Help with the following math problems
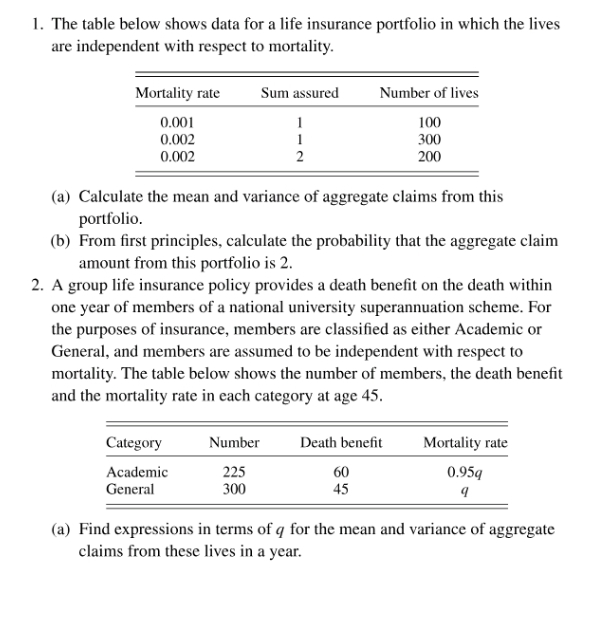
1. The table below shows data for a life insurance portfolio in which the lives are independent with respect to mortality. Mortality rate Sum assured Number of lives 0.001 100 0.002 300 0.002 200 (a) Calculate the mean and variance of aggregate claims from this portfolio. (b) From first principles, calculate the probability that the aggregate claim amount from this portfolio is 2. 2. A group life insurance policy provides a death benefit on the death within one year of members of a national university superannuateon scheme. For the purposes of insurance, members are classified as either Academic or General, and members are assumed to be independent with respect to mortality. The table below shows the number of members, the death benefit and the mortality rate in each category at age 45. Category Number Death benefit Mortality rate Academic 225 60 0.95q General 300 45 9 (a) Find expressions in terms of q for the mean and variance of aggregate claims from these lives in a year.(b) The aggregate claims distribution for this policy can be approximated by a compound Poisson distribution. Under the assumption that the number of claims by each individual has a Poisson distribution whose mean is that individual's mortality rate: (i) fully specify the approximationg compound Poisson distribution; (ii) find expressions for the mean and variance of this compound Poisson distribution in terms of q, and (iii) explain why the expression for variance in (ii) exceeds that in part (a). 3. Consider a portfolio of n insurance policies. For i = 1, 2, ... . n, let S; denote the amount of claims paid under policy / and let Pr(S; = 0) = p; and Pr(S; = x) = qihx for x = 1, 2, 3, . .., where 0 rxhx *=I and C(r, n) = >h,* = B(r)". 1=1 Now define (gx), to be the probability function of S = _._, S;, and let A(r) = E[r$]. (a) Show that " A(r) = A() _(-1)*-1 * 1 d -C (r, k ) 1=l *=1 k dr provided that 2 : B(Y) (-1)4-1 k The mth order approximation to go is (-1)*-1 80 (m) = exp - 1= 1 k Deduce that the first order approximation is a compound Poisson distribution. 4. In a life insurance portfolio the sums assured are 1, 2, ... . I, and for a given sum assured a policyholder is subject to one of / mortality rates. Let ";; denote the number of policyholders with sum assured i and mortality rate qj, j = 1, 2, .... J, and let p; = 1 - q;. Claims from policies are assumed to be independent of each other. Let S denote the aggregate claim amount in one year from this portfolio, let gx = Pr(S = k) for k = 0, 1, 2, . . ., and let Ps(r) = E[r$]. (a) Show that (-1)*+1 log Ps(r) = log go + IM& k i=l Pi(b) Define nij i=1 Pi and K OK (r) = E (-1)*+1 k SK(r) = > b( K). K= where K > 1. Find expressions for be when x is even, and when x is odd. State the values of x for which these expressions are non-zero