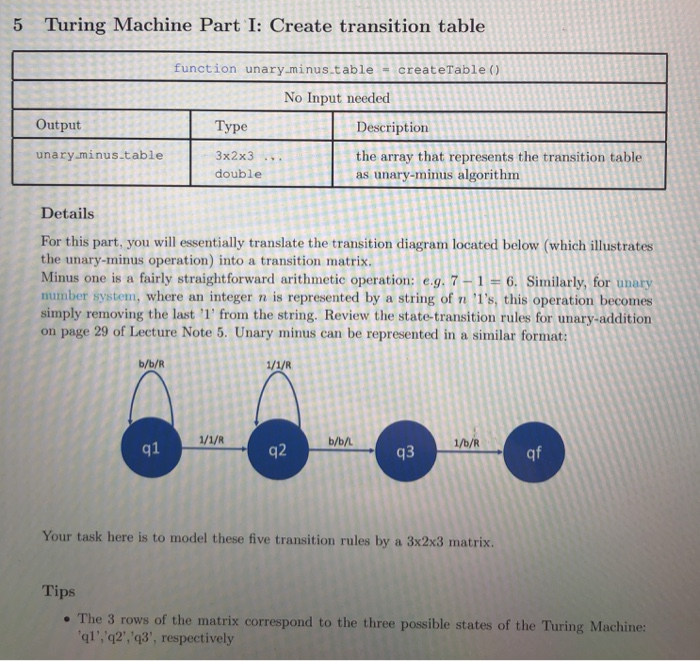
5 Turing Machine Part I: Create transition table function unary minus.tablecreateTable () No Input needed Output Type Description unary.minus.table 3x2x3. double the array that represents the transition table as unary-minus algorithm Details For this part, you will essentially translate the transition diagram located below (which illustrates the unary-minus operation) into a transition matrix. Minus one is a fairly straightforward arithmetic operation: eg, 7-1 6. Similarly, for unary mumber system, where an integer n is represented by a string of n '1's, this operation becomes simply removing the last 1' from the string. Review the state-transition rules for unary-addition on page 29 of Lecture Note 5. Unary minus can be represented in a similar format: b/b/R b/b/L q2 q3 qf Your task here is to model these five transition rules by a 3x2x3 matrix. Tips . The 3 rows of the matrix correspond to the three possible states of the Turing Machine ql','q2','q3', respectively . The 2 columns of the matrix correspond to the two possible values read off the tape T,b respectively . For ease of implementing indexing and transitions in MATLAB, try to replace all charac- ters/strings with a integer. . Note that there could be other state-transition rules that also solve the unary-minus prob- lem, but our grader only accept implementations that represent the state-transition rule provided above. Turing Machine Part II: Lookup the transition table function tnew.value, move, new.statej-transition (table, now.state, now.value) Input table 6 Type Description 3x2x3.. the transition table you made in the last double int int part current state of the Turing Machine value read off the tape now.state now value Output new.value int int int value to write on the tape the direction of next move on tape new state of the Turing Machine move new.state Details This function figures out the next step the Turing Machine will take based on the current condi- tions Tips . Think about how you may have indexed matrices in Lab 2 to access certain pixels in a 3D representation of an RGB image. 7 Turing Machine Part III: Parse the tape You will write two functions for this part. function intTape parseIn (charTape) Input Type Description charTape 1xN char the char array that represents the input tape Description the double array that correponds to the Output TypeE intTape 1xN double input tape function charTapeparseOut (int Tape) Input Type Description the double array that will be decoded into a char array Description the char array that represents the output tape intTape 1xN double Output Type charTape 1xN char Details Our transition table is represented as a matrix with integers. However, the original tape is a char array. Therefore, before you feed the input tape into the Turing Machine, you have to encode the tape using integers that correspond to the characters in the transition table matrix; after the Turing Machine halts, you have to decode the integer array back to a char array that has the same format as the input tape. Tips Look up string compare for how to determine if one string/char array is identical to the other . You can initialize an empty char array by you can initialize an empty integer array by Note that the type for int Tape is default to be double, though its values will only be integers. You can convert it to 1xN int at your wish, but it's unnecessary 5 Turing Machine Part I: Create transition table function unary minus.tablecreateTable () No Input needed Output Type Description unary.minus.table 3x2x3. double the array that represents the transition table as unary-minus algorithm Details For this part, you will essentially translate the transition diagram located below (which illustrates the unary-minus operation) into a transition matrix. Minus one is a fairly straightforward arithmetic operation: eg, 7-1 6. Similarly, for unary mumber system, where an integer n is represented by a string of n '1's, this operation becomes simply removing the last 1' from the string. Review the state-transition rules for unary-addition on page 29 of Lecture Note 5. Unary minus can be represented in a similar format: b/b/R b/b/L q2 q3 qf Your task here is to model these five transition rules by a 3x2x3 matrix. Tips . The 3 rows of the matrix correspond to the three possible states of the Turing Machine ql','q2','q3', respectively . The 2 columns of the matrix correspond to the two possible values read off the tape T,b respectively . For ease of implementing indexing and transitions in MATLAB, try to replace all charac- ters/strings with a integer. . Note that there could be other state-transition rules that also solve the unary-minus prob- lem, but our grader only accept implementations that represent the state-transition rule provided above. Turing Machine Part II: Lookup the transition table function tnew.value, move, new.statej-transition (table, now.state, now.value) Input table 6 Type Description 3x2x3.. the transition table you made in the last double int int part current state of the Turing Machine value read off the tape now.state now value Output new.value int int int value to write on the tape the direction of next move on tape new state of the Turing Machine move new.state Details This function figures out the next step the Turing Machine will take based on the current condi- tions Tips . Think about how you may have indexed matrices in Lab 2 to access certain pixels in a 3D representation of an RGB image. 7 Turing Machine Part III: Parse the tape You will write two functions for this part. function intTape parseIn (charTape) Input Type Description charTape 1xN char the char array that represents the input tape Description the double array that correponds to the Output TypeE intTape 1xN double input tape function charTapeparseOut (int Tape) Input Type Description the double array that will be decoded into a char array Description the char array that represents the output tape intTape 1xN double Output Type charTape 1xN char Details Our transition table is represented as a matrix with integers. However, the original tape is a char array. Therefore, before you feed the input tape into the Turing Machine, you have to encode the tape using integers that correspond to the characters in the transition table matrix; after the Turing Machine halts, you have to decode the integer array back to a char array that has the same format as the input tape. Tips Look up string compare for how to determine if one string/char array is identical to the other . You can initialize an empty char array by you can initialize an empty integer array by Note that the type for int Tape is default to be double, though its values will only be integers. You can convert it to 1xN int at your wish, but it's unnecessary