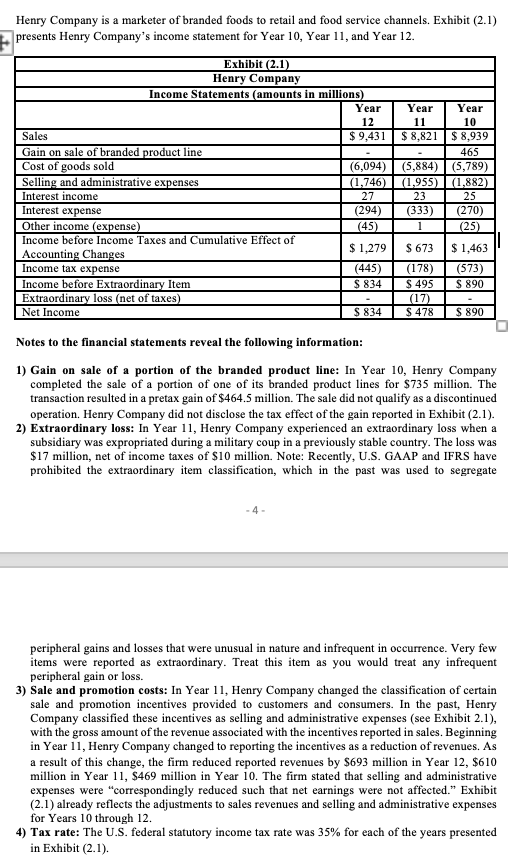

Henry Company is a marketer of branded foods to retail and food service channels. Exhibit (2.1) presents Henry Company's income statement for Year 10, Year 11, and Year 12. Notes to the financial statements reveal the following information: 1) Gain on sale of a portion of the branded product line: In Year 10, Henry Company completed the sale of a portion of one of its branded product lines for $735 million. The transaction resulted in a pretax gain of $464.5 million. The sale did not qualify as a discontinued operation. Henry Company did not disclose the tax effect of the gain reported in Exhibit (2.1). 2) Extraordinary loss: In Year 11, Henry Company experienced an extraordinary loss when a subsidiary was expropriated during a military coup in a previously stable country. The loss was $17 million, net of income taxes of \$10 million. Note: Recently, U.S. GAAP and IFRS have prohibited the extraordinary item classification, which in the past was used to segregate 4 - peripheral gains and losses that were unusual in nature and infrequent in occurrence. Very few items were reported as extraordinary. Treat this item as you would treat any infrequent peripheral gain or loss. 3) Sale and promotion costs: In Year 11 , Henry Company changed the classification of certain sale and promotion incentives provided to customers and consumers. In the past, Henry Company classified these incentives as selling and administrative expenses (see Exhibit 2.1), with the gross amount of the revenue associated with the incentives reported in sales. Beginning in Year 11, Henry Company changed to reporting the incentives as a reduction of revenues. As a result of this change, the firm reduced reported revenues by $693 million in Year 12,$610 million in Year 11, \$469 million in Year 10. The firm stated that selling and administrative expenses were "correspondingly reduced such that net earnings were not affected." Exhibit (2.1) already reflects the adjustments to sales revenues and selling and administrative expenses for Years 10 through 12 . 4) Tax rate: The U.S. federal statutory income tax rate was 35% for each of the years presented in Exhibit (2.1). Answer to_Question 2 (7 marks) A. Discuss whether you would adjust for each of the following items when using earnings to forecast the future profitability of Henry Company: (1) Gain on sale of a portion of the branded product line: (2) Extraordinary loss: B. Indicate the adjustment you would make to Henry Company's net income for each item in Requirement (A). C. Discuss whether you believe the reclassification adjustments made by Henry Company for the sale and promotion incentive costs (Item 3) are appropriate. D. Prepare a common-size income statement for Year 10, Year 11, and Year 12 using the amounts in Exhibit (2.1). Set sales equal to 100%. Round percentages to one decimal point. E. Repeat Requirement (D) after making the income statement adjustments in Requirement (B). F. Assess the changes in the profitability of Henry Company during the three-year period









